The significance of CNC mills in the modern manufacturing industry cannot be overstated. These cutting-edge machines are instrumental in the precise shaping and cutting of materials, ensuring impeccable accuracy. By utilizing computer-controlled movements, CNC mills carry out pre-programmed instructions, effectively converting raw materials into intricate designs and precise components. Through the amalgamation of automation and computer-guided precision, CNC mills have cemented their indispensability across various sectors, encompassing aerospace, automotive, electronics, and woodworking.
If you’re new to the world of CNC milling, fear not! This article has been crafted specifically for beginners like you. We will unravel the ten key features that define CNC mills, explaining each concept in a clear and accessible manner. By the end of this journey, you will have a solid understanding of the remarkable capabilities and functionalities that CNC milling machines offer.
Without further ado, let’s get started.
What Are CNC Milling Machines and How Do They Work?

Before we dive into the key features of CNC milling machines, let’s start by understanding what they are and how they work.
CNC milling machines are powerful manufacturing tools that utilize computer-controlled movements to shape and cut materials with precision. The acronym CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, highlighting the crucial role of computers in guiding these machines. By employing specialized software, operators create programs that outline the desired designs or parts, known as G-code.
Once the program is prepared, it is loaded into the CNC mill’s computer system. The machine’s control panel allows for inputting various parameters, such as spindle speed and feed rate. With everything set up, the CNC mill executes the program, following the instructions to transform the digital design into a physical object.
To illustrate, let’s consider the example of creating a custom metal bracket using a CNC mill:
- Material Preparation: Secure a metal block onto the CNC mill’s worktable.
- Tool Selection: Choose the appropriate cutting tool for the desired design.
- Program Execution: Load the G-code program, which contains instructions on tool movements and interactions with the material.
- Machining Process: The CNC mill starts executing the program, accurately cutting and shaping the metal block along the specified toolpath.
- Precision and Accuracy: The CNC mill ensures exceptional precision and accuracy, eliminating human errors.
- Finishing Touches: Make tool or parameter adjustments as needed to achieve desired features.
- Completion and Evaluation: Inspect the finished bracket for any imperfections or deviations from the design.
By harnessing automation and computer-guided precision, CNC milling machines revolutionize manufacturing, enabling the creation of intricate and accurate components.
Key Features of CNC Mills
Now that we understand the basics of CNC milling, let’s explore the key features that make these machines so remarkable.
1 Automation
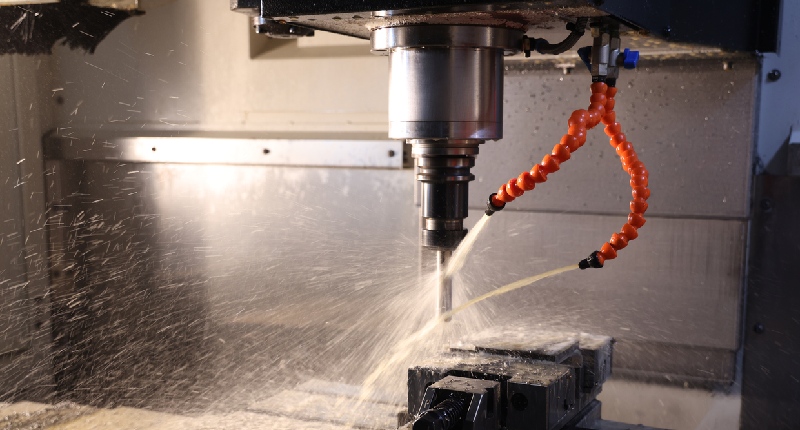

Automation is a key feature of CNC milling machines that significantly enhances operational efficiency and productivity. By automating various processes, CNC mills streamline operations and offer numerous benefits.
CNC milling machines automate the execution of pre-programmed instructions, eliminating the need for manual intervention at every stage of the machining process. Once the program is set up, the machine carries out tasks with precision and consistency, reducing the reliance on human labor.
2 Precision
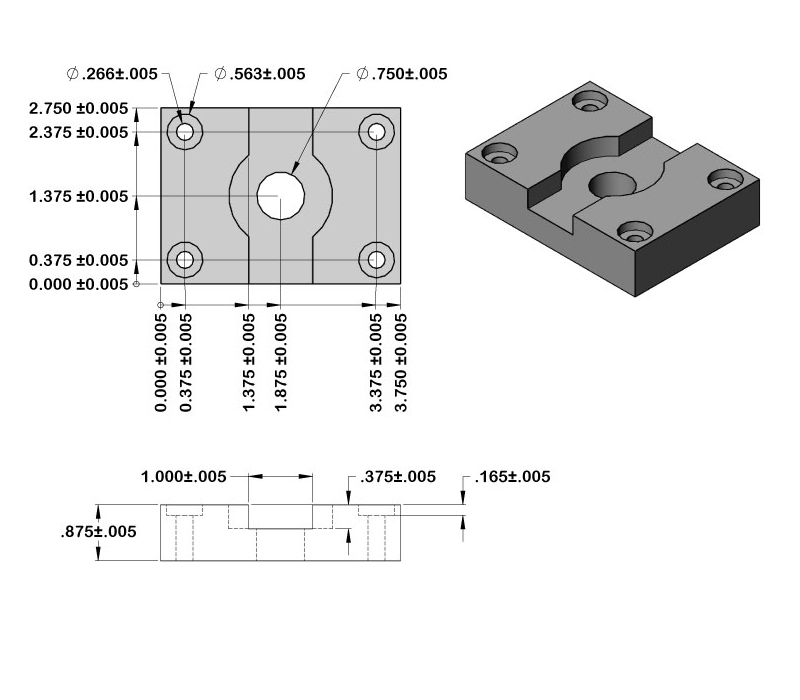
The reputation of CNC milling machines precedes them when it comes to their extraordinary precision and accuracy in material removal. These machines excel in achieving tight tolerances, ensuring that the final parts meet the desired specifications. In comparison to manual milling methods, CNC mills surpass expectations by a significant margin in terms of precision.
In modern CNC milling, achieving accuracy at the micron level is not only feasible but also common. Today’s CNC machines often demonstrate tolerances ranging from 0.01 to 0.05 millimeters, contingent upon factors like the machine’s capabilities, cutting tools employed, and the properties of the material being worked on. It is worth noting, however, that attaining such precision necessitates meticulous setup, appropriate tool selection, and a mastery of programming expertise.
3 Versatility in Material Compatibility
CNC milling machines offer a remarkable level of versatility when it comes to the range of materials that can be worked with. Let’s explore the wide variety of materials that CNC mills can handle:
- Metals: CNC mills excel at machining various metals, including aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass, copper, titanium, and more. These machines can efficiently cut, shape, and drill metal components with precision.
- Plastics: CNC mills are well-suited for working with plastics such as acrylic, polycarbonate, PVC, nylon, ABS, and PEEK. The ability to precisely carve intricate details makes CNC milling an excellent choice for producing plastic parts.
- Composites: CNC milling machines are capable of machining composite materials like carbon fiber, fiberglass, and laminates. These materials, often used in aerospace and automotive industries, require precise cutting to maintain their structural integrity.
- Wood: CNC mills are equally adept at working with wood materials, including hardwoods, softwoods, plywood, and MDF (medium-density fiberboard). Woodworkers can utilize CNC milling to create intricate designs, decorative elements, furniture components, and more.
- Foam and Foam Boards: CNC milling machines can also handle foam materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS) and polyurethane foam. These materials are commonly used in architectural modeling, packaging, and signage applications.
- Ceramics: Some advanced CNC mills equipped with specialized tooling and cooling systems can work with ceramics, including porcelain and various technical ceramics. CNC milling enables precise shaping and intricate patterns in ceramic materials.
- Others: CNC mills can also be employed for machining materials like glass, stone, and even certain types of composites used in the dental and medical fields.
4 Multiple Axes for Complex Machining

In CNC milling, axes represent the directions in which the cutting tool or workpiece can move. Traditional CNC mills have X, Y, and Z axes for horizontal, vertical, and depth movements. Advanced machines may include additional axes like A, B, and C, which provide rotational and tilting capabilities.
The number of axes directly influences a CNC mill’s ability to create complex cuts and shapes. Additional axes offer increased flexibility, allowing the tool to reach difficult areas, perform angular cuts, and produce three-dimensional geometries.
For example, a fourth axis enables rotational movements, facilitating the machining of curved surfaces and intricate features like spiral patterns. A fifth axis with tilting capabilities enables angled cuts, chamfers, and undercuts, ideal for complex molds and sculpting.
5 Speed, Efficiency, and High Production Volume
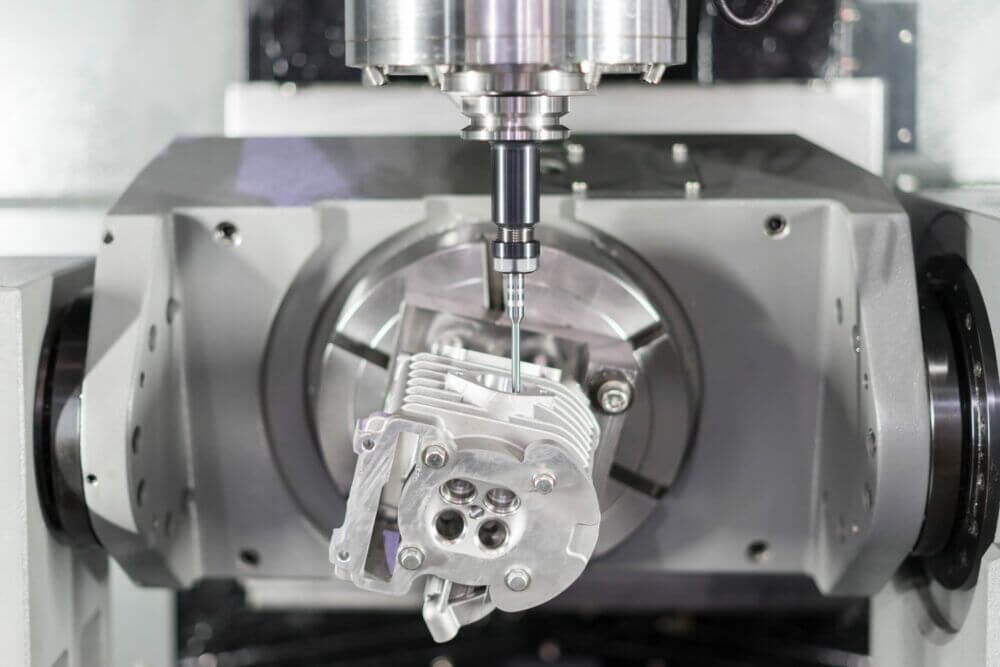

The prowess of CNC milling machines in operating at high speeds is widely acknowledged. Thanks to their automated nature, these machines execute machining processes swiftly, significantly reducing production time when compared to manual milling methods. Through pre-programmed instructions and precise tool movements, CNC mills swiftly and precisely shape materials, leading to enhanced overall efficiency.
Moreover, CNC mills boast advanced features like tool changers, enabling seamless transitions between different cutting tools. This eliminates the need for manual tool changes, further bolstering efficiency and minimizing downtime. Furthermore, CNC mills have the capacity to perform multiple operations in a single setup, diminishing the necessity for manual intervention and streamlining the workflow.
When it comes to handling large work volumes, CNC milling machines are highly suitable. Once the program is established, CNC mills can repetitively manufacture identical parts or designs with consistent accuracy. This level of consistency holds great significance in industries requiring mass production, as it ensures uniformity across a substantial quantity of components.
6 Repeatable and Consistent Results

CNC mills rely on pre-programmed instructions to guide their movements and actions. These instructions specify the exact toolpaths, cutting depths, and other machining parameters necessary to create a particular part or design. By precisely programming these instructions, operators can ensure that the machine performs the same operations each time the program is executed.
Unlike manual milling methods, which can be influenced by human errors and inconsistencies, CNC milling machines are automated systems. This automation eliminates the variability that can arise from differences in operator technique, fatigue, or other factors. Once the program is set, CNC mills execute the instructions with precision, ensuring that the same operations are carried out repeatedly without deviation.
7 Integration with CAD/CAM
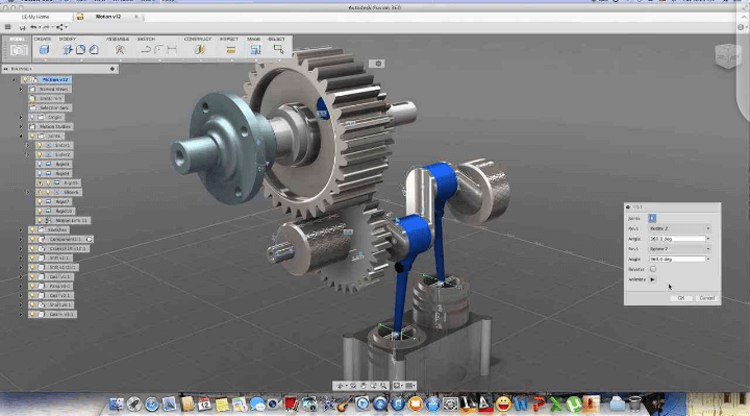
CNC milling machines seamlessly integrate with CAD/CAM software, enabling efficient programming and operation.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) is used to create digital models of parts or designs. It allows designers to visualize and specify dimensions, geometries, and details.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) translates CAD designs into instructions for CNC mills. It generates the G-code, which outlines toolpaths, speeds, and other parameters.
CAD and CAM communicate seamlessly with CNC mills. Designs are exported to CAM for programming, which generates the G-code loaded into the CNC mill’s control system.
This integration streamlines the workflow, ensuring accurate translation of designs into precise machining instructions. It empowers designers and engineers to create complex designs and optimize machining operations efficiently.
8 Tooling Options and Flexibility
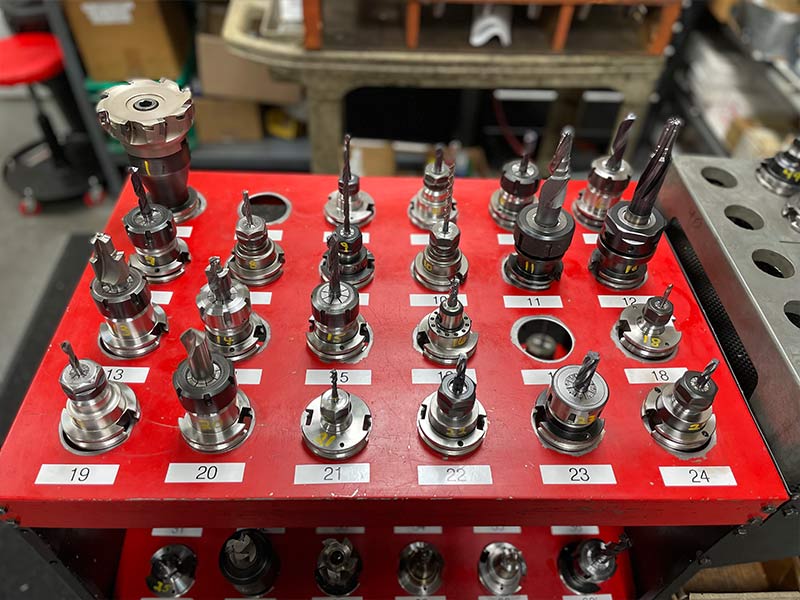

CNC mills are compatible with various cutting tools, allowing operators to choose the most suitable tool for their specific machining needs. These tools include:
- End Mills: Commonly used for milling, drilling, and slotting operations. They come in various shapes and sizes, such as flat end mills, ball end mills, and corner radius end mills.
- Drills: Used for creating holes of different diameters in the workpiece. Twist drills, step drills, and center drills are among the options available.
- Face Mills: Designed for facing and surfacing operations, typically used to create flat surfaces or remove material in larger areas.
- Reamers: Used for precision hole sizing and finishing to achieve tight tolerances.
- Taps: Employed for creating internal threads in holes, allowing for the insertion of screws or bolts.
- Boring Tools: Used to enlarge existing holes or create precise internal features.
The availability of different cutting tools enables CNC milling machines to perform various machining operations, including:
- Contouring: Creating complex shapes and contours in the workpiece.
- Drilling: Producing holes of different sizes and depths.
- Facing: Machining a flat surface perpendicular to the spindle axis.
- Pocketing: Removing material within a defined boundary, often used for creating recesses or pockets.
- Profiling: Cutting along the outline of a specific shape or feature.
- Slotting: Creating narrow and elongated cuts, such as keyways or grooves.
Get more tips about milling operation here.
9 Monitoring and Feedback Systems
Monitoring and feedback systems in CNC mills continuously collect data during the machining process. These systems can include:
- Spindle Load Monitoring: Monitors the load on the spindle motor, providing information on the cutting forces experienced during machining.
- Tool Wear Sensors: Detects the wear and tear of cutting tools, allowing operators to monitor tool conditions and replace them when necessary.
- Temperature Sensors: Measures the temperature of the machine components, ensuring optimal operating conditions and preventing overheating.
- Vibration Monitoring: Detects vibrations in the machine, helping identify potential issues such as tool chatter or imbalance.
The data collected from these monitoring and feedback systems holds significant value for process optimization and tool life management. For example, if a tool wear sensor detects significant wear on a cutting tool, the operator can replace the tool before it becomes excessively worn or damaged. This preventive action ensures consistent cutting performance and reduces the risk of tool failure, saving time and costs.
Safety Features and Operator Protection
CNC milling machines are equipped with various safety features to ensure operator protection and promote a safe working environment.
10 Safety Features
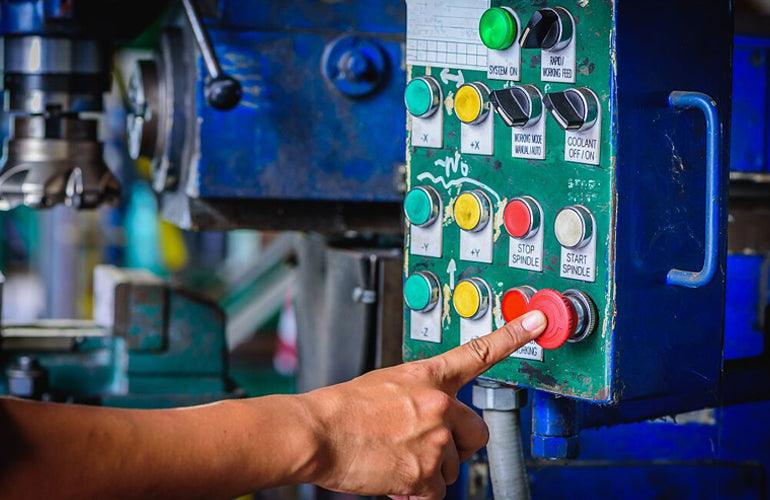

CNC mills incorporate several safety features, including:
- Emergency Stop (E-stop) Button: A prominent button that immediately halts all machine operations when pressed. It provides a quick and accessible means to stop the machine in case of an emergency.
- Protective Enclosures: CNC mills often have enclosed work areas with interlock systems that prevent access to moving parts while the machine is in operation. These enclosures protect operators from potential hazards and flying debris.
- Safety Interlocks: Interlock systems ensure that the machine cannot be operated unless all doors, panels, and enclosures are securely closed and in place. This prevents accidental or unauthorized access to the working area.
- Overload Protection: CNC mills may be equipped with overload protection mechanisms that sense excessive loads or forces and automatically stop or reduce machine operations to prevent damage.
- Safety Sensors: Proximity sensors or light curtains are used to detect the presence of operators near the machine. If an operator gets too close to a hazardous area, these sensors trigger safety measures, such as stopping or pausing the machine.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- 5 Key Differences between CNC Routers and CNC Mills
In the world of CNC machines, two popular contenders stand out: CNC routers and CNC mills. These advanced tools have revolutionized the manufacturing industry, enabling precise and automated production processes.…
- Differences Between CNC Lathes and CNC Mills
In the world of manufacturing, two machines play pivotal roles: CNC lathes and CNC mills. These machines share the purpose of material removal using cutting tools, yet they possess unique…
- 7 Amazing Projects You Can Create with CNC Mills
When it comes to manufacturing and creating innovative designs, CNC mills have revolutionized the industry. These powerful machines offer unparalleled precision and versatility, making them ideal for a wide range…