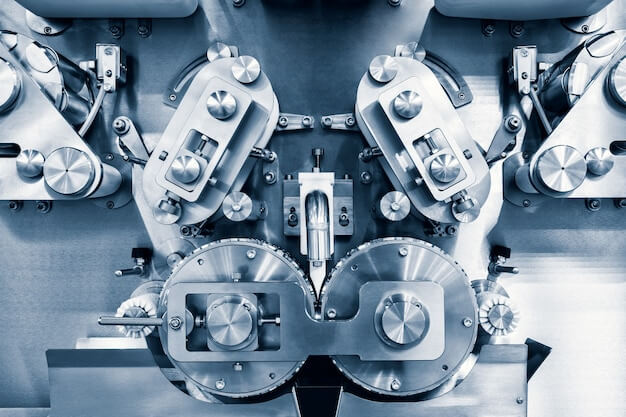
Introduction to Plastics in Food Processing Machinery
The incorporation of plastics into food processing machinery plays a pivotal role in the modern food industry. These synthetic materials are employed for their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness, contributing significantly to the efficiency of production lines. Plastics offer numerous benefits including reduced weight, which eases the handling of equipment, and inertness that minimizes the risk of contamination during food processing. Additionally, they provide excellent resistance to corrosion from various chemicals used in cleaning processes. However, concerns regarding plastics involve potential chemical leaching at high temperatures and the environmental impact of plastic waste. The technical principles behind the use of plastics focus on optimizing the material properties to withstand the mechanical and thermal stresses encountered in food processing operations, while also adhering to strict hygiene standards.
Types of Plastics Used in Food Processing Machinery
In food processing machinery, various plastics are utilized for their unique properties and suitability for specific applications. Polyethylene (PE) and Polypropylene (PP) are commonly used for their chemical resistance and non-toxic nature, making them ideal for contact with food substances. These plastics can handle repeated use and cleaning processes without degradation. Another frequently employed plastic is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), widely known by the brand name Teflon®, which has exceptional non-stick qualities that reduce product wastage and simplify cleaning. For components requiring rigidity and dimensional stability, Acetal, also known as polyoxymethylene (POM), serves excellently due to its low friction coefficient and good wear resistance. Each material is chosen based on its performance under working temperatures, exposure to food acids or bases, and mechanical stress, ensuring both food safety and equipment longevity.
Benefits of Using Plastics in Food Processing
The integration of plastics into food processing machinery offers tangible benefits, mainly cost-effectiveness. Being comparatively less expensive than metals, plastics reduce initial setup and ongoing maintenance costs. Their inherent flexibility empowers manufacturers to tailor components to specific demands with ease, enhancing efficiency through bespoke solutions. Furthermore, plastics hold an advantage in chemical environments due to their corrosion resistance and inert nature; they do not react with foods or cleaning agents, ensuring longevity and safety. An example that underscores these advantages is plastic conveyor belts used in packaging lines. These belts are less prone to wear, require minimal lubrication, and can transport goods in diverse conditions without degradation, attributes integral to streamlining the packaging process and preserving the hygienic standards requisite in food handling.
Safety Considerations in the Use of Plastics for Food Processing Machinery
When it comes to food processing machinery, safety is paramount. One key aspect of this involves adhering strictly to regulations governing plastic use in food contact equipment. These guidelines ensure that plastics used are able to withstand the rigorous conditions of food processing without degrading and potentially contaminating food products. To guarantee safety, selecting the appropriate food-safe plastics is essential; for example, using high-density polyethylene (HDPE) for its chemical resistance or polypropylene (PP) because of its heat tolerance and lack of additives can prevent harmful substances from leaching into foods. Every component coming in direct contact with edibles must be made out of materials compliant with regulatory standards like those set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). This deliberate choice of suitable plastics mitigates risks, ensuring consumer health and maintaining industry credibility.
Challenges and Solutions for Plastic Wear and Tear in Food Processing Machinery
In the realm of food processing machinery, plastic components are valued for their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. However, one of the primary challenges is the significant wear and tear they undergo during operations, leading to premature equipment failure. To combat this, various strategies have been implemented. One notable solution involves the use of reinforced plastics in areas subjected to high stress. These materials blend polymers with fibers, such as glass or carbon, enhancing the structural integrity and durability of components without sacrificing the benefits of traditional plastics. Reinforced plastics can effectively prolong the lifespan of machine parts that encounter persistent friction and mechanical force, ensuring more robust operational capacity and reduced maintenance frequency.
Innovation and Sustainability in Food Processing Machinery
Recent developments in biodegradable plastics are paving the way for more sustainable food processing machinery. Innovators in the field have begun to replace conventional petroleum-based parts with those made from plant-based materials, which decompose naturally and reduce long-term waste. As these components break down more easily than traditional plastics, the environmental impact of disposing used machine parts is significantly lessened. Additionally, many manufacturers have initiated recycling programs aimed at reprocessing plastic elements of food processing equipment. This approach not only minimizes the input of raw manufacturing materials but also decreases the accumulation of plastic debris in landfills. Through these efforts, the food processing industry takes notable strides towards balancing efficiency with ecological responsibility.
Maintenance and Hygiene: Cleaning Protocols for Plastic Machinery Components
Ensuring the longevity and food safety of plastic machinery used in food processing requires adherence to strict cleaning protocols. Plastics, due to their non-porous nature, are susceptible to harboring bacteria if not properly sanitized. A standard protocol involves dismantling removable components followed by thorough washing with detergent and warm water to remove residual food particles. Subsequently, a disinfectant approved for food contact surfaces is applied to eliminate microbial threats. These components must then be rinsed with potable water to remove any chemical traces and dried before reassembly, keeping cross-contamination risks at bay. Implementing such best practices for maintenance not only extends the service life of the machinery but also ensures compliance with food hygiene standards.
Maintenance and Hygiene: Best Practices for Maintenance
To maintain both longevity and food safety in food processing operations, it’s crucial to follow best practices for maintaining plastic-based equipment. Regular inspection plays a key role; inspect seals and gaskets for integrity as these can house pathogens if damaged. Lubrication should involve food-grade lubricants to prevent contamination. All machine interfaces that come into contact with food products ought to be regularly checked for wear and tear, ensuring they remain smooth and free from scratches or grooves where bacteria might collect. Adequate training on handling and repair procedures minimizes downtime and maintains consistent cleanliness levels. These steps are vital, keeping plastic machinery in optimal condition, safeguarding against potential hazards associated with compromised food safety.
Conclusion: The Significance and Future of Plastics in Food Processing Machinery
The pivotal role that plastics play in the food processing industry cannot be overstated. Durable, hygienic, and versatile, these materials have become integral in machinery for their ability to meet stringent safety standards while offering considerable cost efficiencies and design flexibility. Looking ahead, advancements in polymer science are poised to lead to more sustainable options—biodegradable and recyclable plastics—that align with environmental goals without compromising functionality. Innovations promise to enhance performance parameters like temperature resistance and mechanical strength, further cementing plastics as the material of choice in developing cutting-edge food processing technologies.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Analysis of processing difficulty of different materials in CNC processing
Introduction to CNC Processing and Material Selection CNC processing, a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, stands for Computer Numerical Control machining, a method where pre-programmed software commands the movement of factory…
- Environmental Impact of CNC Machining: Recyclable Metals vs. Biodegradable Plastics
Introduction to CNC Machining and its Environmental Impact CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a prevalent manufacturing process wherein pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery.…
- The Battle of the Plastics: PVC vs. Polyurethane in Manufacturing
The Battle of the Plastics: PVC vs. Polyurethane in Manufacturing In the realm of manufacturing, two plastics dominate - Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) and Polyurethane. PVC is one variant of plastic…