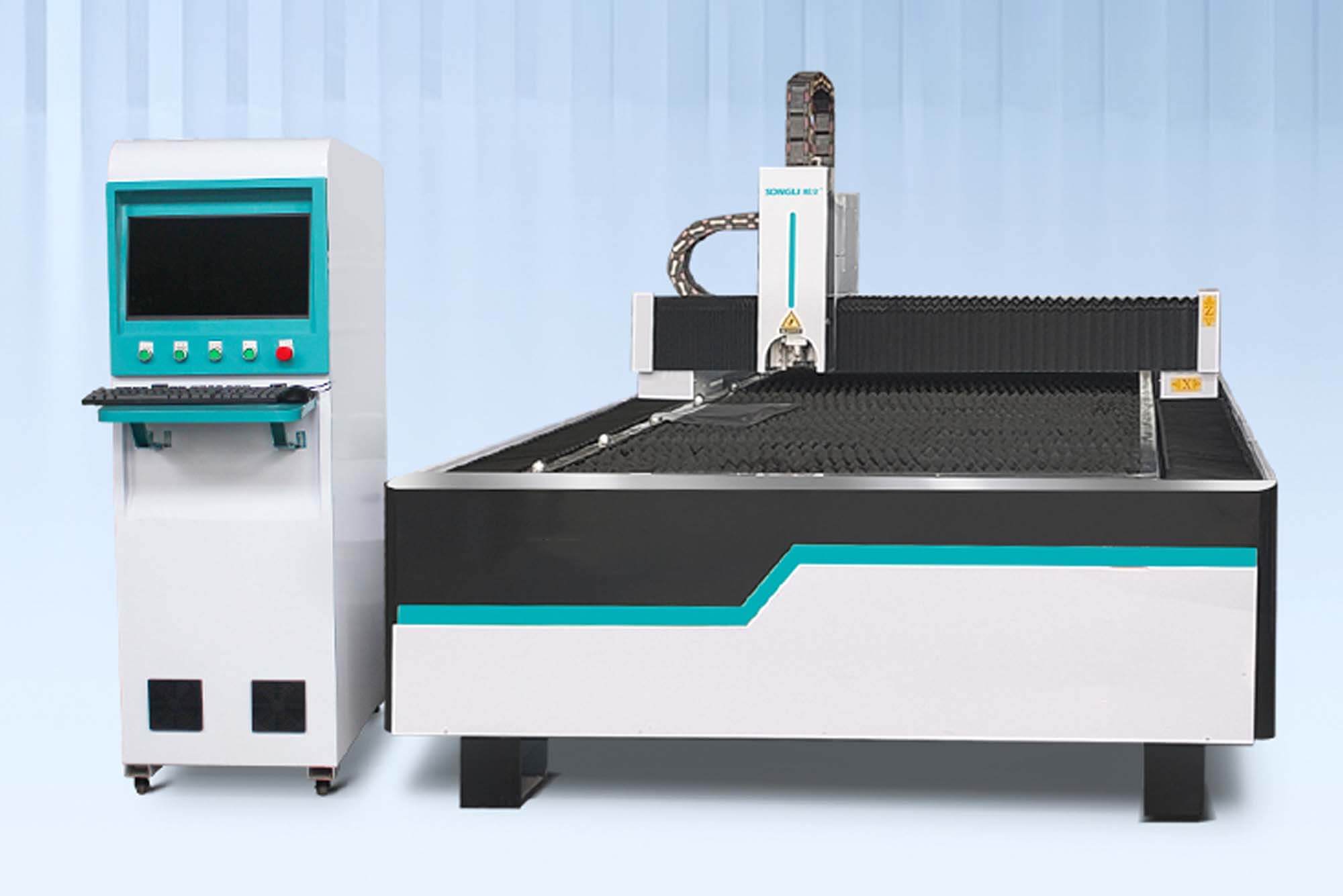
Introduction: The Role of Metal Laser Cutter in Modern Manufacturing
Metal laser cutters are one of the most transformative tools in modern manufacturing. By integrating cutting-edge laser technology with CNC control, they have revolutionized precision cutting, enabling manufacturers to produce intricate designs with unmatched accuracy. These machines not only reduce production times but also enhance material utilization by minimizing waste. Whether creating lightweight components for aerospace or detailed patterns for architectural projects, metal laser cutter consistently pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in manufacturing. They combine speed, precision, and versatility to meet the demands of various industries, from automotive to aerospace. With the ability to cut, engrave, and shape metal surfaces without direct contact, these machines have become a staple for manufacturers worldwide.
Having worked with these tools in various projects, I’ve seen firsthand how metal laser cutter can simplify complex tasks and deliver exceptional results. Their ability to handle a variety of materials and intricate designs sets them apart as a cornerstone of manufacturing efficiency and innovation. By reducing waste, increasing precision, and enabling customizations that were once unthinkable, these tools have earned their reputation as essential equipment for modern industries.
This article will explore the magic behind these machines, their working principles, advantages, and applications. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of why a metal laser cutter is an essential investment for industries prioritizing precision and efficiency.
How Metal Laser Cutter Work: Principles and Processes
Metal laser cutter rely on a focused laser beam to cut, melt, or vaporize material. The process involves the following steps:
- Laser Generation: The laser cutter’s power source generates a high-energy laser beam. This beam is amplified and directed through a series of mirrors or fiber optics to concentrate its energy.
- Focusing the Beam: Using lenses, the beam is focused to a pinpoint, allowing it to reach temperatures high enough to melt or vaporize metal. This precise focus is what enables intricate cuts and clean edges.
- Cutting the Metal: The focused laser beam interacts with the metal surface, while an assist gas (such as oxygen or nitrogen) blows away the molten material, leaving a clean cut. This non-contact process minimizes material stress and deformation.
- CNC Control: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology guides the laser’s movements with incredible accuracy, ensuring intricate designs and consistent results. The CNC controller translates digital designs into precise cutting paths.
Types of Metal Laser Cutter
Metal laser cutter comes in various forms, each suited for specific tasks:
| Type | Best For | Key Features | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Laser Cutter | High precision, fast cutting | Compact, efficient, low maintenance | Steel, aluminum, copper |
| CO2 Laser Cutter | Versatile material compatibility | Larger footprint, good for thick materials | Mild steel, stainless steel |
| Solid-State Laser | Ultra-high precision | Ideal for micro-cutting | Thin metals, specialty alloys |
Fiber laser cutters, in particular, are gaining popularity due to their efficiency and ability to handle reflective materials like aluminum and copper. Their smaller size and lower maintenance requirements also make them a cost-effective choice for many manufacturers.
Key Metrics in Metal Laser Cutting
| Metric | Typical Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Power | 500W – 12kW | Determines cutting speed and material range |
| Cutting Speed | Up to 1200 in/min | Affects productivity |
| Cutting Tolerance | ±0.001 inches | Ensures precision |
| Material Thickness | 0.02 – 1.0 inches (varies) | Defines compatibility |
Understanding these metrics is crucial for selecting the right cutter for your needs. A high-power laser, for instance, can handle thicker materials, while a machine with higher speed capabilities is better suited for high-volume production.
Key Features and Advantages of Metal Laser Cutter
Precision and Accuracy
A metal laser cutter can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches. This makes it indispensable for industries requiring intricate designs or tight fitments. Whether it’s complex automotive parts or detailed architectural designs, precision is key. Unlike traditional cutting methods, laser cutting ensures repeatability, producing identical parts even in large quantities.
Non-contact Processing
Unlike traditional methods, a metal laser cutter doesn’t physically touch the material. This eliminates wear on tools and minimizes deformation, ensuring a clean, polished finish every time. The non-contact nature also reduces the risk of material contamination, which is particularly important in industries like medical device manufacturing.
Speed and Efficiency
With cutting speeds reaching up to 1200 inches per minute, metal laser cutters outperform traditional tools like plasma cutters in both speed and quality. For instance, while a plasma cutter typically achieves cutting speeds of around 500-800 inches per minute for thin materials, a laser cutter nearly doubles this, making it the preferred choice for high-volume operations. Additionally, laser cutters produce cleaner edges with minimal dross, often eliminating the need for secondary finishing processes. In contrast, plasma cutting, although faster for very thick materials (over 1 inch), tends to leave a rougher edge that requires additional polishing or grinding. This distinction highlights the laser cutter’s superiority in precision-critical applications such as automotive and aerospace manufacturing. High throughput is a significant advantage for industries producing large volumes. For instance, in the automotive sector, laser cutters can drastically reduce production times for components like brackets and panels.
Versatility
Metal laser cutter handles a wide variety of metals, including:
| Material | Thickness Range | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | 0.02 – 1 inch | Most commonly used |
| Aluminum | 0.02 – 0.8 inches | Reflective, requires fiber lasers |
| Copper | 0.02 – 0.5 inches | High thermal conductivity, fiber-friendly |
| Titanium | 0.02 – 0.6 inches | Ideal for aerospace and medical fields |
The ability to work with such a diverse range of materials makes metal laser cutter an asset across industries. From aerospace to jewelry making, their adaptability is unmatched.
Environmental Benefits
Laser cutting produces minimal waste and uses less energy compared to other methods. With growing environmental awareness, this eco-friendly approach is an additional advantage. Additionally, the precision of laser cutting reduces the need for rework, further minimizing material wastage and energy consumption.
Applications of Metal Laser Cutter Across Industries
1. Automotive Industry
Metal laser cutters are used to produce components like brackets, heat shields, and custom exhaust systems. Their precision ensures that every part meets strict safety and performance standards. In addition, the ability to cut lightweight materials like aluminum contributes to the production of fuel-efficient vehicles.
2. Aerospace
The ability to cut lightweight yet strong materials like titanium makes metal laser cutter invaluable in aerospace. From turbine blades to structural components, precision cutting is critical. The aerospace industry also benefits from the laser cutter’s ability to handle complex geometries, which are often required in high-performance aircraft.
3. Architecture and Art
Laser cutters allow for the creation of intricate designs on metal panels used in facades, gates, or sculptures. Artists and architects alike benefit from their ability to realize complex designs. For example, custom-designed metal panels can transform a simple building into an architectural masterpiece.
4. Medical Devices
Medical-grade components, such as implants or surgical instruments, require high precision and sterile conditions—areas where metal laser cutter excel. The ability to achieve micro-level precision ensures that medical tools meet the highest standards of safety and functionality.
5. Electronics
From heat sinks to metal enclosures, the electronics industry relies on laser cutters for high-quality finishes and tight tolerances. As devices become smaller and more complex, the precision of laser cutting becomes increasingly important.
Choosing the Right Metal Laser Cutter for Your Needs
Selecting the right metal laser cutter involves evaluating several factors. To simplify this decision-making process, here is a detailed table summarizing key considerations:
| Factor | Description | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Ensure the machine supports metals you work with, e.g., steel, aluminum, copper. | Different lasers perform better with specific materials. |
| Power Output | Machines range from 500W to 12kW; higher power handles thicker materials effectively. | Impacts cutting speed and material versatility. |
| Bed Size | Size of the machine’s workspace, e.g., 4’x8’ for large projects. | Larger beds reduce repositioning for bigger materials. |
| Software Integration | CNC-enabled models with user-friendly software like nesting optimization. | Enhances workflow efficiency and material utilization. |
| Cost and Maintenance | Initial investment and ongoing expenses like lens cleaning or part replacements. | Determines overall affordability and operational ease. |
Using this table as a reference can help you focus on the most critical factors for your specific requirements, ensuring you select a machine that aligns with your production goals.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine supports the metals you frequently work with. Different machines are optimized for specific materials, such as reflective metals or thick steel.
- Power Output: Higher power is needed for thicker materials. A 10kW machine, for example, can cut through an inch of steel with ease, whereas lower-power machines are better suited for thinner materials.
- Bed Size: Match the machine’s workspace with the size of your projects. Larger beds accommodate bigger sheets of metal, reducing the need for manual repositioning.
- Software Integration: Look for CNC-enabled models with user-friendly software. Features like automatic nesting can optimize material usage and reduce waste.
- Cost and Maintenance: Factor in initial costs, operating expenses, and maintenance needs. Fiber lasers, for instance, have lower maintenance costs compared to CO2 lasers.
The Intersection of Metal Laser Cutting and CNC Technology
CNC technology enhances the performance of metal laser cutter by providing precise motion control and programmability. Together, they:
- Improve Efficiency: Automate complex cuts, reducing manual intervention.
- Increase Accuracy: Maintain consistent quality across batches.
- Enhance Flexibility: Adapt quickly to design changes, enabling rapid prototyping and production shifts.
For example, a manufacturer might use a laser cutter for initial profiling and a CNC mill for finishing touches. This synergy maximizes productivity and reduces waste.
Case Studies: Real-world Examples of Metal Laser Cutting Applications
Case 1: Automotive Manufacturing
An automotive supplier reduced production time by 30% after switching from plasma cutting to fiber laser cutters for thin steel components. This change not only improved efficiency but also enhanced the precision of their parts.
Case 2: Architectural Design
A metal laser cutter enabled a design firm to create intricate patterns on aluminum panels for a high-profile building facade. The project was completed ahead of schedule, showcasing the speed and precision of laser technology.
Case 3: Medical Devices
A medical device company achieved tighter tolerances on surgical instruments, improving patient outcomes while reducing costs. The use of metal laser cutter allowed them to scale production without compromising on quality.
FAQ
- What is the maximum thickness a metal laser cutter can handle?
Most machines cut up to 1 inch, depending on power and material. - Can metal laser cutters handle reflective materials?
Yes, especially fiber lasers designed for aluminum and copper. - How do I maintain a metal laser cutter?
Regular cleaning, lens calibration, and software updates are essential. - What industries benefit most from laser cutting?
Automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and architecture. - How does laser cutting compare to plasma cutting?
Laser cutting is more precise and produces cleaner edges but has higher initial costs. - What are the environmental benefits of using a metal laser cutter?
Laser cutting minimizes waste, reduces energy usage, and avoids material contamination. - Can laser cutters engrave as well as cut?
Yes, many metal laser cutters can engrave intricate designs and patterns on metal surfaces. - How do CNC systems enhance the functionality of metal laser cutter?
CNC systems enable precise control, repeatability, and the automation of complex designs. - What is the lifespan of a typical metal laser cutter?
With proper maintenance, most machines last 10-15 years or longer. - Are there portable metal laser cutters available?
Yes, compact and portable models are available for smaller projects or workshops.
Most machines cut up to 1 inch, depending on power and material. - Can metal laser cutter handle reflective materials?
Yes, especially fiber lasers designed for aluminum and copper. - How do I maintain a metal laser cutter?
Regular cleaning, lens calibration, and software updates are essential. - What industries benefit most from laser cutting?
Automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and architecture. - How does laser cutting compare to plasma cutting?
Laser cutting is more precise and produces cleaner edges but has higher initial costs.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- How CNC Machining and Laser Cutting Enhance Sheet Metal Hinge Production
Introduction In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, industries such as automotive, aerospace, and furniture production rely on precision components like sheet metal hinges. Hinges may seem like a small part of…
- Metal Engraving Techniques Explained: From CNC to Laser
Introduction: The Art and Science of Metal Engraving with CNC Metal engraving has always been a craft that combines precision, artistry, and functionality. Historically, it was the realm of skilled…
- From Vision to Reality: CNC Machining for Custom Furniture Design
Introduction to CNC Machining in Custom Furniture Design The advent of computer numerical control (CNC) machining has revolutionized the field of custom furniture design, allowing precise and intricate patterns to…
- CNC Machining of Hardened Steel: Techniques and Tips for Effective Manufacturing?
Introduction to CNC Machining The technology of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has revolutionized industrial manufacturing processes. At its core, CNC machining harnesses the power of computers and advanced software…
- Masterful Precision: Elevating Aluminum Craftsmanship with Laser Cutting
Laser cutting penetrates and slices through materials with a high-powered laser beam guided by CNC (Computer Numerical Control). The process achieves high-precision cuts, intricate detail work, and polished edges on…
- CNC Machining of Composite Materials: Challenges and Opportunities?
Introduction to CNC Machining and Composite Materials CNC, or Computer Numerical Control machining refers to a manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory machinery and tools.…
- The Industrial Magic of Precision
In modern industrial production, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology has become indispensable. With its characteristics of high precision, high efficiency, and high automation, CNC technology plays a crucial role in…