In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software has become an indispensable tool for CNC machinists. The integration of CAD software in CNC machining processes has revolutionized the way parts and components are designed and manufactured.
The purpose of this article is to present a comprehensive and comparative guide to the top CAD software options available for CNC machinists. With numerous CAD software choices on the market, it can be a daunting task for machinists to determine which one best suits their specific needs. By examining and evaluating the leading CAD software solutions, we aim to equip CNC machinists with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions and streamline their design and manufacturing processes.
Criteria for Evaluation
To ensure a comprehensive assessment of the top CAD software options for CNC machinists, it is crucial to establish the criteria by which these software solutions will be evaluated. When selecting CAD software for CNC machining, several key factors come into play, each with its own significance and impact on the machinist’s workflow and productivity.
Key factors to consider when selecting CAD software for CNC machining
- Usability: The software should have an intuitive interface and user-friendly features for easy navigation and quick adoption. A steep learning curve can hinder productivity and impede design realization.
- Features and capabilities: CAD software should offer a robust feature set that enables machinists to create complex geometries, generate toolpaths, simulate machining operations, and perform precise measurements. Advanced features like parametric modeling and assembly design enhance the design process.
- Compatibility: Seamless integration with CNC machining hardware and other software tools is crucial for a smooth workflow. Support for industry-standard file formats allows for easy data exchange and collaboration with suppliers, manufacturers, and clients.
- Support and documentation: Timely technical support, comprehensive documentation, and an active user community are vital for machinists to overcome challenges and make the most of the CAD software. Regular updates and bug fixes showcase the software vendor’s commitment to improvement.
In this comparative guide, we will evaluate the top CAD software options for CNC machinists based on the aforementioned criteria. Each software solution will be assessed and scored on various parameters, including usability, features, compatibility, and support. Additionally, we will consider real-world feedback and user reviews to provide a holistic and unbiased evaluation. By following this evaluation process, we aim to present an objective comparison that assists CNC machinists in selecting the CAD software that best aligns with their specific requirements and goals.
#3 Autodesk Fusion 360

Autodesk Fusion 360 is a comprehensive CAD software solution designed for both mechanical and industrial design. It offers a wide range of tools and features that cater to the needs of CNC machinists. Fusion 360 provides an integrated platform that combines CAD, CAM, and CAE capabilities, allowing users to seamlessly transition from design to manufacturing.
Autodesk Fusion 360 boasts an extensive set of features that empower CNC machinists to create precise and complex designs. It offers parametric modeling, which enables users to easily modify design dimensions and update associated features. Additionally, Fusion 360 provides tools for generating toolpaths, simulating machining operations, and performing finite element analysis (FEA) to ensure design integrity.
Recommended Read: How to Optimize Your CAD Models for CNC Machining
One of the key strengths of Autodesk Fusion 360 is its user-friendly interface and intuitive workflow. The software incorporates a modern and visually appealing design that facilitates efficient navigation and ease of use. However, it’s important to note that while Fusion 360 offers extensive capabilities, mastering all its features may require some learning and practice.
Pros:
- Comprehensive CAD, CAM, and CAE capabilities in a single platform.
- Intuitive user interface and workflow.
- Parametric modeling for efficient design modifications.
- Extensive toolset for generating toolpaths and simulating machining operations.
- Seamless compatibility with CNC machines and file formats.
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve for mastering all the software’s features.
- Some advanced functionalities may require additional training.
- Limited offline access and reliance on an internet connection for certain features.
#2 Siemens NX
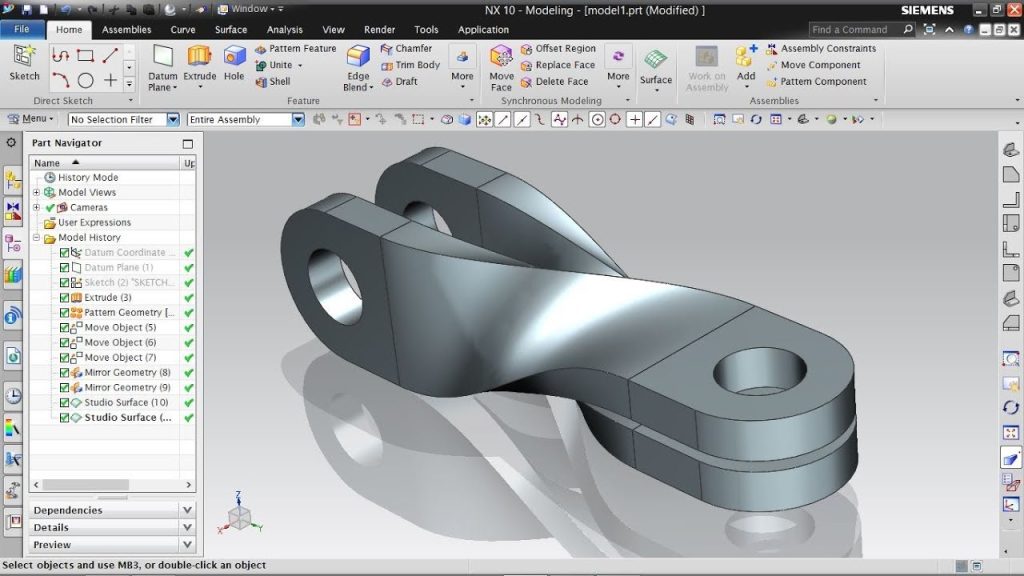
Siemens NX is a powerful CAD software solution widely used in various industries, including CNC machining. It offers a comprehensive suite of tools and functionalities that cater to the needs of CNC machinists. Siemens NX is known for its robust capabilities in product design, simulation, and manufacturing.
Siemens NX offers a rich and feature-packed environment, but it does come with a steeper learning curve compared to some other CAD software options. The software’s interface and workflow may require some time and training to become proficient. However, once users become familiar with the software, they can leverage its extensive capabilities for complex design and manufacturing tasks.
Pros:
- Comprehensive suite of CAD tools for CNC machining.
- Advanced features for parametric modeling, surface modeling, and assembly design.
- Powerful capabilities for generating toolpaths and simulating machining operations.
- Strong compatibility with CNC machines and industry-standard file formats.
- Established presence and wide adoption in various industries.
Cons:
- Steeper learning curve and initial training required to fully utilize the software’s capabilities.
- Higher cost compared to some other CAD software options.
- Resource-intensive software that may require robust hardware specifications for optimal performance.
#1 SolidWorks
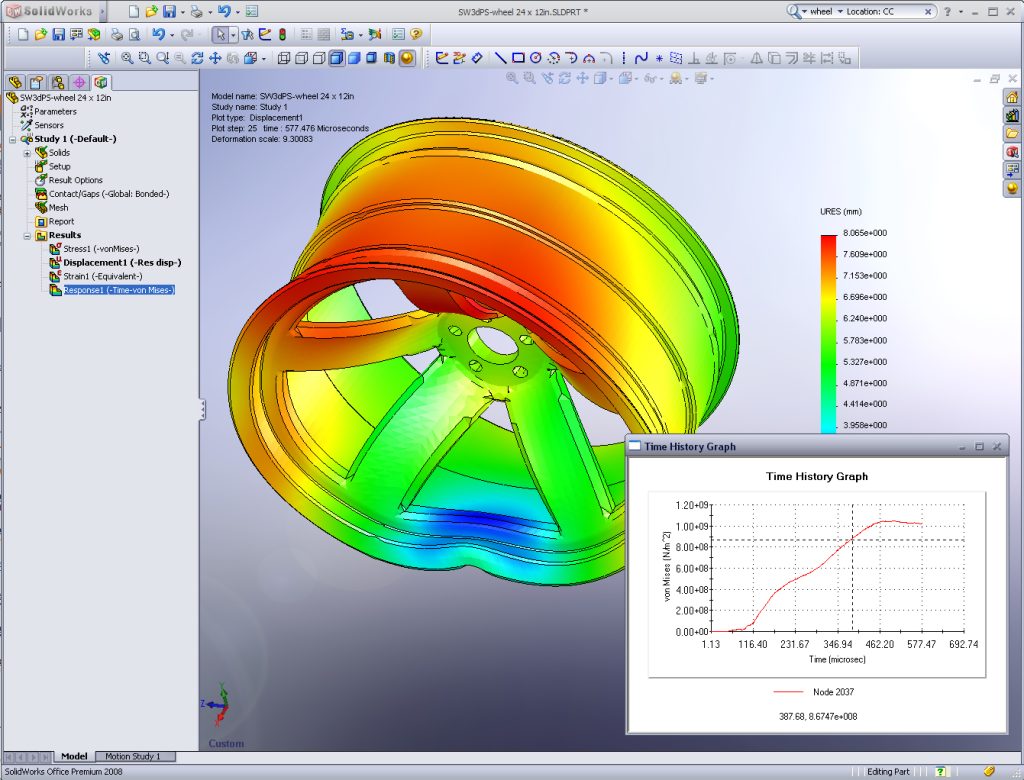
SolidWorks provides a broad range of powerful features and functionalities tailored for CNC machining. It offers robust 3D modeling capabilities, allowing machinists to create complex geometries with ease. SolidWorks also includes advanced assembly design tools, simulation capabilities for analyzing designs, and tools for generating toolpaths and CNC code.
SolidWorks employs a parametric modeling approach, enabling users to easily modify designs and make iterative changes. With its extensive library of tutorials, training resources, and a supportive user community, SolidWorks minimizes the learning curve and empowers machinists to quickly grasp its functionalities.
Pros:
User-friendly interface and intuitive workflow, reducing the learning curve.
Powerful 3D modeling capabilities for creating complex geometries.
Advanced assembly design tools and simulation capabilities for optimized designs.
Efficient generation of toolpaths and CNC code for machining operations.
Extensive library of tutorials, training resources, and a supportive user community.
Cons:
Higher cost compared to some other CAD software options.
Advanced functionalities may require additional training to fully utilize.
Limited direct support for certain file formats, requiring conversion in some cases.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Preparing Your CAD Model for CNC Machining
CNC machining has emerged as a go-to solution for manufacturing prototypes and parts involving cutting or drilling. This technology harnesses the power of a rotating cylindrical cutting tool to shape…
- How to Optimize Your CAD Models for CNC Machining
In this article, we will explore the essential steps to optimize your CAD models for CNC machining. We will delve into various aspects such as geometry, tolerances, material selection, and…
- 8 Must-Know Features of CAD Software for CNC Machining
In the world of computer-aided design (CAD) and CNC machining, CAD software plays a pivotal role in transforming design concepts into precise and intricate machine instructions. CAD software allows engineers,…