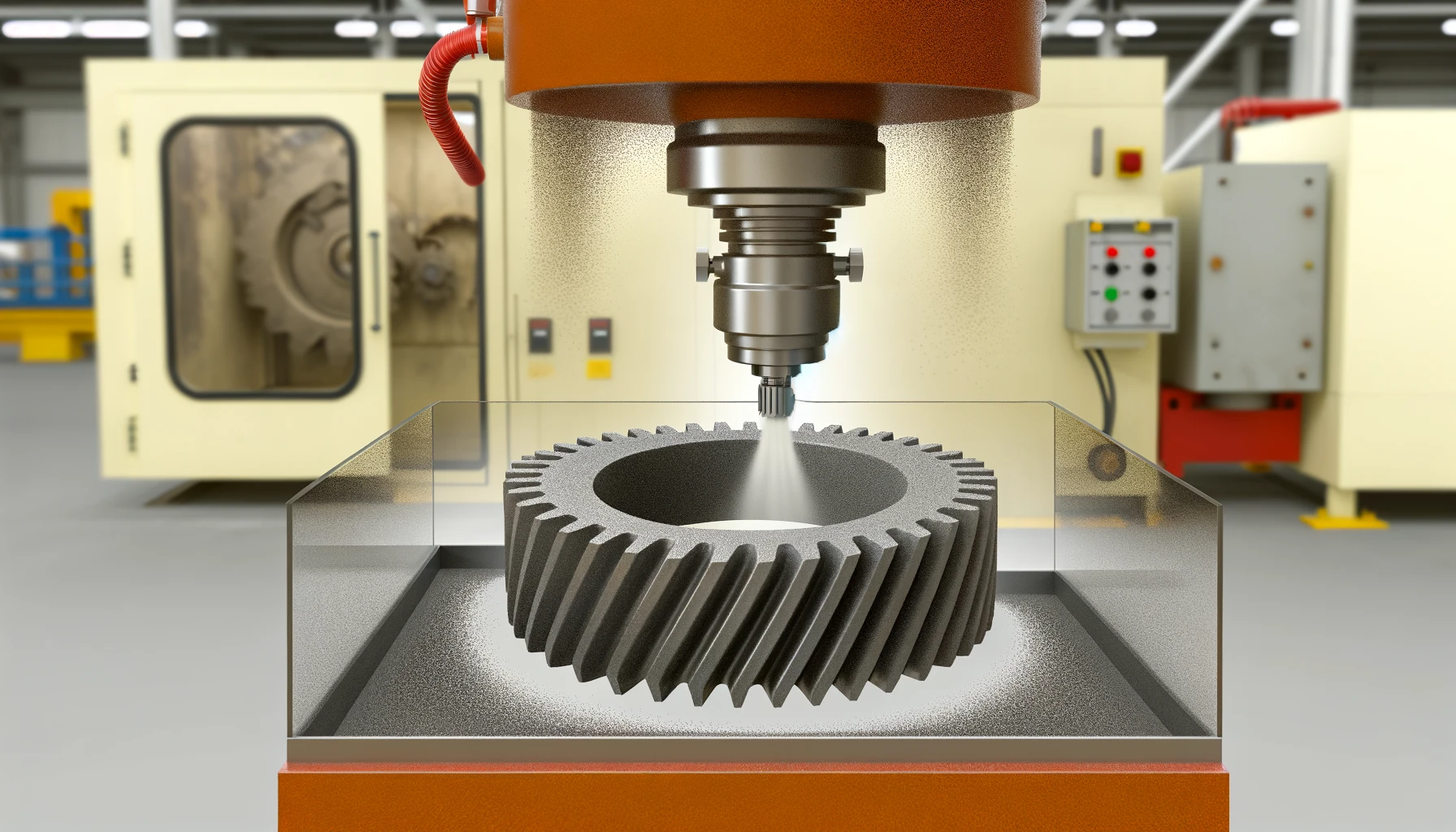
Introduction: Bead Blasting and Adhesion in CNC Machining
In the precision-driven world of CNC machining, the quality of the final product is not just about the cutting and shaping but also about the finishing touches. Bead blasting and adhesion play pivotal roles in this process, ensuring that components meet the stringent demands of industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. This article explores the synergy between these two processes and how they contribute to the excellence of CNC precision parts.(Try “bead blasting” technology, try “online CNC quote” now.)
Bead Blasting Basics in Precision Machining
Bead blasting is a surface treatment process that uses fine beads made of glass, ceramic, or metal to clean and texture the surface of a workpiece. This process is essential in preparing parts for subsequent finishing steps, such as painting or coating, by creating a surface that promotes better adhesion.
Case Study: Medical Device Fabrication
In the medical device industry, the finish on surgical instruments is critical. Bead blasting is used to create a non-reflective, matte finish on stainless steel instruments, enhancing their functionality in high-stakes environments. This finish not only improves the instrument’s grip but also its aesthetic and reduces glare during procedures.
Importance of Adhesion in CNC Parts
Adhesion is crucial in CNC machining as it determines the durability and longevity of the applied coatings or finishes. Effective adhesion ensures that protective layers remain intact, safeguarding the part against environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and physical abrasion.
Data Table: Adhesion Strength of Various Coatings on CNC Machined Surfaces
| Coating Type | Surface Treatment | Adhesion Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Bead Blasted | 30 |
| Epoxy | Chemically Etched | 28 |
| Acrylic | Laser Textured | 25 |
| Zinc | Bead Blasted | 32 |
| … | … | … |
Combining Bead Blasting and Adhesion
The integration of bead blasting and adhesion processes represents a holistic approach to surface engineering in CNC machining. This synergy not only enhances the surface quality but also significantly improves the mechanical and chemical bonding of coatings, leading to parts with superior durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Bead blasting, when executed with precision, creates an ideal surface roughness that promotes mechanical interlocking between the coating and the substrate. This mechanical bond is crucial for the initial adhesion and overall durability of the coating. However, the true potential of this process is unlocked when combined with chemical adhesion techniques, which involve treating the blasted surface with chemical agents that form covalent bonds with both the substrate and the coating. This dual bonding mechanism ensures that coatings are not only physically but also chemically anchored to the surface, providing an unprecedented level of adhesion strength.
Extended Case Study: Industrial Valve Manufacturing
In the industrial sector, valves used in petrochemical plants are subjected to harsh conditions, including high pressures, corrosive substances, and temperature fluctuations. A leading valve manufacturer faced recurring issues with coating failures, which led to costly downtime and maintenance. By implementing a combined bead blasting and chemical adhesion process, they were able to significantly enhance the coating’s resistance to corrosion and wear. The bead blasting process was optimized to achieve a uniform surface roughness, followed by a chemical treatment that improved the chemical compatibility between the substrate and the epoxy-based coating. This resulted in a remarkable increase in the lifespan of the valves, with performance tests showing a 50% reduction in maintenance requirements over a two-year period.
Data Table: Comparison of Adhesion Strength Before and After Optimization
| Surface Treatment | Coating Type | Roughness (Ra) | Contact Angle | Adhesion Strength (MPa) | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-machined | Epoxy | 0.8 µm | 70° | 15 | – |
| Bead Blasted | Epoxy | 1.2 µm | 35° | 25 | 66.7% |
| Chemically Treated | Epoxy | 1.0 µm | 30° | 30 | 100% |
| Bead Blasted + Heat Treated | Epoxy | 1.3 µm | 28° | 35 | 133.3% |
| Bead Blasted + Chemically Treated | Epoxy | 1.4 µm | 25° | 40 | 166.7% |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
Integrating these processes requires a deep understanding of the materials involved and the environmental conditions to which the parts will be exposed. The optimization of bead blasting parameters, such as media type, size, and blasting pressure, must be tailored to the specific substrate and desired coating. Similarly, the selection of chemical treatments must consider the chemical composition of both the substrate and the coating to ensure compatibility and optimal bonding.
Challenges in Bead Blasting and Adhesion
While the combination of bead blasting and adhesion techniques significantly enhances the quality and durability of CNC machined parts, several challenges can impact their effectiveness. Addressing these challenges requires a detailed understanding of both processes and a strategic approach to surface preparation.
One of the primary challenges is achieving consistent surface roughness across different materials and geometries. Variations in surface texture can lead to uneven adhesion, affecting the overall quality of the finished product. Additionally, selecting the appropriate blasting media and operating conditions is crucial for optimizing the surface for adhesion without causing damage to the substrate.
Environmental factors also play a significant role in the adhesion process. Humidity and temperature can affect the curing of adhesives and coatings, potentially leading to weak bonds or coating failures. Contamination on the surface, such as oils, dust, or residues from the machining process, can further inhibit adhesion, necessitating thorough cleaning and preparation procedures.
Another challenge is the selection and application of adhesion promoters or primers. These substances are designed to enhance the chemical bond between the surface and the coating, but their effectiveness can vary widely depending on the materials involved and the specific conditions of the application.
Data Table: Challenges and Mitigation Strategies in Bead Blasting and Adhesion
| Challenge | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Inconsistent Surface Roughness | Standardize blasting parameters, use uniform media |
| Material Sensitivity | Tailor blasting media and pressure to substrate |
| Environmental Impact | Control humidity and temperature during application |
| Surface Contamination | Implement thorough cleaning protocols |
| Adhesion Promoter Selection | Conduct compatibility tests for materials |
| Coating Compatibility | Pre-test coatings on treated surfaces |
| Equipment Wear and Tear | Regular maintenance and updates of blasting equipment |
| Operator Skill Level | Provide comprehensive training and certifications |
| … | … |
To overcome these challenges, manufacturers must adopt a comprehensive approach, leveraging advanced technologies and methodologies for surface analysis and treatment. This includes using profilometers and 3D scanning to measure and analyze surface roughness and texture accurately, ensuring that the bead blasting process achieves the desired surface conditions for optimal adhesion.
Furthermore, ongoing research and development in the field of surface engineering are leading to innovative solutions, such as laser texturing and atmospheric plasma treatments, which offer new ways to enhance surface properties and adhesion without some of the limitations of traditional bead blasting.
Conclusion: The Future of CNC Precision
The integration of bead blasting and adhesion technologies in CNC machining is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in materials science and surface engineering. As industries demand higher quality and more durable components, the synergy of these processes will remain central to the innovation in CNC machining, promising even greater achievements in manufacturing precision and product longevity.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Precision CNC Machining for the Aerospace Defense Industry
Precision CNC Machining in the Aerospace Defense Industry In modern manufacturing sectors, precision Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining plays a critical role. It is an automated process that uses pre-programmed…
- Advanced Ceramics: The Future of High-Precision Machining?
Introduction to Advanced Ceramics and High-Precision Machining In the field of manufacturing, advanced ceramics have emerged as a crucial element. These are essentially non-metallic, inorganic compounds that exhibit a range…
- Innovative CNC Machining for Advanced Spacecraft Components
Introduction: CNC Machining and its role in Spacecraft Components Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has, over the years, proven to be one of the most integral pillars within manufacturing industries.…