CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a leading manufacturing process that involves the use of pre-programmed computer software to dictate movements of factory machinery and tools. The precision enabled by this digital approach transcends the classic manual controls where live operators were necessary for guiding cutting tools, lathes, mills, or routers. This article shines light on two crucial aspects of CNC machining – riveting and tack welding.
Rivets are permanent mechanical fasteners used during assembling. A considerable portion of the aircraft industry relies heavily on rivets due to their high shear strength and ability to hold together different materials like plastic, metal, and leather. Given their importance, hitting optimal accuracy in producing them via CNC machining can ensure overall product quality.
The art of creating rivets with CNC machines starts with choosing a suitable material according to the desired end-product’s properties. Steel, aluminum, copper, monel, and brass are some commonly used materials. These are then processed under different CNC processes such as milling, turning, grinding, drilling, or boring operated within microns’ stringent tolerances.
The cut-to-size raw material blocks get inspected before being placed onto a CNC lathe machine for actual machining using compatible tool bits mounted into the turret. Computer-aided design (CAD) or manufacturing (CAM) software provides accurate measurements for the desired dimensions, which form data files read by the CNC machines. Next follows an automated series of actions from roughing, semi-finishing, through to finishing, ensuring all exterior features match the set specifications. For hollow rivets, another layer of operation – deep hole drilling – may be implemented after the product has taken shape.
Given that providing superior-radius junctions between the head and body is crucial to enhance fatigue life, a special broaching setup on the CNC machine accomplishes this, followed by surface finishing processes and inspections.
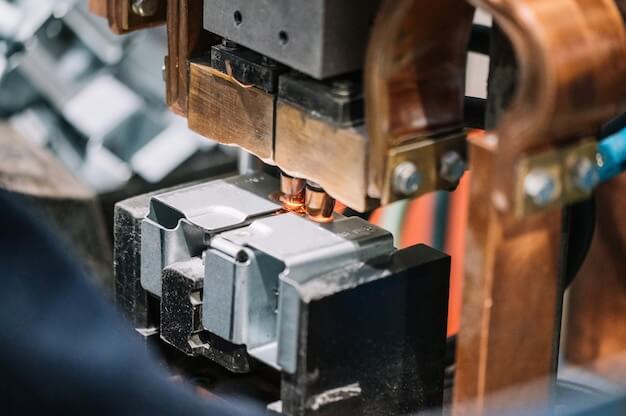
Another critical phase in the CNC machining field is tack welding – a rapid welding process that holds down workpieces before an extensive or full-length welding operation. It creates ‘tacks’ to serve as temporary joints, maintaining the product dimensions intact until finalizing with seam or spot welding.
Handling tack welding optimally during CNC operations requires significant care due to its fast nature and high risk of distortions. Firstly, it’s vital to clean the workpiece surfaces to remove any dust, oil, or rust beforehand since contaminants can impede fusion and compromise weld quality. Then, depending on the material type and thickness, appropriate filler rods and torch settings need adjustments for achieving excellent control over heat input.
The art of mastering tack welding via CNC also involves applying specific sequences – directional offsetting from distortion forces helps correct potential deviations. Moreover, cooling time between each tack weld needs apt attention; going too quickly could permit heat buildup leading to deformations, while waiting too long risks corrosion attacks on parts left unshielded without the protective gas. Lastly, once all tacks solidify appropriately, completing the formal welding ensues under carefully adjusted parameters ensuring meeting the desired standards.
In summary, both riveting and tack welding play pivotal roles within CNC machining. Producing rivets necessitate compliance with strict specifications aligned with fatigue performance, whereas tack welding requires acute attentiveness towards preventing distortions and protecting overall component integrity. By understanding these intricate aspects, manufacturers can ensure optimized productivity and superior craftsmanship for CNC machined products.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Unlocking New Possibilities in CNC Machined Titanium Medical Devices
Introduction to CNC Machined Titanium Medical Devices The prevalence of CNC machined titanium medical devices in the healthcare sector demonstrates their immense significance and usefulness. This technology furnishes an essential…
- CNC Aluminum Machining Services: Advanced Techniques for Perfect Parts
CNC Aluminum Machining Services In the current manufacturing landscape, CNC aluminum machining services play a pivotal role. CNC which simply translates to 'Computer Numerical Control', is an advanced technique used…
- Hastelloy vs. Stainless Steel in Chemical Processing Equipment: CNC Machining Perspectives?
Hastelloy vs. Stainless Steel in Chemical Processing Equipment: An Introduction In the realm of chemical processing equipment, two commonly used materials include Hastelloy and stainless steel. Hastelloy, a reputed superalloy…