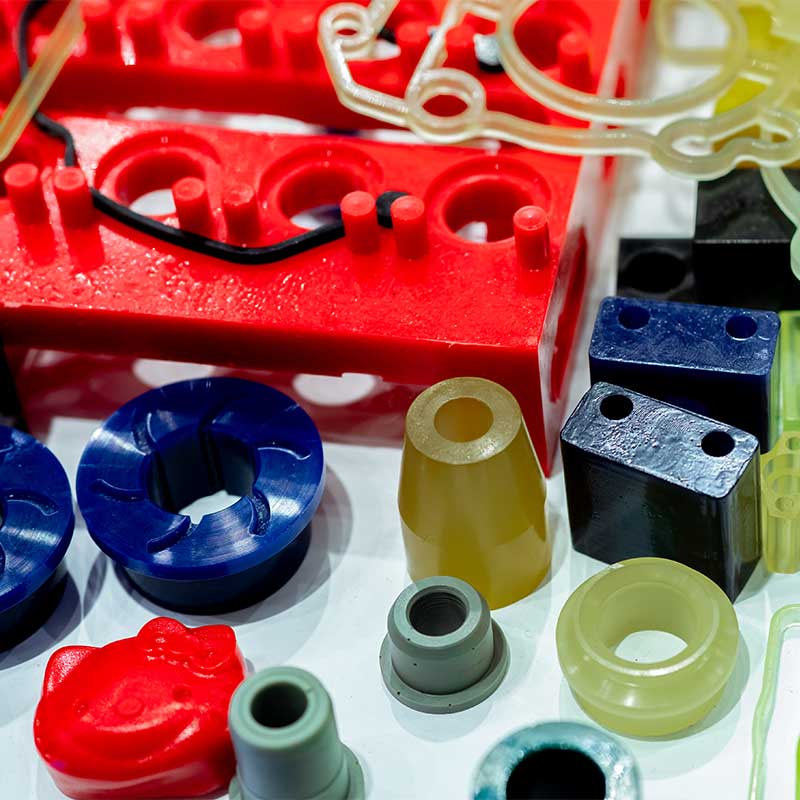
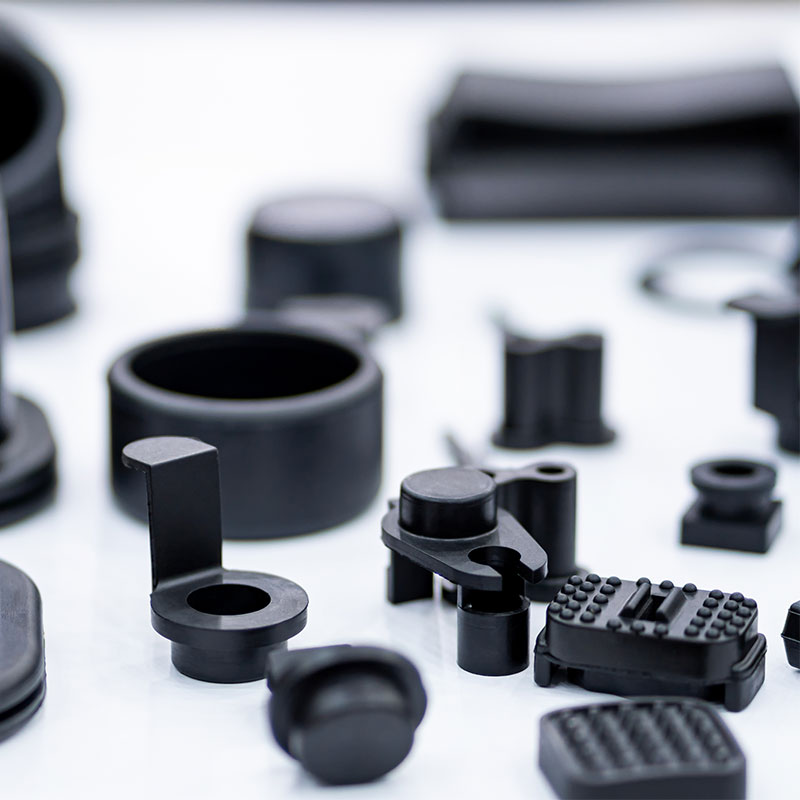
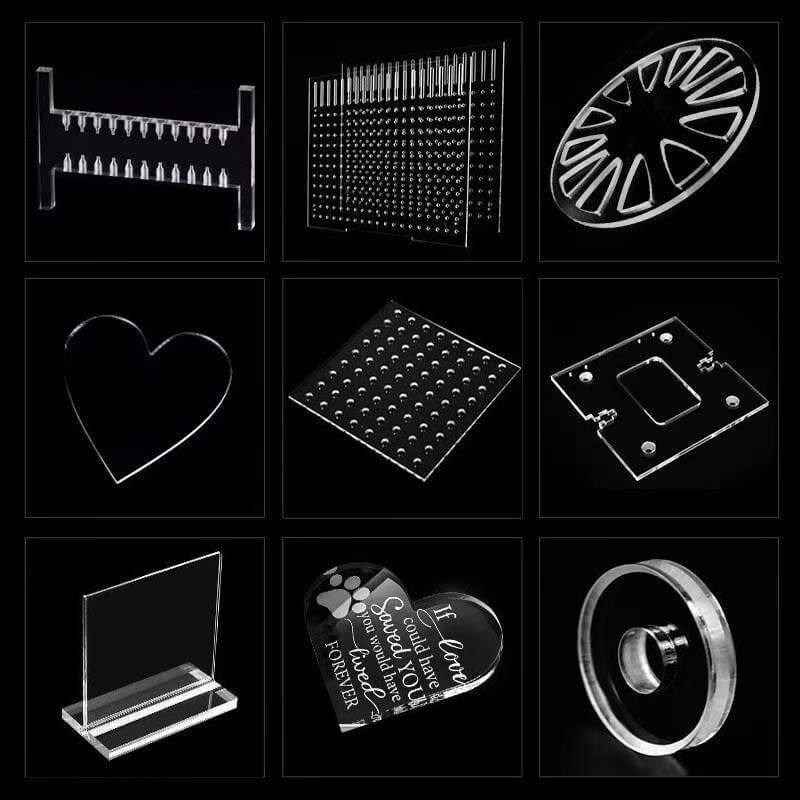
Plastic materials can primarily be divided into thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. Thermoplastics soften when heated and harden when cooled, and they can be reprocessed multiple times. On the other hand, thermosetting plastics, once hardened, cannot be reshaped by heating.
Thermoplastics: These plastics become soft upon heating and can harden again upon cooling, making them suitable for large-scale production. Common thermoplastics include:
-
Polyethylene (PE): A widely used thermoplastic with excellent chemical resistance and low cost, commonly used in packaging, piping, and containers.
-
Polypropylene (PP): Known for its good rigidity, chemical resistance, and heat resistance, polypropylene is used in automotive parts, appliances, medical devices, and more.
-
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC has good mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, commonly used in pipes, cables, and construction materials.
-
Polycarbonate (PC): Polycarbonate has excellent transparency, impact resistance, and high-temperature stability. It is commonly used for safety shields, CDs, optical lenses, and more.
Other Common Thermoplastics:
-
Acrylic (PMMA): Known for its high transparency, acrylic is used in applications that require clear materials, such as display screens and signage.
-
Polyamide (Nylon): Nylon has excellent mechanical properties, wear resistance, and low friction, making it ideal for bearings, gears, and other high-wear applications.
-
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): PET is commonly used in bottles and packaging, as it is strong, lightweight, and has good barrier properties.
Thermosetting Plastics: Unlike thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics harden permanently after heating and cannot be remelted. These materials are typically used in applications where heat resistance and structural integrity are essential, such as in electrical components and high-performance applications.