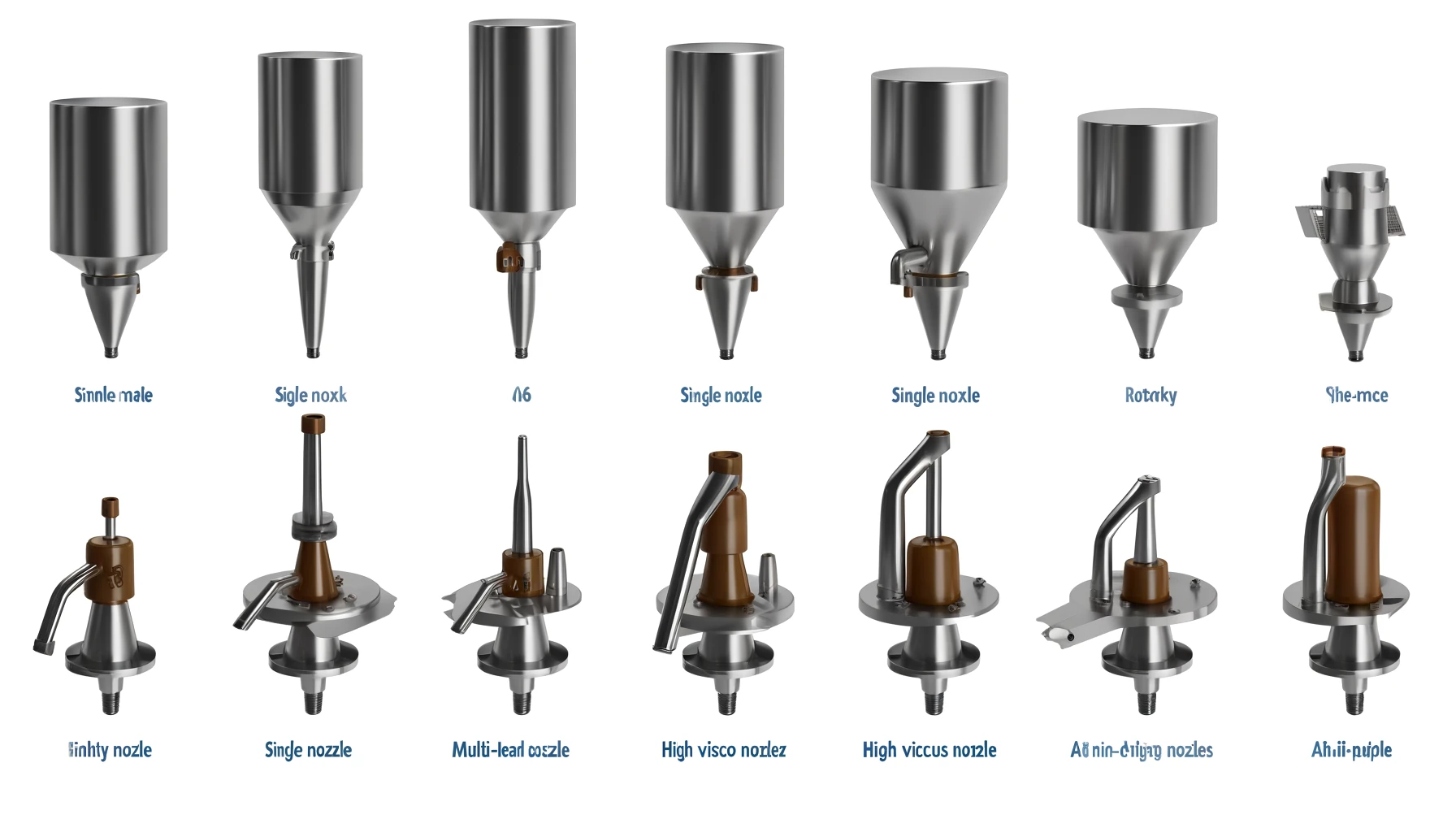
Introduction: The Role of CNC Machined Filling Nozzles in Food Automation?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has revolutionized the production of precise and intricate components across various industries, with food automation being one of the significant sectors benefiting from its advancements. And ,among them, the filling nozzles are also CNC machining parts.Filling nozzles, crucial for the accurate and hygienic dispensing of food products, are exemplary of parts that require the high precision and customization that CNC machining offers.
Filling nozzles must meet strict criteria related to food safety, durability, and compatibility with machinery. These components are integral to ensuring that food products are processed and packaged efficiently, maintaining quality and safety from production to consumption. However, the question arises: are these CNC machined nozzles compatible with all food automation machinery, or are there limitations and specific considerations that must be addressed? This article delves into these questions, exploring the interplay between nozzle design, material selection, and machine requirements.
What Are the Key Design Features of CNC Machined Filling Nozzles?
The design of CNC machined filling nozzles directly influences their compatibility with food automation machinery. Key features include:
- Precision: CNC machining allows for high precision in manufacturing nozzles that can have complex shapes and fine features, necessary for controlling the flow and volume of food products.
- Customization: Depending on the type of food processing machine, nozzles may require specific designs, such as varying diameters, lengths, or shapes to fit into particular machinery without causing disruptions in automated lines.
- Surface Finish: A high-quality surface finish is critical for preventing food residue buildup and ensuring easy cleaning and sanitation, which is paramount in food processing.
These design features ensure that nozzles not only fit mechanically into different machines but also perform their functions efficiently, adhering to the rigorous standards required in the food industry.
How Do Material Choices Affect the Compatibility of CNC Nozzles with Food Machinery?
The material used to manufacture CNC nozzles plays a crucial role in their compatibility with food processing machinery. Common materials include:
- Stainless Steel: Highly favored for its resistance to corrosion and ease of sanitation, stainless steel is commonly used for nozzles in food processing machinery. It’s durable and capable of withstanding the harsh environments of food processing, including exposure to extreme temperatures and corrosive cleaning chemicals.
- Titanium: Known for its strength and lightweight properties, titanium is used where weight is a concern, and its superior corrosion resistance makes it ideal for highly acidic or saline environments.
- Plastic: High-grade plastics like PEEK are used for nozzles when flexibility and cost are more significant concerns. Plastics can be tailored for specific non-reactive properties and are often used in non-heat-intensive stages of food processing.
Each material offers distinct advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the food processing task and the machinery used. This section would include a table or diagram illustrating the properties of each material and their typical applications in food processing.
Case Study: Success and Limitations of Stainless Steel Nozzles in Dairy Equipment
In the dairy industry, the demands on filling nozzles are particularly high due to the sensitivity of dairy products to contamination and spoilage. Stainless steel is predominantly used due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning. However, despite these benefits, stainless steel nozzles encounter specific limitations in dairy applications:
- Thermal Conductivity: Stainless steel’s relatively high thermal conductivity poses challenges in environments where temperature control is crucial. For example, during the filling of ice cream or yogurt, variations in nozzle temperature can affect product consistency.
- Wear and Tear: While stainless steel is durable, the frequent cleaning cycles required in dairy processing can lead to surface wear over time, affecting the nozzle’s performance and the sanitary conditions.
- Case Example: A leading dairy equipment manufacturer faced issues with nozzle clogging and maintenance costs. They experimented with a surface treatment technique that enhanced the wear resistance of stainless steel nozzles, thereby extending their operational life and reducing downtime for cleaning and maintenance.
This case study underscores the importance of material engineering and process adaptations in overcoming the challenges faced by CNC machined nozzles in specific food industry applications.
Are There Industry Standards Governing the Compatibility of CNC Nozzles?
The compatibility of CNC machined nozzles with various food automation machinery is not just a matter of design and material choice but also of adhering to industry standards. These standards ensure that components like nozzles meet rigorous health, safety, and operational benchmarks:
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Standards: In the United States, the FDA provides regulations for materials that come into contact with food. These standards help ensure that materials like stainless steel or certain plastics used in nozzles do not leach harmful substances into food products.
- ISO Standards: The International Organization for Standardization provides guidelines on the manufacture and design of food processing equipment, which includes dimensions and tolerances that affect the compatibility of nozzles across different machines.
- European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group (EHEDG): This organization focuses on the hygienic design of equipment and machinery for the food industry, influencing how nozzles should be designed to facilitate cleaning and prevent contamination.
Adherence to these standards not only ensures safety and efficiency but also impacts the design choices that manufacturers of CNC nozzles must make to ensure their products can be universally compatible and meet global market needs.
Data Analysis: Variability in Equipment Interfaces and CNC Nozzle Adaptations
The compatibility of CNC nozzles with various types of food automation machinery can be significantly influenced by the variability in equipment interfaces. An analysis of common interface dimensions and required nozzle adaptations across different types of machinery reveals:
- Bottling Machinery: Typically requires nozzles with precise flow control to handle liquids of varying viscosities. Custom threading adaptations are often necessary to match specific bottling line setups.
- Dairy Equipment: Nozzles must withstand acidic environments and frequent cleaning, necessitating specific materials and surface treatments for durability.
- Baking Machinery: Involves nozzles designed for high-viscosity materials, requiring wide flow paths and special coatings to prevent sticking.
| Equipment Type | Interface Standard | Common Adaptations | Compatibility Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bottling Lines | ISO 8317 | Thread adjustments | Viscosity management |
| Dairy Machines | EHEDG guidelines | Corrosion-resistant coatings | Chemical exposure |
| Baking Systems | FDA regulations | Non-stick surfaces | Temperature management |
This data illustrates the complexity of ensuring that CNC machined nozzles are compatible with all food automation machinery, highlighting the need for manufacturers to offer customizable solutions and maintain flexibility in design and production.
How Can Adjustments in CNC Machining Enhance Nozzle Compatibility?
Making strategic adjustments in the CNC machining process is crucial for enhancing the compatibility of nozzles with various types of food automation machinery. These adjustments focus on several key areas:
- Adaptive Tooling: Utilizing advanced CNC tooling that can adapt to different product specifications allows for the creation of nozzles that can seamlessly integrate with various machines without requiring significant modifications.
- Precision Engineering: Improving the precision of CNC machining processes ensures that nozzles meet strict dimensional and shape requirements, which is vital for maintaining compatibility with machinery that may have tight interface tolerances.
- Modular Design: Developing nozzles with a modular design can offer flexibility, allowing parts of the nozzle to be swapped out or adjusted depending on the specific requirements of the food processing machinery they will be used with.
By focusing on these adaptive and precise machining strategies, manufacturers can significantly reduce compatibility issues and enhance the versatility of their nozzle products across different food processing applications.
Case Study: Retrofitting CNC Nozzles for Multifunctional Food Processing Lines
This case study details the challenges and solutions involved in retrofitting CNC machined nozzles for use in multifunctional food processing lines:
- Background: A major food processing company needed to retrofit its existing CNC machined nozzles to accommodate a new line of beverage products that required different viscosity handling capabilities.
- Challenge: The existing nozzles were not compatible with the new product line’s viscosity and temperature requirements, leading to production inefficiencies and product wastage.
- Solution: The company collaborated with nozzle manufacturers to redesign the nozzle geometry and incorporate temperature control capabilities. This involved using CNC machining to adjust nozzle dimensions and introducing materials better suited to handle higher temperatures.
- Outcome: The retrofitted nozzles improved product flow control and reduced waste, leading to a significant increase in production efficiency and a reduction in downtime.
This example illustrates how retrofitting, combined with precise CNC adjustments, can extend the functionality of existing machinery and adapt to evolving production demands.
Data Analysis: Longevity and Maintenance Needs of CNC Machined Nozzles in Various Machines
To further understand the practical implications of using CNC machined nozzles across different types of machinery, this section provides a comprehensive analysis of their longevity and maintenance requirements:
| Machine Type | Average Nozzle Lifespan | Maintenance Frequency | Common Failure Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bottling Machinery | 3 years | Bi-annually | Seal wear, clogging |
| Dairy Equipment | 4 years | Annually | Corrosion, gasket failure |
| Baking Machinery | 5 years | Every 2 years | Wear due to abrasive mixes |
| Meat Processing | 2 years | Quarterly | Fouling from high-fat content |
This table highlights the need for tailored maintenance strategies based on the specific operating conditions associated with different machinery, ensuring optimal nozzle performance and longevity.
Conclusion: Future Trends in CNC Machining for Enhanced Equipment Compatibility
In conclusion, as the food processing industry continues to evolve, so too must the technologies that support it. Future trends in CNC machining are likely to focus on increasing automation, enhancing material science to develop more durable and versatile nozzles, and furthering standardization efforts to simplify compatibility across global markets. Innovations in smart manufacturing and real-time monitoring may also play a significant role in the adaptive production of CNC nozzles, ensuring they meet the diverse and changing needs of food automation machinery efficiently and effectively.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- What Makes Chinese CNC Machining Ideal for Producing Food Automation Machinery Shafts
Introduction to CNC Machining in China China's prowess in manufacturing has grown significantly, with CNC machining at the forefront of its industrial capabilities. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a…
- How Do CNC Machining Parts Help Food Automation Machinery Comply with Strict Food Safety Regulations?
Introduction CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, providing unparalleled precision and efficiency. In the context of food automation machinery, CNC machining parts play a critical…
- How to Evaluate a CNC Supplier’s Capability in Producing Sealing Rings for Food Automation Machinery?
Introduction to CNC Machining and Its Importance in Food Automation Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining represents a critical technology in modern manufacturing, noted for its precision, efficiency, and adaptability. This…