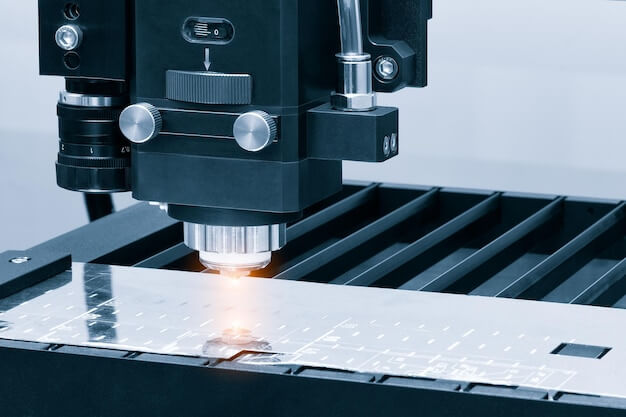
So therefore, delivering precise execution in these products’ designs and assembly using CNC machinery upholds both economic viability and customer satisfaction.
Real-world Applications of CNC Machining in Consumer Electronics
In the field of consumer electronics, CNC machining plays a crucial role. The high precision requirement in modern devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and even wearables is significantly achieved through this technology. For instance, Apple Inc., one of the tech industry leaders, utilizes CNC machines for their iPhones’ meticulous design process. Every single iPhone body undergoes CNC drilling to create precise holes for speakers and ports.
- The aluminum bodies of MacBook laptops are also created using extensive CNC machining processes for exactness in build and form factor.
- Other mainstream tech companies like Samsung and Sony leverage on CNC capabilities for high-end product lines.
- Even drone technology uses CNC-machined parts for frames and propellers critical for flight stability and control maneuvers.
Sophisticated, compact designs combined with robust performance standards wouldn’t be achievable without the precision allowed by CNC machining.
Advantages of Using CNC Machines for High-End Electronic Products
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining offers significant advantages to the manufacturing process of high-end electronic products, playing a pivotal role in their quality, consistency, efficiency and customizability. Due to its automated nature, precision is unmatched, resulting in an improved product quality with less variability.
- Improved Quality: Through precise measurements and cutting abilities, CNC machines eliminate human error, achieving higher accuracy levels.
- Consistency: Unlike manual machining, CNC ensures that each part produced is identical to the last, critical for electronics where parts interchangeability is vital.
- Efficiency: CNC machines can operate around the clock with minimal supervision. They also reduce waste material, making the production process economically efficient.
- Customizability: With simple design changes on the computer, new and unique pieces can be created without time-consuming and costly retooling, allowing easy customization.
An excellent illustration of these benefits can be seen in the production of smartphones’ intricate internal components, where CNC machining’s precise cuts are essential to deliver optimal product performance.
Addressing Common Pain Points/Problems in CNC Machining: Safety Issues, Costs, and Learning Curves
The complex nature of CNC machining for high-end consumer electronics inherently raises certain challenges. Among these are safety concerns, cost-efficiency, and steep learning curves. Adherence to strict safety protocols is vital due to the risks associated with operating heavy machinery; mishandling can lead to severe harm or fatality. However, many manufacturers resort to extensive training programs which can prove to be expensive. Furthermore, mastering the minutiae of precision engineering poses its daunting learning curve.
Yet, there exist viable solutions for each problem. For example, accident prevention measures such as placing machines in well-ventilated areas or using protective equipment can effectively mitigate safety-related issues. To cope with price surges, implementing lean manufacturing principles that eliminate waste and boost productivity is helpful. Meanwhile, adopting an effective onboarding system that utilizes digital simulators can expedite the familiarising process for new hires, reducing the gravity of the learning curve.
Latest Trends in CNC Machinery for Consumer Electronics Manufacturing
In the ever-evolving sector of consumer electronics manufacturing, the application of computer numerical control (CNC) machining continues to undertake revolutionary changes. Currently, two notable trends are noticeably shaping the dynamics of this domain: 3D printing and Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration.
- 3D Printing: With exceptional agility over design adjustments and the ability to yield complex components, 3D printing has become integral in contemporaneous CNC Machining practices. By refining prototyping processes through quicker alterations and rectifications, it significantly escalates product time-to-market.
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI automation is progressively being incorporated with CNC systems to impel uninterrupted production, enhance precision, improve quality controls, and optimize operational efficacy. Machine learning algorithms can assimilate patterns from past data to predict system failures or maintenance needs, thereby preventing expensive downtimes.
These current advancements signify an intersection of technology and manufacturing, enriching accuracy in production while simultaneously accelerating pace and cost efficiencies. As these trends continue to mature, CNC machinery becomes increasingly more important in shaping the future of the consumer electronics industry.