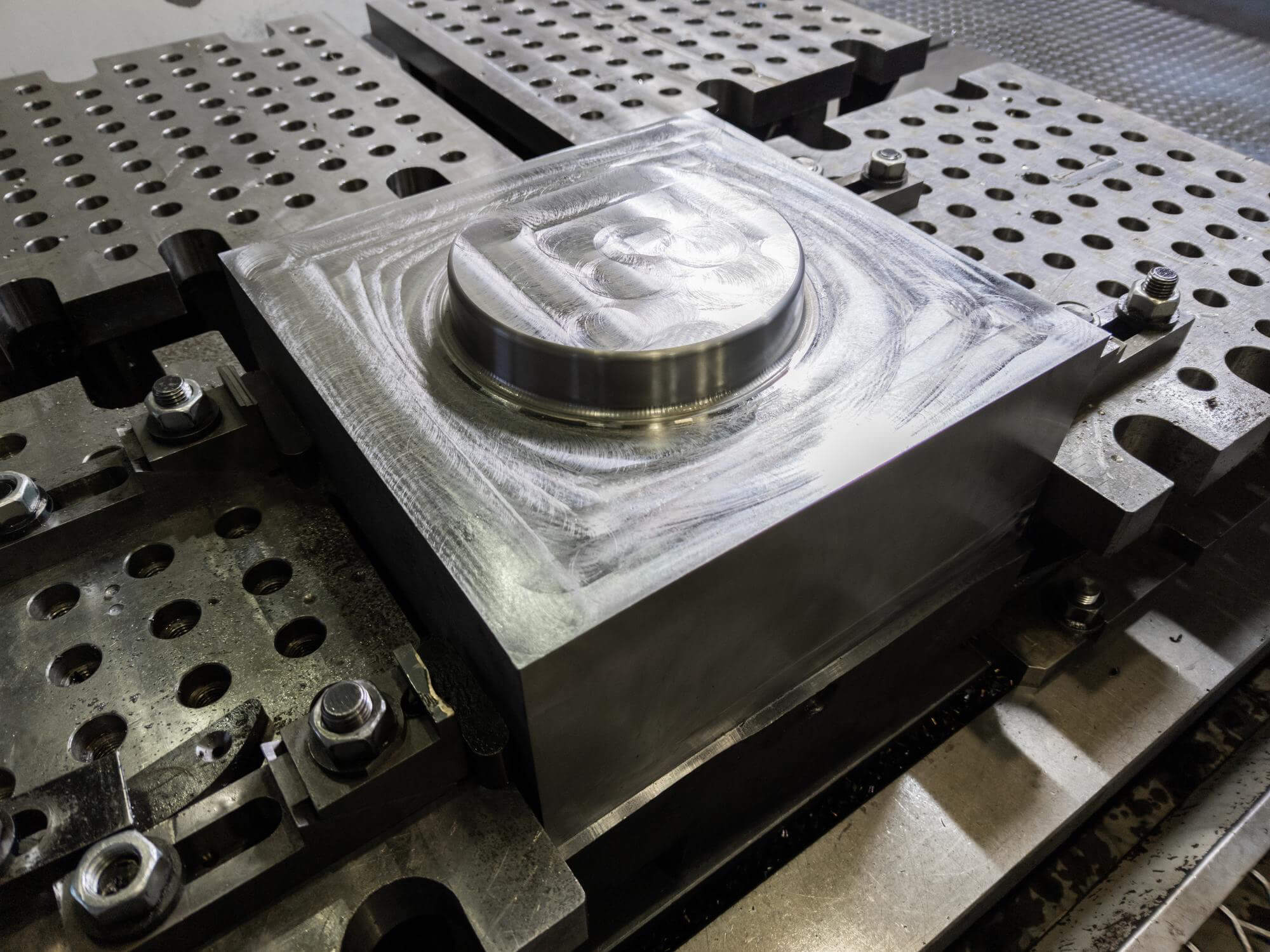
In the world of CNC precision machining, managing and refining moulding lines is a critical aspect that can significantly impact the quality of the final product, particularly in mold-making processes. For technical professionals and procurement specialists, understanding the techniques involved in CNC machining—especially milling and filing—can be crucial in evaluating a supplier’s capabilities and ensuring that the end products meet the highest standards. This article will delve into these machining techniques, offering insights into how they contribute to effective moulding line management and the production of superior molds.
1. Introduction to CNC Precision Machining and Moulding Lines
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) precision machining is a manufacturing process that involves the use of computer-controlled machine tools to produce high-precision parts. It is widely used in mold making, where accuracy and surface quality are paramount. One of the challenges in this process is the management of moulding lines—those subtle ridges or lines that appear on a part where two halves of a mold meet. Proper management of these lines is essential to produce high-quality, aesthetically pleasing, and functional molds.
Key Points:
- CNC Precision Machining ensures high accuracy and consistency in part production.
- Moulding Lines need careful attention to avoid compromising the quality and functionality of the final product.
- Milling and Filing Techniques are critical in managing and refining these lines to ensure superior mold quality.
2. Overview of Milling Techniques in CNC Precision Machining
Milling is one of the most versatile and widely used machining processes in CNC precision machining. It involves the use of rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece. In the context of mold making, milling is particularly important for managing and refining moulding lines.
a. Horizontal Milling
- Process: In horizontal milling, the cutter’s axis of rotation is parallel to the workpiece surface. This method is often used for cutting grooves, slots, and other features that require a consistent, horizontal cut.
- Application: Horizontal milling is ideal for creating the parting lines in molds. By precisely controlling the milling cutter’s path and depth, operators can ensure that the parting lines are clean and minimal.
b. Face Milling
- Process: Face milling uses a cutter that rotates on an axis perpendicular to the workpiece surface. This process is used to produce flat surfaces or to refine the surface finish of a part.
- Application: Face milling is particularly useful in reducing the prominence of moulding lines. By removing a thin layer of material, face milling can smooth out the lines, enhancing the surface quality of the mold.
c. High-Speed Milling
- Process: High-speed milling involves using a cutter at significantly higher speeds, which allows for faster material removal and finer finishes.
- Application: High-speed milling is advantageous for detailed and intricate mold features, where minimizing the appearance of moulding lines is critical. This technique can achieve a high surface finish, reducing the need for additional post-processing.
Table 1: Key Milling Techniques and Their Applications in Moulding Line Management
| Milling Technique | Description | Application in Moulding Line Management | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Milling | Cutter rotates parallel to workpiece | Creating and refining parting lines | Precision in parting line formation |
| Face Milling | Cutter rotates perpendicular to workpiece | Smoothing out surfaces and lines | Enhanced surface finish |
| High-Speed Milling | High-speed cutter rotation | Detailed features, fine line management | Faster production, reduced post-processing |
3. Filing Techniques for Moulding Line Refinement
While milling is essential for the initial creation and refinement of moulding lines, filing plays a crucial role in the final finishing stage. Filing can be done manually or with the aid of CNC-controlled tools to achieve the desired level of precision and surface quality.
a. Manual Filing
- Process: Manual filing involves using hand tools to carefully remove material from the workpiece, focusing on areas where milling may not have achieved the required finish.
- Application: Manual filing is often used to refine intricate mold details, particularly in areas where the moulding lines are still visible after milling. It allows for fine adjustments and precision finishing.
b. Rotary Filing
- Process: Rotary files, also known as burrs, are used in CNC machines to achieve fine surface finishes on complex mold geometries. These tools rotate at high speeds to remove small amounts of material.
- Application: Rotary filing is ideal for smoothing out moulding lines in hard-to-reach areas of the mold. It provides a high level of control and can be used on both metal and plastic molds.
c. Automated Filing
- Process: Automated filing involves the use of CNC-controlled filing tools that can be programmed to follow specific paths, ensuring consistent results across multiple parts.
- Application: This method is particularly useful in large-scale production, where consistency and speed are crucial. Automated filing can effectively manage moulding lines across various parts, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Table 2: Filing Techniques and Their Role in Moulding Line Refinement
| Filing Technique | Description | Application in Moulding Line Refinement | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Filing | Hand tools for precision material removal | Refining intricate details, manual precision | High control, adaptability |
| Rotary Filing | High-speed rotary tools for fine finishes | Smoothing lines in complex geometries | High precision, suitable for detailed work |
| Automated Filing | CNC-controlled filing tools | Consistent results in large-scale production | Speed, consistency, reduced manual labor |
4. CNC Precision Machining: Integrating Milling and Filing for Optimal Moulding Line Management
In CNC precision machining, the integration of milling and filing techniques is key to achieving superior mold quality. By combining these methods, manufacturers can ensure that moulding lines are effectively managed and that the final product meets the required standards.
a. Sequential Processing
- Process: In a typical CNC machining workflow, milling is used first to create the basic shape and features of the mold, including the parting lines. Following milling, filing is employed to refine these lines and achieve the desired surface finish.
- Benefits: This sequential approach allows for precise control over each step of the process, ensuring that moulding lines are minimized and surface quality is optimized.
b. Real-Time Adjustments
- Process: CNC machines equipped with advanced sensors and software can make real-time adjustments during milling and filing. This capability is particularly useful in managing moulding lines, as it allows for immediate correction of any issues that arise.
- Benefits: Real-time adjustments lead to higher accuracy and consistency, reducing the likelihood of defects and improving overall mold quality.
c. Automation and Efficiency
- Process: The automation of both milling and filing processes in CNC machining has greatly improved the efficiency of mold production. Automated systems can handle complex geometries and multiple parts simultaneously, ensuring consistent quality across all products.
- Benefits: Automation reduces the need for manual labor, decreases production time, and enhances the consistency of the final product.
5. Challenges in Moulding Line Management
While CNC precision machining offers many advantages in managing moulding lines, there are also challenges that need to be addressed to achieve the best results.
a. Material Considerations
- Different materials respond differently to milling and filing techniques. For instance, hard metals like steel may require slower milling speeds and more careful filing to avoid damaging the mold. Conversely, softer materials like aluminum may be more prone to burr formation, which needs to be managed during the filing process.
b. Tool Wear and Maintenance
- The precision required for managing moulding lines means that tools must be kept in excellent condition. Tool wear can lead to inconsistencies in milling and filing, resulting in poor surface finishes and visible moulding lines. Regular maintenance and tool replacement are necessary to maintain high-quality results.
c. Complex Geometries
- Molds with complex geometries present additional challenges in managing moulding lines. Achieving a uniform finish across intricate surfaces requires careful planning and the use of advanced CNC machining techniques.
6. Evaluating Supplier Capabilities in CNC Precision Machining for Mold Making
For procurement specialists and technical professionals, assessing a supplier’s capabilities in CNC precision machining is crucial. The ability to manage moulding lines effectively is a key indicator of a supplier’s proficiency in mold making.
a. Experience and Expertise
- Suppliers with extensive experience in CNC precision machining and a deep understanding of moulding line management are more likely to deliver high-quality molds. Look for suppliers who have a proven track record in producing molds with minimal moulding lines and excellent surface finishes.
b. Equipment and Technology
- The quality of the equipment used by a supplier is another critical factor. Advanced CNC machines with capabilities for high-speed milling, automated filing, and real-time adjustments are essential for producing high-quality molds.
c. Quality Control and Inspection
- A robust quality control process is vital in ensuring that moulding lines are properly managed throughout the production process. Suppliers should have comprehensive inspection protocols in place, including the use of advanced measurement tools to verify surface finishes and dimensional accuracy.
Table 3: Key Factors in Evaluating CNC Precision Machining Suppliers
| Evaluation Criteria | Importance in Mold Making | What to Look For in a Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| Experience and Expertise | Critical for high-quality mold production | Proven track record, case studies |
| Equipment and Technology | Necessary for precision and consistency | Advanced CNC machines, high-speed milling |
| Quality Control Processes | Ensures proper management of moulding lines |
Comprehensive inspection protocols, advanced measurement tools |
7. The evolution of CNC precision machining is set to shape the future of mold making
As technology continues to evolve, the future of CNC precision machining in mold making looks promising. Advances in automation, tooling, and software are set to further improve the management of moulding lines and the overall quality of molds.
a. Automation and AI Integration
- The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with CNC machining processes is expected to revolutionize mold making. AI can optimize milling and filing operations in real-time, reducing the occurrence of defects and enhancing overall efficiency.
b. Advanced Tooling Materials
- The development of new tooling materials, such as diamond-coated cutters and advanced ceramics, will allow for even greater precision in managing moulding lines. These materials offer improved wear resistance and can handle the demands of high-speed machining.
c. Sustainable Manufacturing
- As sustainability becomes increasingly important, CNC machining processes are evolving to reduce waste and energy consumption. Suppliers who adopt eco-friendly practices will not only improve their environmental impact but also offer a competitive advantage to customers seeking sustainable solutions.
Managing moulding lines is a critical aspect of CNC precision machining in mold making. Through the effective use of milling and filing techniques, manufacturers can produce molds with minimal lines and superior surface finishes. For technical professionals and procurement specialists, understanding these processes and evaluating supplier capabilities is essential for ensuring that the molds they purchase meet the highest standards of quality and precision.
As CNC machining technology continues to advance, the ability to manage moulding lines will only improve, leading to better products and more efficient production processes. By staying informed about the latest developments in milling, filing, and CNC precision machining, industry professionals can maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving field of mold making.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Using the Right Milling Technique: Down Milling vs. Back Milling
In the world of CNC milling, experts employ a myriad of techniques to maximize the capabilities of their CNC machines. These techniques are tailored to the size, shape, features, and…
- Face Milling Essentials for CNC Machining Parts
Face milling is an essential operation in CNC machining, aimed at controlling the height of the workpiece and ensuring a smooth surface finish. This process often uses multi-tooth cutters, known…
- Elevating Precision Standards through Chamfer in CNC Machining
1. Introduction: The Pursuit of Unparalleled Precision In the realm of CNC machining, precision is paramount. This section introduces the article by exploring the significance of precision in manufacturing and…
- Precision Prowess: Unveiling the Advantages of China CNC Machining
1. Introduction: The Role of Precision in Manufacturing Excellence In this introductory section, we delve into the critical role that precision plays in manufacturing and set the stage for an…
- Revolutionizing CNC Machining for Complex Aerospace Assemblies
Introduction to CNC Machining in Aerospace Assemblies Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining represents a significant technological development playing a notable role in the creation of complex aerospace assemblies. CNC machining…
- Revolutionizing Renewable Energy with CNC Machined Components
Introduction: Renewable Energy and CNC Machined Components Renewable energy harnesses power from natural sources such as the sun, wind, and water, making it a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional…