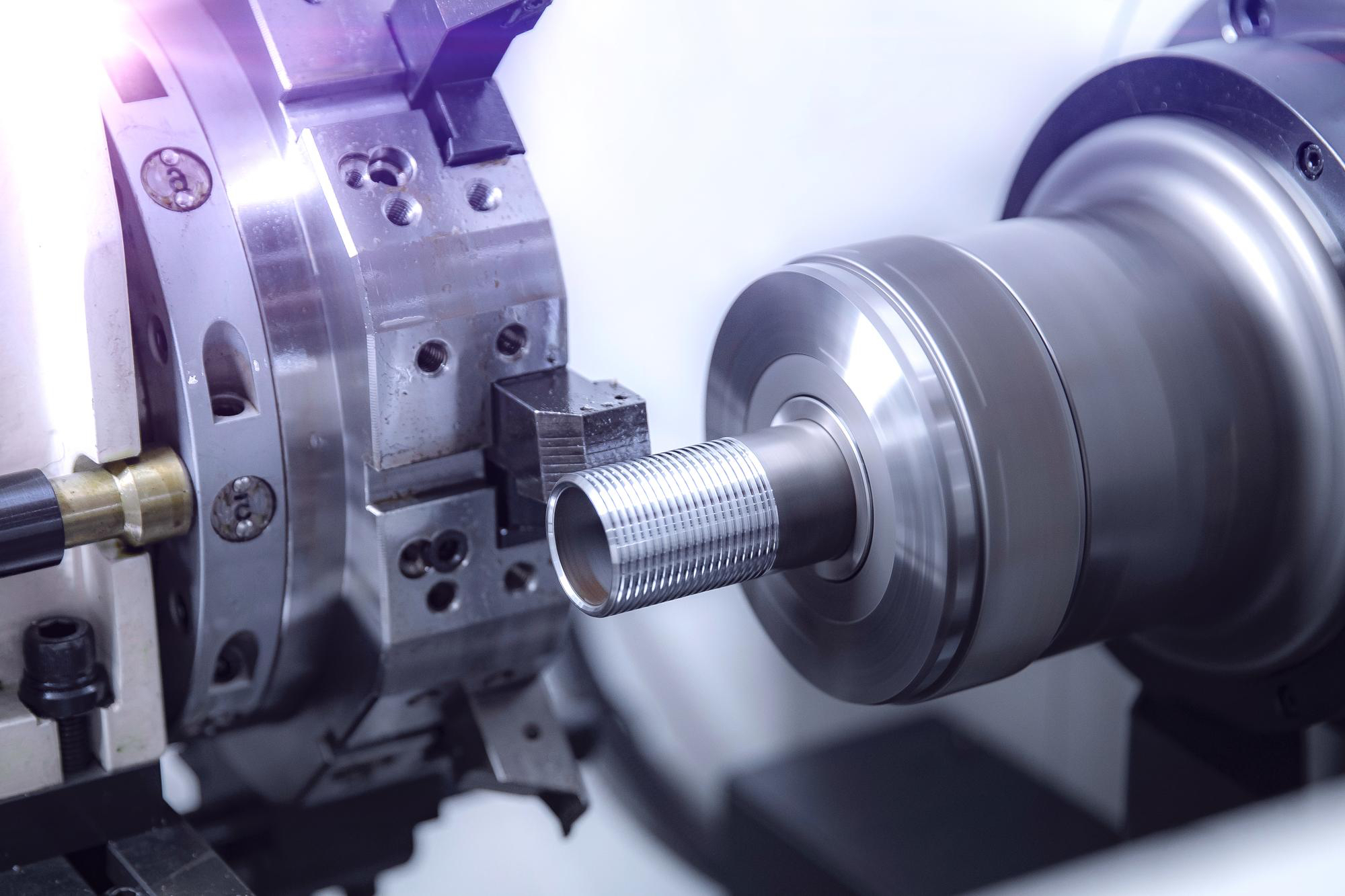
To high-speed CNC machining, the selection of tool materials is crucial. Imagine you’re a chef preparing a gourmet meal; the ingredients you choose will significantly impact the final dish. Similarly, the materials used for cutting tools in CNC machining determine the quality, efficiency, and precision of the finished parts. Let’s dive into the world of tool materials and uncover the secret sauce that makes high-speed CNC machining parts stand out.
The Basics of CNC Tool Materials
In the realm of CNC machining, a variety of tool materials are available, each with specific properties suited for different machining tasks. Some of the most commonly used materials include:
- Diamond Tools: Known for their unparalleled hardness and wear resistance, diamond tools are ideal for non-metallic materials and non-ferrous metals. They excel in applications requiring high precision and surface finish.
- Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN): CBN tools are second only to diamond in hardness. They are perfect for machining hard ferrous materials like hardened steels and cast irons. CBN tools maintain their cutting edge at high temperatures, making them suitable for high-speed machining.
- Ceramic Tools: These tools offer excellent hardness and thermal stability. They are primarily used for high-speed machining of cast iron and superalloys. Ceramic tools are also resistant to chemical wear, making them ideal for abrasive materials.
- Coated Carbides: Carbide tools with coatings like TiN, TiCN, or Al2O3 enhance wear resistance and reduce friction. These tools are versatile and can handle a wide range of materials, from soft non-ferrous metals to hardened steels.
- TiC(N)-Based Hard Alloys: Combining the hardness of ceramics with the toughness of metals, these alloys are excellent for machining steel and other ferrous materials at high speeds.
- Ultra-Fine Grain Carbides: These carbides offer high wear resistance and toughness, making them suitable for precision machining applications.
- Powder Metallurgy High-Speed Steel (PM-HSS): PM-HSS tools provide a good balance of toughness and wear resistance, suitable for interrupted cuts and complex geometries.
Matching Tool Materials to Workpiece Materials
Selecting the right tool material is not just about its inherent properties; it’s about matching these properties to the workpiece material. Here’s a quick guide on which tool materials work best with different workpiece materials:
Aluminum Alloys
- Recommended Tool Materials: Diamond, Coated Carbides
- Reason: Aluminum alloys are soft and can stick to the cutting edge. Diamond and coated carbides prevent buildup and provide excellent surface finishes.
Hardened Steels
- Recommended Tool Materials: CBN, Coated Carbides, TiC(N)-Based Alloys
- Reason: These materials retain their hardness at high temperatures and provide the necessary wear resistance for hard steels.
Cast Iron
- Recommended Tool Materials: Ceramic, CBN
- Reason: Cast iron is abrasive, and ceramic tools offer the hardness required to handle it. CBN tools are also effective, especially for high-speed operations.
Superalloys
- Recommended Tool Materials: Ceramic, Coated Carbides
- Reason: Superalloys are tough and generate high cutting temperatures. Ceramic tools maintain their hardness and resist wear under these conditions.
Non-Ferrous Metals (Copper, Brass)
- Recommended Tool Materials: Diamond, Coated Carbides
- Reason: These materials prevent adhesion and provide excellent finishes on soft, sticky metals.
Advantages of Different Tool Materials
Let’s explore the advantages of each tool material in more detail:
Diamond Tools
- Advantages: Extreme hardness, high wear resistance, excellent surface finish
- Applications: Precision machining of non-ferrous metals, composites, and ceramics
CBN Tools
- Advantages: High hardness, thermal stability, chemical resistance
- Applications: Hard turning of steels, cast irons, and superalloys
Ceramic Tools
- Advantages: High thermal stability, hardness, chemical inertness
- Applications: High-speed machining of cast iron and superalloys
Coated Carbides
- Advantages: Versatility, wear resistance, reduced friction
- Applications: General-purpose machining of a wide range of materials
TiC(N)-Based Hard Alloys
- Advantages: Combination of hardness and toughness, resistance to thermal shock
- Applications: High-speed machining of steels and ferrous alloys
Ultra-Fine Grain Carbides
- Advantages: High precision, wear resistance, toughness
- Applications: Precision machining, aerospace, and medical components
PM-HSS Tools
- Advantages: Toughness, wear resistance, suitability for complex geometries
- Applications: Interrupted cuts, complex shapes, tool and die making
Practical Data for Tool Selection
To make informed decisions, let’s look at some practical data comparing the performance of different tool materials in specific applications. The table below summarizes tool life, surface finish quality, and cutting speed for various tool materials when machining aluminum and hardened steel.
| Tool Material | Workpiece Material | Tool Life (min) | Surface Finish (Ra µm) | Cutting Speed (m/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond | Aluminum | 1200 | 0.2 | 1200 |
| Coated Carbide | Aluminum | 600 | 0.4 | 800 |
| CBN | Hardened Steel | 300 | 0.6 | 200 |
| Coated Carbide | Hardened Steel | 150 | 1.0 | 150 |
| Ceramic | Cast Iron | 250 | 0.8 | 500 |
| TiC(N)-Based Alloy | Steel | 400 | 0.7 | 300 |
In the world of high-speed CNC machining, the selection of tool materials is the secret sauce that enhances performance, productivity, and precision. By understanding the properties of different tool materials and matching them to the workpiece materials, machinists can achieve optimal results. Whether it’s the unmatched hardness of diamond, the thermal stability of CBN, or the versatility of coated carbides, each material has its unique advantages. By making informed choices, we can push the boundaries of what’s possible in CNC machining and create parts that are not only high in quality but also cost-effective and efficient to produce.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Revolutionizing High-Speed Cutting in CNC Machining Parts with Ceramic Tools
Ceramic tools have brought a significant transformation in the realm of high-speed cutting for CNC machining parts. These tools are celebrated for their superior hardness, exceptional wear resistance, and impressive…
- Optimizing for Speed: Lightweight Materials in High-Speed CNC Machining
Introduction to CNC Machining and the Importance of Speed Optimization In the manufacturing industry, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining plays a crucial role. It is a process employing computerized devices…
- Superior Performance of CBN Tools in High-Speed CNC Machining Parts
In the realm of high-speed CNC machining, the choice of cutting tool material is paramount. Over the last three decades, the development of advanced cutting tool materials has seen significant…
- High-Speed Spiral Milling Techniques for CNC Machining Parts
In the world of mold and aerospace machining, two-dimensional cavity machining stands out as one of the most material-intensive and time-consuming processes. For example, the machining of integral wall panels…
- The Impact of Material Selection on CNC Machining Speed and Tool Wear
Introduction to CNC Machining CNC machining stands as a cornerstone in modern manufacturing, offering precision and efficiency in producing parts. At its core, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining involves the…
- High-Speed Machining Techniques in CNC Machining Parts: Secrets to Enhanced Efficiency and Quality
High-speed machining (HSM) is an intriguing and evolving field within CNC machining. The term "high-speed" is relative and varies depending on the machining method, workpiece material, and tool material. Defining…
- High-Speed Cutting Legends Transforming CNC Machining Parts
High-speed cutting (HSM or HSC) is not just a technological advancement; it's a fascinating journey of innovation that has transformed CNC machining parts over the decades. Let's take a trip…