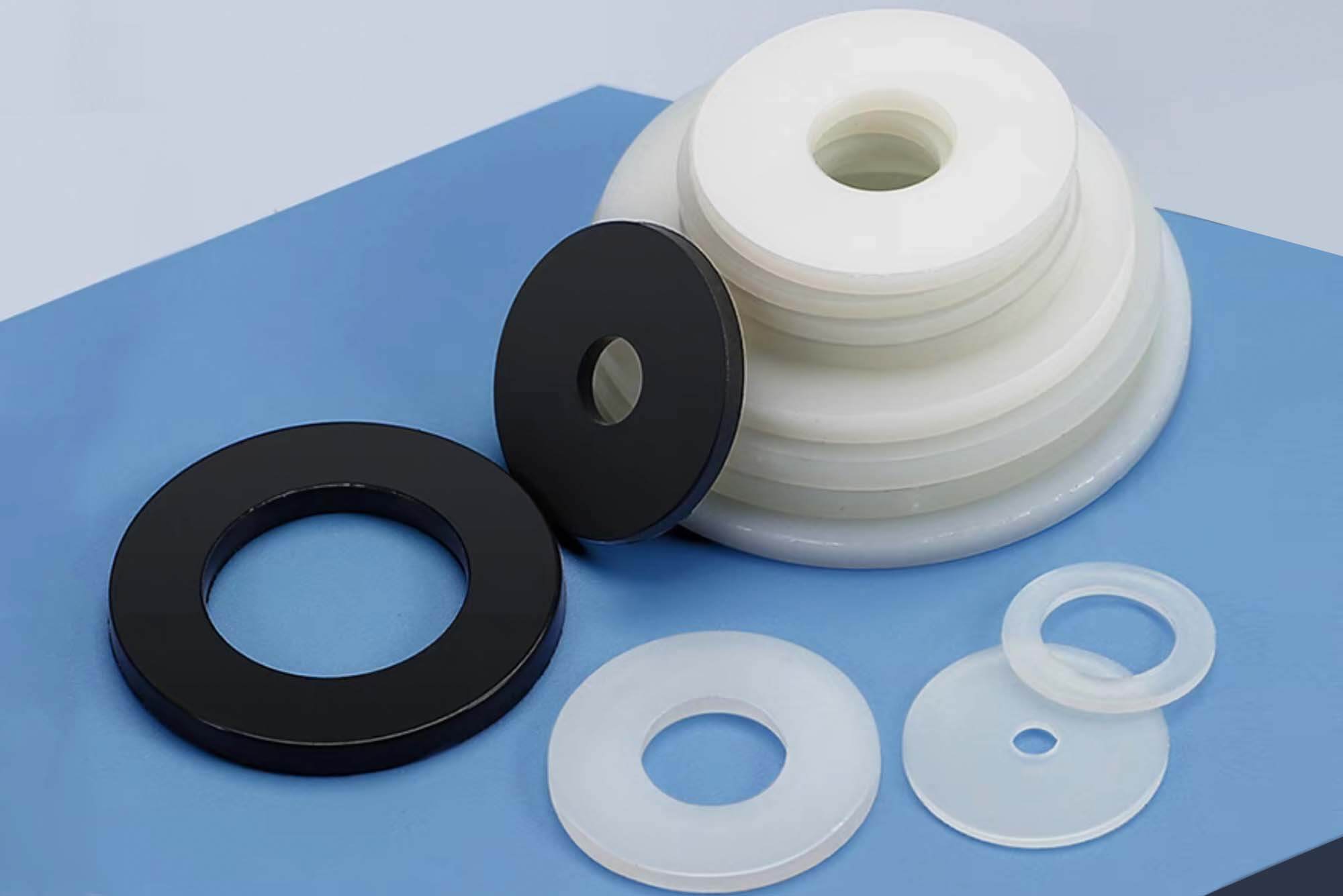
Introduction: What Are Nylon Washers and Why They Matter in Machining?
Nylon washers are one of the unsung heroes of modern manufacturing. These simple yet versatile components are indispensable in a wide range of industries, including automotive, electronics, aerospace, and medical equipment. While their small size may make them seem insignificant, nylon washers play a vital role in ensuring the functionality, safety, and durability of countless products.
As someone who has worked on projects requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and non-conductive materials, I’ve seen first-hand how nylon washers can solve engineering challenges. Whether it’s reducing vibrations in a mechanical assembly, insulating electrical connections, or providing a cost-effective alternative to metal washers, nylon washers are an essential part of the manufacturing toolkit.
1.1 What Are Nylon Washers?
Nylon washers are thin, flat, circular components made from nylon, a synthetic polymer known for its durability and versatility. These washers are typically used to:
- Distribute load across a surface to prevent damage.
- Act as spacers between components.
- Provide insulation in electrical assemblies.
- Reduce friction and wear in mechanical systems.
They come in various shapes, sizes, and thicknesses, depending on the application. Some washers are designed with specific properties, such as heat resistance, UV resistance, or enhanced strength, to meet the needs of specialized industries.
1.2 Why Nylon Washers Are Important in Machining
When it comes to machining, nylon washers stand out due to their adaptability and performance in demanding environments. Here’s why they matter:
Lightweight but Strong
Nylon washers are significantly lighter than metal washers, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in aerospace or automotive components.
Corrosion-Resistant
Unlike metal washers, nylon washers are not susceptible to rust or corrosion. This makes them an excellent choice for applications in humid or chemically aggressive environments, such as pipelines or marine equipment.
Electrical Insulation
One of the unique advantages of nylon washers is their non-conductive nature. They provide insulation in electrical assemblies, ensuring safety and preventing short circuits.
Noise and Vibration Reduction
Nylon washers help dampen vibrations and reduce noise, making them a popular choice in automotive and industrial machinery.
Cost-Effective
Compared to metal washers, nylon washers are generally more affordable, especially for large-scale production. Their long lifespan and low maintenance requirements add to their cost-effectiveness.
1.3 Real-World Applications of Nylon Washers
To understand the significance of nylon washers, let’s look at some real-world examples:
- Automotive Industry:
Nylon washers are used in car door hinges to reduce friction and wear, ensuring smooth operation over time. They are also used in suspension systems to dampen vibrations and enhance passenger comfort. - Electronics:
In printed circuit boards (PCBs), nylon washers are used to create a non-conductive barrier between the board and its mounting hardware, protecting delicate circuits from damage. - Aerospace:
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, nylon washers are essential in aircraft construction. They are often used in fastening systems to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity. - Medical Equipment:
Nylon washers play a critical role in sterile environments, such as in surgical tools or diagnostic machines. Their resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning make them a reliable choice. - Industrial Machinery:
In high-friction environments, nylon washers act as spacers and buffers, extending the lifespan of components by minimizing wear.
1.4 How Nylon Washers Relate to Machining
The relationship between nylon washers and machining is straightforward yet multifaceted. Nylon washers are either:
- Produced through machining, such as CNC cutting for custom shapes and dimensions.
- Incorporated into machined assemblies as essential components for insulation, spacing, or load distribution.
CNC machining plays a critical role in manufacturing nylon washers for specialized applications. Custom shapes, tight tolerances, and small batch production often require CNC processes to meet exact specifications.
Advantages of CNC Machining for Nylon Washers:
- High Precision: Achieves tight tolerances for washers used in sensitive applications.
- Customization: Allows for unique designs tailored to specific needs.
- Efficiency: Reduces material waste and ensures uniformity in batch production.
1.5 Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, nylon washers are not without limitations. Understanding these challenges can help manufacturers and engineers make informed decisions:
- Temperature Limitations:
Nylon has a lower melting point compared to metals, which can limit its use in high-temperature environments. - Load Capacity:
While strong, nylon washers are not suitable for extremely heavy loads that require the strength of metal washers. - Frictional Heat:
Machining nylon can generate heat that may deform the material if not properly managed. Coolants and optimized cutting speeds are essential during CNC machining.
1.6 Why This Guide Matters
Choosing the right nylon washer for your project isn’t always straightforward. Factors like size, shape, material grade, and manufacturing method all play a role. Through this guide, I aim to simplify the decision-making process and provide practical insights into how nylon washers are made and used effectively.
Key Properties of Nylon Washers
Nylon washers are a popular choice in industries that demand lightweight, durable, and versatile components. Their unique properties set them apart from metal and other plastic washers, making them an indispensable part of modern manufacturing. In this chapter, we’ll dive deep into the key material characteristics of nylon washers and compare them with alternative materials.
2.1 Material Characteristics
Lightweight
Nylon washers are significantly lighter than metal washers, reducing the overall weight of assemblies. This property is especially valuable in:
- Aerospace: Where reducing weight directly translates to fuel efficiency.
- Automotive: To improve vehicle performance and reduce emissions.
Corrosion-Resistant
Unlike metal washers, nylon washers are highly resistant to rust and corrosion. This makes them suitable for:
- Marine Applications: Where exposure to saltwater can degrade metal components.
- Chemical Environments: Such as laboratories or chemical processing plants.
Electrically Insulating
Nylon is a natural insulator, making it ideal for electrical applications. Nylon washers are commonly used in:
- PCB Mounting: To prevent electrical shorts.
- Cable Assemblies: Where non-conductive properties are essential.
Noise and Vibration Dampening
In mechanical assemblies, nylon washers help reduce noise and absorb vibrations. Applications include:
- Industrial Machinery: Reducing operational noise levels.
- Consumer Electronics: Enhancing the user experience by minimizing sound disturbances.
Durability
Nylon washers are tough and can withstand wear and tear over time. They are resistant to cracking, making them suitable for environments with mechanical stress or frequent movement.
2.2 Specialized Properties of Nylon Washers
Some nylon washers are manufactured with specific enhancements to cater to niche applications:
| Specialized Property | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | Resistant to sunlight exposure, preventing degradation | Outdoor machinery, solar equipment |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Formulated to withstand higher temperatures | Automotive engine compartments |
| Enhanced Strength | Reinforced with fibers for additional durability | Aerospace, heavy machinery |
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands harsh chemicals | Laboratories, chemical processing plants |
2.3 Comparison: Nylon Washers vs. Metal Washers
While nylon and metal washers serve similar purposes, their properties make them suitable for different applications. Here’s a comparison:
| Property | Nylon Washers | Metal Washers |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Low (requires coating) |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Poor |
| Noise Reduction | High | Low |
| Temperature Tolerance | Limited | High |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies by metal type |
When to Choose Nylon Washers
- Weight reduction is critical.
- Electrical insulation is required.
- Components are exposed to corrosive environments.
When to Choose Metal Washers
- Extreme temperatures or heavy loads are expected.
- High strength and rigidity are necessary.
2.4 Environmental Considerations
Recyclability
Nylon washers are made from synthetic polymers, which can often be recycled. Many manufacturers offer recycled nylon options, reducing environmental impact.
Longevity
Due to their resistance to corrosion and wear, nylon washers have a longer lifespan in suitable environments, reducing replacement frequency and material waste.
2.5 Real-World Examples
To better understand how nylon washers perform in different scenarios, here are some real-world applications:
- Aerospace:
- Nylon washers are used in fastener assemblies to reduce weight and provide insulation. For example, they are critical in securing lightweight panels in aircraft interiors.
- Automotive:
- Car manufacturers use nylon washers in suspension systems to absorb vibrations and ensure a quieter ride.
- Electronics:
- In consumer electronics, nylon washers prevent electrical shorts by acting as non-conductive barriers between components.
- Industrial Equipment:
- Nylon washers in heavy machinery reduce friction and protect surfaces, extending the lifespan of metal parts.
2.6 Challenges and Limitations
While nylon washers have numerous advantages, they do come with some limitations:
- Temperature Tolerance: Standard nylon washers may not perform well in environments above 120°C. High-temperature nylon variants are available but at a higher cost.
- Load Capacity: Nylon washers cannot support as much weight as metal washers. For heavy-load applications, reinforced nylon or metal washers may be necessary.
- UV Sensitivity: Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can degrade standard nylon washers. UV-resistant grades are recommended for outdoor use.
2.7 Why These Properties Matter
The properties of nylon washers directly impact their performance in machining and manufacturing. By understanding these characteristics, engineers and manufacturers can:
- Select the most appropriate washer for their application.
- Optimize designs for weight, cost, and durability.
- Improve the reliability and lifespan of assemblies.
Conclusion of Chapter 2
Nylon washers bring a unique combination of lightweight design, corrosion resistance, and durability to machining projects. By tailoring their properties to specific applications, they provide unmatched versatility across industries. In the next chapter, we’ll explore the various manufacturing methods for nylon washers, from injection molding to CNC machining, and compare their benefits and limitations.
How Nylon Washers Are Made
The manufacturing of nylon washers involves several techniques, each tailored to meet specific requirements for precision, volume, and cost. The choice of method depends on factors like the washer’s size, thickness, complexity, and intended application. In this chapter, we’ll explore the primary methods of manufacturing nylon washers: injection molding, CNC machining, and laser cutting, along with their advantages and limitations.
3.1 Injection Molding
Overview
Injection molding is the most common method for mass-producing nylon washers. It involves melting nylon pellets and injecting the molten material into a pre-designed mold under high pressure. Once the material cools and solidifies, the washers are ejected from the mold.
Process Steps
- Material Preparation: Nylon pellets are fed into the injection molding machine.
- Melting: The pellets are heated to a molten state.
- Injection: The molten nylon is injected into the mold cavity.
- Cooling: The mold cools the nylon, solidifying the washers.
- Ejection: The washers are ejected and prepared for packaging or secondary processes.
Advantages
- Highly efficient for large-scale production.
- Consistent dimensions and quality.
- Low per-unit cost for high volumes.
- Suitable for standard shapes and sizes.
Limitations
- High initial tooling cost.
- Limited flexibility for small batches or custom designs.
3.2 CNC Machining
Overview
CNC machining is widely used for custom nylon washers or low-volume production. This process involves using computer-controlled tools to cut or carve washers from nylon sheets, rods, or blocks.
Process Steps
- Material Setup: Nylon sheets or rods are secured on the CNC machine.
- Programming: The desired washer dimensions are programmed into the CNC software.
- Cutting: Cutting tools, such as end mills or drills, shape the washer with high precision.
- Finishing: The washer’s edges are smoothed, and surface finishes are applied if needed.
Advantages
- Exceptional precision, allowing for tight tolerances.
- Ideal for unique designs and complex geometries.
- Flexible for prototypes or small-batch production.
Limitations
- Higher cost per unit compared to injection molding for large volumes.
- Slower production rates.
3.3 Laser Cutting
Overview
Laser cutting is primarily used for thin nylon washers or intricate designs. It employs a high-powered laser beam to precisely cut washers from a nylon sheet.
Process Steps
- Material Setup: Nylon sheets are placed on the cutting bed.
- Design Programming: The washer’s design is uploaded to the laser cutter.
- Laser Cutting: The laser beam vaporizes the nylon along the design lines.
- Finishing: Any residual material or sharp edges are removed.
Advantages
- High precision with minimal material waste.
- Quick setup and no need for tooling.
- Suitable for prototyping and small-scale production.
Limitations
- Limited to thin materials.
- Higher cost per unit for larger orders.
3.4 Comparison of Manufacturing Methods
Each method has its strengths and is suited to specific requirements. Here’s a side-by-side comparison:
| Method | Best For | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | Mass production | Cost-effective for large quantities | High initial tooling cost |
| CNC Machining | Custom and small batches | High precision, custom designs | Slower production rate |
| Laser Cutting | Prototyping, thin washers | High precision, minimal waste | Limited to thinner materials |
3.5 Material Considerations for Manufacturing
The type of nylon used in manufacturing washers significantly impacts the process and performance. Here are some common types of nylon and their applications:
| Nylon Type | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | Good strength and flexibility | General-purpose washers |
| Nylon 66 | Higher strength and temperature resistance | Automotive and industrial parts |
| Reinforced Nylon | Enhanced strength with fillers like glass | Heavy-duty applications |
| UV-Resistant Nylon | Resistant to sunlight degradation | Outdoor applications |
3.6 Choosing the Right Manufacturing Method
Selecting the appropriate manufacturing method depends on factors such as:
- Volume: Large-scale production favors injection molding, while small batches or prototypes benefit from CNC machining or laser cutting.
- Design Complexity: CNC machining and laser cutting excel at intricate designs.
- Cost: Injection molding is cost-effective for high volumes, but CNC machining is better for unique, low-volume needs.
Case Example: Custom Nylon Washers
A client in the aerospace industry needed lightweight, high-strength washers with unique dimensions for a structural component. CNC machining was chosen due to its ability to meet the tight tolerances and produce a small batch efficiently. The result was a set of washers that met both the design and performance requirements.
3.7 Challenges in Manufacturing Nylon Washers
Despite their versatility, manufacturing nylon washers comes with challenges:
- Heat Sensitivity: Nylon can deform or warp under excessive heat, requiring careful temperature control during machining or molding.
- Material Waste: Minimizing waste during cutting or machining requires optimized designs and processes.
- Surface Finish: Achieving a smooth finish can be challenging with certain nylon grades, requiring post-processing steps like polishing.
Conclusion of Chapter 3
The manufacturing of nylon washers is a versatile process, offering multiple methods to meet diverse needs. Injection molding, CNC machining, and laser cutting each bring unique benefits to the table, ensuring that nylon washers can be produced efficiently, precisely, and cost-effectively. By understanding these methods, manufacturers and engineers can choose the right process for their specific requirements.
Common Applications of Nylon Washers
Nylon washers are versatile components that find applications across various industries due to their lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant properties. In this chapter, we’ll explore how nylon washers are used in key industries and highlight their role in specific applications.
4.1 Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on nylon washers to enhance vehicle performance, reduce noise, and improve durability.
Applications
- Vibration Dampening: Nylon washers are used in suspension systems to absorb vibrations, improving passenger comfort and reducing wear on mechanical components.
- Electrical Insulation: In modern vehicles, nylon washers are essential for insulating electrical connections, especially in high-voltage systems for electric vehicles (EVs).
- Noise Reduction: They are used in door hinges and fasteners to minimize noise caused by movement and friction.
Example
A car manufacturer used nylon washers in the assembly of an EV battery housing. The washers provided electrical insulation and reduced the overall weight of the assembly, contributing to improved energy efficiency.
4.2 Electronics and Electrical Engineering
Nylon washers are indispensable in the electronics industry, where precision and insulation are critical.
Applications
- PCB Mounting: Used as spacers to prevent electrical shorts between circuit boards and their enclosures.
- Cable Management: Nylon washers ensure that cables and wiring systems are securely fastened without damage.
- Heat-Sensitive Applications: Nylon’s low thermal conductivity makes it ideal for insulating components in devices that generate heat.
Example
A consumer electronics company used nylon washers in the mounting of a printed circuit board for a laptop. The washers ensured proper spacing and prevented short circuits, enhancing the device’s reliability.
4.3 Aerospace Industry
In aerospace applications, where weight reduction and durability are paramount, nylon washers provide an effective solution.
Applications
- Fastening Systems: Used in securing lightweight panels and components without adding significant weight.
- Corrosion Resistance: Essential in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals, such as aircraft cabins and wings.
- Insulation: Provides non-conductive barriers in electronic systems.
Example
An aerospace company employed nylon washers in the assembly of a satellite’s electronic payload. The washers reduced weight while maintaining insulation and mechanical stability.
4.4 Industrial Machinery
In industrial machinery, nylon washers are used to extend the lifespan of equipment and ensure efficient operation.
Applications
- Friction Reduction: Nylon washers act as buffers between moving parts, reducing wear and extending the life of components.
- Load Distribution: Used in fastening systems to evenly distribute loads and prevent surface damage.
- Noise Reduction: Minimize noise in high-vibration environments, such as conveyor systems.
Example
A food processing plant utilized nylon washers in the assembly of a conveyor system. The washers provided corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance frequency, ensuring smooth operation in a moist environment.
4.5 Medical Equipment
The medical industry requires components that are lightweight, non-corrosive, and easy to sterilize—qualities that nylon washers readily provide.
Applications
- Surgical Instruments: Used in non-metallic tools and devices to ensure sterility and lightweight operation.
- Diagnostic Machines: Provide precision spacing in equipment like MRI machines or CT scanners.
- Sterile Environments: Nylon washers are resistant to chemical cleaning agents, making them suitable for repeated sterilization.
Example
A manufacturer of diagnostic imaging equipment used nylon washers in the assembly of an MRI machine. The washers ensured non-magnetic properties and durability in a sterile environment.
4.6 Outdoor and Marine Applications
Nylon washers are also popular in environments where resistance to moisture and UV exposure is critical.
Applications
- Marine Equipment: Used in fastening systems for boats, docks, and underwater machinery.
- Outdoor Structures: Provide corrosion resistance in components exposed to sunlight and rain.
- Solar Panels: Secure mounting systems without adding unnecessary weight or risking rust.
Example
A solar energy company used UV-resistant nylon washers in the mounting systems for rooftop solar panels. The washers provided long-term durability against sun exposure and weathering.
4.7 Summary of Industry Applications
| Industry | Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Vibration dampening, insulation | Noise reduction, lightweight |
| Electronics | PCB mounting, cable management | Electrical insulation, precision |
| Aerospace | Fastening, insulation | Weight reduction, corrosion resistance |
| Industrial Machinery | Friction reduction, load distribution | Durability, noise minimization |
| Medical Equipment | Surgical tools, diagnostic machines | Sterility, chemical resistance |
| Outdoor/Marine | Solar panels, marine equipment | Corrosion resistance, UV stability |
4.8 Why Nylon Washers Excel Across Industries
Nylon washers stand out because of their:
- Material Versatility: Customizable for various applications.
- Durability: Resistant to corrosion, wear, and environmental stress.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Affordable without compromising on performance.
By understanding the diverse applications of nylon washers, manufacturers and engineers can leverage their properties to optimize product performance and durability.
Conclusion of Chapter 4
Nylon washers are indispensable in industries ranging from automotive to medical equipment, showcasing their versatility and reliability. Their ability to adapt to various environments and applications ensures they remain a critical component in modern manufacturing.
CNC Machining for Nylon Washers
CNC machining has revolutionized the manufacturing of nylon washers by offering unmatched precision, customization, and efficiency. This method is particularly suited for applications requiring unique designs, tight tolerances, or small-batch production. In this chapter, we’ll explore the advantages of CNC machining, the parameters for machining nylon washers, common challenges, and practical case studies.
5.1 Why CNC Machining for Nylon Washers?
CNC machining is a go-to method for producing nylon washers due to its versatility and precision. Unlike injection molding, which is ideal for mass production, CNC machining caters to unique and complex designs.
Advantages of CNC Machining
- High Precision:
CNC machines can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm, ensuring uniformity and reliability in critical applications. - Custom Designs:
Complex geometries, non-standard sizes, and intricate features can be achieved with CNC machining. - Flexibility:
Suitable for both prototyping and low- to medium-volume production. - Material Efficiency:
Minimal material waste compared to other methods like laser cutting. - Consistency:
Every washer in a batch is identical, meeting strict quality standards.
5.2 CNC Machining Parameters for Nylon Washers
Machining nylon requires careful optimization of parameters to achieve the best results. Here are the key parameters:
| Parameter | Recommended Value | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | Medium | Prevents melting or deformation |
| Feed Rate | Low to Moderate | Ensures smooth surface finish |
| Coolant Use | Required | Reduces heat and improves accuracy |
| Tool Type | Sharp, high-speed steel | Prevents material fraying |
| Depth of Cut | Shallow passes | Avoids excessive heat buildup |
Pro Tip: Always use sharp tools and apply proper cooling to avoid heat-induced deformation, a common issue when machining nylon.
5.3 Challenges in CNC Machining Nylon Washers
Despite its advantages, CNC machining of nylon washers comes with challenges that require specific solutions:
- Heat Sensitivity:
Nylon has a relatively low melting point, and friction from machining can cause localized melting.
Solution: Use cooling fluids and reduce cutting speed. - Tool Wear:
Nylon’s fibrous nature can lead to tool dulling over time.
Solution: Use sharp, durable tools and replace them as needed. - Surface Finish:
Achieving a smooth surface can be difficult due to nylon’s tendency to deform under stress.
Solution: Use fine-grit tools and optimize feed rates. - Material Movement:
Nylon’s flexibility can cause it to shift during machining, impacting accuracy.
Solution: Secure the material firmly and minimize vibration.
5.4 Steps for CNC Machining Nylon Washers
- Material Selection:
Choose the appropriate nylon grade (e.g., Nylon 6, Nylon 66) based on application requirements. - Machine Setup:
Secure the nylon sheet or rod in place using a stable fixture. - Programming:
Input the washer’s dimensions and specifications into the CNC software. - Machining:
Execute the cutting process, ensuring optimal cooling and tool rotation. - Finishing:
Smooth the edges and apply any additional surface treatments, such as polishing.
5.5 Applications of CNC-Machined Nylon Washers
Prototyping
- CNC machining is ideal for developing prototypes of nylon washers with unique designs or unconventional dimensions. Engineers can quickly test and refine designs before mass production.
Custom Assemblies
- Industries like aerospace and medical equipment often require washers with non-standard shapes or features. CNC machining can produce these with ease.
High-Precision Components
- For applications demanding tight tolerances, such as electrical insulation or load-bearing assemblies, CNC machining ensures accuracy and reliability.
5.6 Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Aerospace Industry
An aerospace client needed lightweight, high-strength washers for a satellite component. CNC machining allowed the production of washers with a tolerance of ±0.01 mm, ensuring perfect alignment in the satellite’s assembly. The nylon washers provided insulation while reducing the satellite’s overall weight.
Case Study 2: Medical Equipment
A manufacturer of diagnostic imaging equipment required sterile, custom-shaped nylon washers. CNC machining was chosen for its ability to produce washers with smooth, polished edges, meeting both functional and hygienic standards.
Case Study 3: Industrial Machinery
A company specializing in conveyor systems needed nylon washers to act as spacers and friction reducers. CNC machining provided washers with precise dimensions, enabling seamless integration into the machinery.
5.7 Comparison: CNC Machining vs. Other Methods
| Aspect | CNC Machining | Injection Molding | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | High | Moderate | High |
| Setup Cost | Low | High | Low |
| Production Speed | Moderate | High | Low to Moderate |
| Customization | Excellent | Limited | Excellent |
| Material Waste | Minimal | Minimal | Moderate |
5.8 Tips for Optimizing CNC Machining of Nylon Washers
- Use Specialized Tools:
Select tools designed for plastic machining to ensure clean cuts. - Optimize Programming:
Fine-tune feed rates and cutting speeds to match the material properties. - Regular Maintenance:
Keep CNC machines and tools in optimal condition to maintain precision. - Monitor Material Behavior:
Watch for signs of deformation or excessive heat during machining.
Conclusion of Chapter 5
CNC machining offers unparalleled advantages in the production of nylon washers, from precision and customization to efficiency and material conservation. By understanding the nuances of this process and addressing potential challenges, manufacturers can consistently produce high-quality washers that meet the demands of diverse industries.
Cost Analysis and Optimization Tips
Cost is a critical factor in the production of nylon washers, influencing decisions from material selection to manufacturing methods. In this chapter, we’ll break down the costs associated with nylon washer production, compare manufacturing methods, and provide strategies to optimize expenses without compromising quality.
6.1 Cost Factors in Nylon Washer Production
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of producing nylon washers. Understanding these factors is essential for effective cost management.
Material Costs
- The type of nylon used significantly affects costs. For example:
- Nylon 6: Lower cost, suitable for general applications.
- Nylon 66: Higher cost, offers better heat resistance and strength.
- Reinforced Nylon: The most expensive due to added fillers like glass fibers.
- Material thickness and grade also influence costs.
Manufacturing Method
- The production method directly impacts costs:
- Injection Molding: Economical for large volumes but has high initial tooling costs.
- CNC Machining: Higher per-unit cost but suitable for small batches and custom designs.
- Laser Cutting: Ideal for prototypes but expensive for larger orders.
Batch Size
- Small batches increase costs due to setup time and machine programming.
- Larger batches spread fixed costs, reducing the per-unit expense.
Complexity of Design
- Simple designs are cheaper to produce, while intricate shapes or tight tolerances increase machining time and tooling costs.
Post-Processing
- Additional steps, such as polishing or surface treatments, add to the overall expense.
6.2 Cost Comparison: Manufacturing Methods
| Cost Factor | Injection Molding | CNC Machining | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup Costs | High | Moderate | Low |
| Per-Unit Cost | Low for large volumes | High | High |
| Design Flexibility | Limited | Excellent | Excellent |
| Lead Time | Long (tooling required) | Moderate | Short |
6.3 Strategies to Optimize Costs
1. Choose the Right Material
- Select a nylon grade that matches the application without over-specifying.
- For non-critical applications, consider lower-cost alternatives like recycled nylon or blended materials.
2. Match Production Method to Volume
- For large volumes, opt for injection molding to minimize per-unit costs.
- For small batches or custom designs, CNC machining is more cost-effective.
- For prototyping, use laser cutting to save on setup time and costs.
3. Simplify Designs
- Reduce the number of complex features, such as unnecessary holes or intricate edges.
- Use standard sizes where possible to avoid custom tooling.
4. Increase Batch Size
- Consolidate orders to increase batch sizes, reducing setup costs per unit.
5. Minimize Post-Processing
- Design washers that require minimal finishing by optimizing cutting parameters and tool selection.
6. Partner with Reliable Suppliers
- Establish long-term relationships with trusted suppliers who can offer competitive pricing and consistent quality.
- Negotiate bulk discounts for regular orders.
6.4 Real-World Cost Optimization Examples
Case Study 1: Automotive Industry
A car manufacturer needed 50,000 nylon washers for an EV battery assembly. By switching from CNC machining to injection molding and using Nylon 6 instead of Nylon 66, the company reduced costs by 30% without compromising performance.
Case Study 2: Aerospace Industry
An aerospace firm required 500 custom-shaped nylon washers for a prototype. CNC machining was selected to meet the precision requirements, and by simplifying the design, the firm saved 15% on machining costs.
Case Study 3: Electronics Industry
A startup producing consumer electronics used laser cutting for its initial prototype batch of nylon washers. Once production scaled, they transitioned to injection molding, reducing the per-unit cost by over 40%.
6.5 Total Cost of Ownership
When analyzing costs, it’s important to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes:
- Material Costs: Initial expenses for nylon sheets, rods, or pellets.
- Production Costs: Expenses for manufacturing, including labor and machine operation.
- Replacement Costs: Nylon washers’ durability often reduces the need for frequent replacements, saving long-term costs.
- Environmental Costs: Opting for recyclable or eco-friendly materials can reduce waste management expenses.
6.6 Tips for Balancing Cost and Quality
- Invest in Prototyping:
Use small batches to test designs before scaling production.
Identify potential design inefficiencies that could inflate costs. - Standardize Components:
Use standardized washers whenever possible to save on tooling and customization. - Leverage Technology:
Use advanced CNC software to optimize tool paths and minimize material waste.
Consider automation for repetitive tasks to reduce labor costs. - Monitor Material Usage:
Track material consumption to identify areas where waste can be minimized.
6.7 Cost-Effectiveness of Nylon Washers
Compared to other materials, nylon washers offer excellent value for money:
- Lower Initial Cost: Cheaper than metal washers for equivalent performance.
- Longer Lifespan: Resistant to corrosion and wear, reducing replacement frequency.
- Environmentally Friendly: Options for recycled nylon lower environmental impact.
Conclusion of Chapter 6
Optimizing the cost of nylon washer production requires a strategic approach, from material selection to manufacturing methods. By understanding the factors driving costs and implementing smart strategies, manufacturers can achieve high-quality results while staying within budget.
FAQ
1. Why choose nylon washers over metal washers?
Nylon washers offer several advantages over metal washers:
- Lightweight: Ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as aerospace and automotive.
- Corrosion Resistance: Nylon doesn’t rust, making it suitable for marine and chemical environments.
- Electrical Insulation: Provides excellent insulation, unlike metal washers that conduct electricity.
- Noise Reduction: Dampens vibrations and minimizes noise in mechanical assemblies.
- Cost-Effective: Often cheaper than metal washers for equivalent applications.
2. What CNC techniques are best for machining nylon washers?
CNC machining is highly effective for producing nylon washers, especially for custom designs or small batches. Key techniques include:
- Milling: For cutting complex geometries and precise dimensions.
- Drilling: Used for creating holes or spacers with tight tolerances.
- Turning: Ideal for producing washers from nylon rods.
Tips for Success:
- Use sharp tools to prevent material fraying.
- Apply coolant to reduce frictional heat and maintain dimensional accuracy.
- Opt for moderate cutting speeds to avoid material deformation.
3. What industries rely most on nylon washers?
Nylon washers are used in a wide range of industries:
- Automotive: Noise dampening, vibration reduction, and electrical insulation.
- Electronics: Preventing electrical shorts and providing insulation for PCBs.
- Aerospace: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant fastening systems.
- Industrial Machinery: Reducing friction and distributing loads in high-wear environments.
- Medical Equipment: Sterile, non-corrosive components in diagnostic machines and surgical tools.
4. How does nylon compare to other materials for washers?
Here’s a quick comparison of nylon washers with other common materials:
| Material | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, insulating | Limited heat and load tolerance |
| Metal | High strength, heat resistance | Heavy, prone to corrosion |
| Rubber | Flexible, good for sealing | Wears out quickly, limited durability |
| Teflon (PTFE) | Excellent chemical resistance | Expensive, limited mechanical strength |
5. Can nylon washers handle high temperatures?
Standard nylon washers can handle temperatures up to 120°C (248°F). For higher-temperature applications, consider using:
- Nylon 66: Offers better heat resistance.
- Reinforced Nylon: Enhanced with fillers to withstand extreme conditions.
If the application exceeds these limits, alternative materials like Teflon or metal washers may be more appropriate.
6. Are nylon washers customizable?
Yes, nylon washers are highly customizable in terms of:
- Size and Thickness: Custom dimensions can be machined or molded to fit specific requirements.
- Shape: CNC machining allows for complex geometries and non-standard designs.
- Material Grade: Options include UV-resistant nylon, reinforced nylon, or high-temperature grades.
Customization is often achieved through CNC machining, which provides the precision and flexibility needed for unique designs.
7. Is nylon eco-friendly?
Nylon is partially eco-friendly, depending on the grade and manufacturing process:
- Recyclable: Nylon can be recycled into new components, reducing environmental impact.
- Durable: Long lifespan minimizes waste from frequent replacements.
- Blends: Recycled or bio-based nylon options are available for environmentally conscious applications.
8. Does nylon degrade over time?
Nylon washers are resistant to most forms of degradation, but they can be affected by:
- UV Exposure: Prolonged sunlight exposure can cause standard nylon to weaken. UV-resistant grades are recommended for outdoor use.
- Moisture Absorption: Nylon can absorb moisture, slightly impacting its dimensions and mechanical properties in high-humidity environments.
- Chemical Exposure: Certain chemicals, such as strong acids, can degrade nylon over time.
9. How do you ensure precision when machining nylon washers?
Precision is critical in applications like aerospace and electronics. Follow these tips:
- Use Sharp Tools: Prevents rough edges and ensures clean cuts.
- Optimize Speeds and Feeds: Use moderate cutting speeds and feed rates to minimize heat buildup.
- Apply Coolant: Reduces friction and prevents material warping.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep CNC machines calibrated for consistent accuracy.
10. What is the most cost-effective way to produce nylon washers?
The most cost-effective method depends on your production needs:
- Large Volumes: Injection molding offers low per-unit costs for high-volume production.
- Custom Designs or Small Batches: CNC machining provides flexibility and precision without the need for expensive molds.
- Prototyping: Laser cutting is an affordable option for small runs or initial designs.
11. Are nylon washers suitable for heavy-load applications?
Standard nylon washers are not ideal for heavy loads due to their lower strength compared to metal washers. However:
- Reinforced Nylon: Filled with glass or other materials, these washers can handle moderate loads.
- Alternatives: For extreme loads, metal washers remain the better choice.
12. Can nylon washers be used in food-grade applications?
Yes, food-grade nylon washers are available and are commonly used in food processing and packaging equipment. These washers meet strict safety standards and are resistant to cleaning agents and moisture.
Conclusion of Chapter 7
This FAQ section addresses the most common questions about nylon washers and machining, providing actionable insights for engineers, manufacturers, and procurement professionals. Whether you’re selecting a washer for a specific industry or optimizing production methods, understanding these key details ensures better decision-making and successful project outcomes.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Nylon CNC Machining Service for Custom Parts
Nylon is an engineering plastic known for its high strength, wear resistance, and chemical inertness. It possesses excellent mechanical properties and durability, making it widely used in various fields including…
- CNC Machining Plastics: Delrin vs. Nylon for High-Precision Parts
Introduction to CNC Machining Plastics The Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining process plays a vital role in manufacturing various high-precision parts and components. This advanced technology uses pre-programmed computer software…
- Polyamide vs Polyester: Cost, Durability & CNC Machining Tips
When it comes to CNC machining custom parts, material selection is one of the most critical decisions. Two of the most popular engineering plastics—polyamide (commonly known as nylon) and polyester…
- 10 plastic materials frequently used in CNC machining
Introduction to CNC Machining and Plastics CNC machining stands for Computer Numerical Control machining, a manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. This…
- Nickel vs. Cobalt Alloys in High-Temperature CNC Machining: A Detailed Analysis?
Nickel and Cobalt Alloys in High-Temperature CNC Machining Both Nickel and Cobalt alloys play an essential role in high-temperature CNC machining. These metal alloys are popular choices due to their…
- Material Versatility in CNC Machining: From Titanium to Thermoplastics
Introduction to CNC Machining CNC machining stands as a cornerstone in the manufacturing sector, enabling the precise creation of parts and components. This process utilizes computer numerical control (CNC) to…
- Precision CNC Machining for High-Performance Industrial Machinery
Precision CNC Machining for High-Performance Industrial Machinery The process of Precision CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is at the core of manufacturing high-performance industrial machinery. This technique leverages a computer's…