Introduction to CNC Machining and Composite Materials
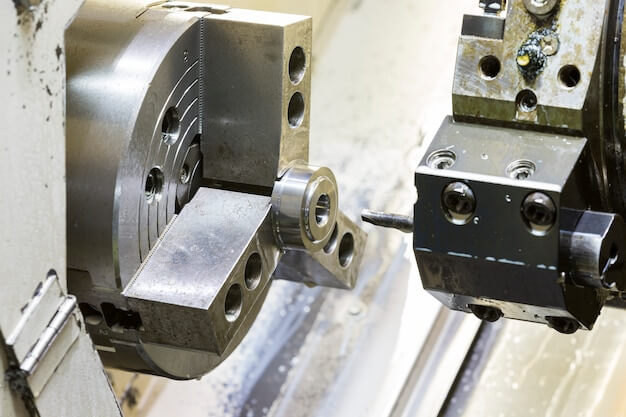
CNC machining stands as a pivotal technology in modern manufacturing, utilizing computer-controlled systems to accurately cut and shape materials into final products or components. This process is renowned for its precision, repeatability, and efficiency, making it indispensable across various industries. Composite materials, on the other hand, are engineered by combining two or more constituent materials with differing physical or chemical properties. The synergy of these materials results in a composite that inherits the beneficial properties of its constituents, such as enhanced strength, reduced weight, or improved thermal resistance. For instance, carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRPs) are a type of composite material widely used in aerospace and automotive sectors for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
Common Misunderstandings about Manufacturing
One prevalent misconception in the field of manufacturing, particularly when it involves advanced materials like composites, is the overemphasis on functionality at the expense of aesthetics. This view overlooks the significant role that aesthetics play in modern product development. In reality, the integration of both aesthetics and functionality is crucial for the success of a product. For instance, in CNC machining with composite materials, the precision and capabilities of the machinery allow for the creation of parts that not only meet strict functional requirements but also achieve a high level of aesthetic appeal. This dual focus is essential in sectors where the visual aspect of a component can influence consumer perception and value, such as in the automotive or consumer electronics industries.
- Functionality: Ensures the product meets performance and durability standards.
- Aesthetics: Enhances product appeal and influences consumer choice.
Ignoring the aesthetic aspect can lead to undervaluing products that could otherwise stand out in the competitive market. Therefore, balancing aesthetics and functionality is not just a matter of design but a strategic approach to manufacturing that can significantly impact the product’s market success.
The Challenge of Balancing Aesthetics and Functionality in CNC Machining with Composite Materials
Balancing aesthetics and functionality in CNC machining with composite materials presents a unique set of challenges. The inherent properties of composite materials, such as their layered structure and the combination of different material types, can significantly affect the machining process. For instance:
- Material Behavior: Composite materials can exhibit unpredictable behavior when subjected to the cutting forces of CNC machining, potentially leading to delamination or splintering, which compromises aesthetics.
- Tool Wear: The abrasive nature of some composites can lead to increased tool wear, affecting the precision of the cut and, consequently, the functionality of the machined part.
- Surface Finish: Achieving a smooth surface finish, crucial for both aesthetics and functionality, is more challenging with composites due to their heterogeneous composition.
For example, machining a carbon fiber-reinforced composite requires careful consideration of tool path and cutting speed to prevent fraying or splintering, which would detract from the visual appeal and could also introduce weak points that reduce the component’s functional integrity.
Case Study: A Real-World Example
In the realm of CNC machining with composite materials, a notable case study involves the production of high-performance bicycle frames. These frames are engineered to achieve an optimal balance between aesthetics and functionality. The process involves:
- Material Selection: The use of carbon fiber composites, known for their strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility in achieving sleek designs.
- Design Consideration: CAD software is utilized to model the frame, emphasizing aerodynamic shapes while ensuring structural integrity for rider safety.
- Machining Process: CNC machining precisely cuts and shapes the composite materials, allowing for intricate designs that are both visually appealing and functionally superior.
- Finishing Touches: A final layer of coating not only protects the material but also allows for customizable aesthetics, such as vibrant colors or patterns, without compromising the frame’s performance.
This case study exemplifies how CNC machining with composite materials can be leveraged to produce components that do not sacrifice functionality for aesthetics, demonstrating a harmonious blend of both aspects.
Techniques for Achieving Balance
When balancing aesthetics and functionality in CNC machining with composite materials, several techniques can be employed:
- Material Selection: Choose composite materials that offer both visual appeal and functional properties suitable for the intended application.
- Surface Finishing: Implement finishing techniques that enhance the aesthetic qualities of the composite while maintaining its structural integrity.
- Design Optimization: Optimize the design to ensure that the composite material contributes to both the visual and functional aspects of the final product.
The Role of Design in the Machining Process
Product design plays a crucial role in balancing aesthetics and functionality during CNC machining with composite materials. The design dictates not only the appearance but also how effectively a product can be manufactured and its performance characteristics. For instance:
- Material Selection: The choice of composite materials can influence both the look and the structural integrity of the final product. Designers must understand the properties of different composites to make informed decisions.
- Geometric Complexity: Design intricacies determine the machining strategy. Complex shapes may enhance aesthetics but could complicate the machining process, affecting functionality and manufacturability.
- Surface Finish: The design phase also decides the required surface finish, impacting both the tactile and visual quality of the product. This decision affects the choice of machining parameters and tools.
For example, designing a lightweight yet durable drone frame requires a deep understanding of composite materials and CNC machining capabilities. The design must ensure that the frame is not only visually appealing but also capable of withstanding operational stresses, balancing both aesthetics and functionality effectively.
Future Trends in Manufacturing with Composite Materials
The manufacturing sector is poised for transformative changes with the advent of innovative composite materials. These materials are set to revolutionize both the aesthetic appeal and functionality of manufactured products. One main trend is the development of smart composites that can adapt their properties in real-time to environmental changes, enhancing product durability and performance. For instance:
- Self-healing composites that repair minor cracks or damages without human intervention, prolonging the product’s lifespan.
- Thermally conductive composites that efficiently manage heat in electronic devices, improving performance and reliability.
These advancements underscore a shift towards materials that not only meet structural requirements but also contribute to the overall design and efficiency of the final product.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- CNC Machining Precision: How Material Choice Affects Tolerance and Accuracy
Introduction to CNC Machining CNC Machining stands for Computer Numerical Control Machining, a cornerstone in modern manufacturing. This process uses computer-controlled machines to achieve high precision and accuracy in creating…
- Boosting CNC Machining Throughput: The Role of Composite Materials
Introduction to CNC Machining and Composite Materials CNC, or Computer Numerical Control machining, is a essential manufacturing process where programmed software controls the movement of factory machinery seamlessly. It can…
- The Future of CNC Machining: Smart Materials and Innovations
Introduction to CNC Machining and its Current Status in Manufacturing CNC Machining, short for Computer Numerical Control Machining, represents a process used in the manufacturing sector where pre-programmed computer software…