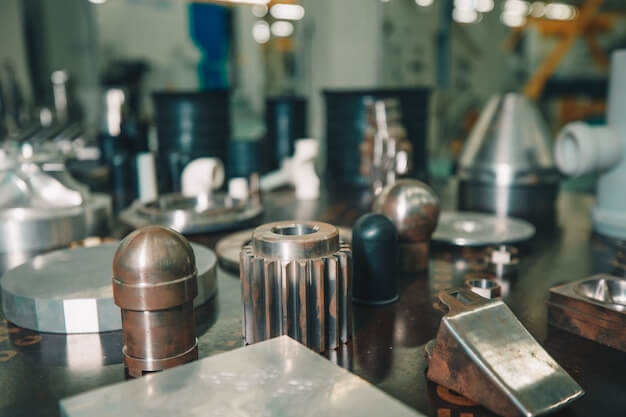
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, enabling the production of complex parts with precision and efficiency. This article aims to shed light on two critical aspects within the CNC manufacturing process – rivets and tack welding.
Rivets are mechanical fasteners that hold together material pieces firmly for long-lasting results. They provide excellent shear strength making them a reliable choice for applications requiring durable fixing or assembly like automotive, aerospace, garment industries, etc. On the other hand, tack welding is a temporary method used to hold the workpieces together during final welding processes. It provides stability and maintains alignment preventing distortions due to heat induced expansions.
Producing Rivets through CNC Machining:
The manufacture of rivets utilizing CNC technology brings out high-quality products with impressive tolerance capabilities. The automation ensures consistency and uniformity across batches providing an advantage over traditional manual methods. Here’s an overview of how it works;
1. Programming: Given their specifications, dimensions of the desired rivet can be programmed into the CNC machine software. Technicians need to ensure that input data accuracy as programming errors might cause defective output.
2. Material Selection: Depending upon the application requirement, alloy steels, aluminum, stainless steel, copper alloys, nickel-copper alloys or titanium may be used. The chosen stock is positioned on the CNC machine for processing.
3. Cutting Process: Utilising the information provided by CAD/CAM programs, the CNC machine begins transforming raw stock into the desired geometries via cutting, drilling or milling operations. For ensuring smooth finishes, proper care must be taken regarding cutter speeds and tool paths.
4. Inspection & Quality Check : Completed rivets undergo inspection against original calculations including measurements of diameter, length, head-size, etc. Strict quality adherence aids in reducing rejected items thus improving overall productivity.
Applying Tack Welding in CNC Operations:
Tack welding, although manually intensive has found its use within automated CNC processes. Here’s how;
1. Setting up parts: During multi-part assemblies, pieces are first positioned according to final blueprints and secured with lightweight clamps or fixtures.
2. Tacking: Technicians then lay a ‘tacks’ or small welds at strategic locations for preliminary attachments. The tack should be strong enough to hold the pieces together yet weak enough for easy modifications during fit-up stages.
3. Main Weld: Once satisfactory alignment is achieved, functional weld can proceed without risk of movement due to thermal distortions. 
4. Final Inspection: Post-weld, joints are inspected for gaps, cracks, dimensional discrepancies etc. If need arises, technicians may retrace their steps, correct errors and redo welds. A proper tack not only speeds up main welding but also helps in achieving better quality finishes as it mitigates warping issues hitherto associated with prolonged welding.
In conclusion, both rivets and tack welding play essential roles within CNC machining operations, providing robustness and quality assurance respectively. Knowledge and expertise in handling these techniques add value whilst optimizing production workflows. Manufacturers must invest in training technicians about effective utilization thereby ensuring superior outcomes in less time. So while CNC technology provides unparalleled precision, integrating simple yet powerful methods like rivets and tack welding bring out cost-effective and highly efficient manufacturing strategies.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Understanding Rivets and Tack Welding Through CNC Machining( lightweight metal Brian)
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is an advanced technology that has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. This transformative technique allows for precise control in processing materials such as metal, plastic, foam,…
- CNC Machining of Stainless Steel: Tips and Common Pitfalls?
CNC Machining and the Importance of Stainless Steel Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a production process whereby pre-programmed computer software directs the movement of factory machinery or tools, enabling…
- Unlocking New Possibilities in CNC Machined Titanium Medical Devices
Introduction to CNC Machined Titanium Medical Devices The prevalence of CNC machined titanium medical devices in the healthcare sector demonstrates their immense significance and usefulness. This technology furnishes an essential…