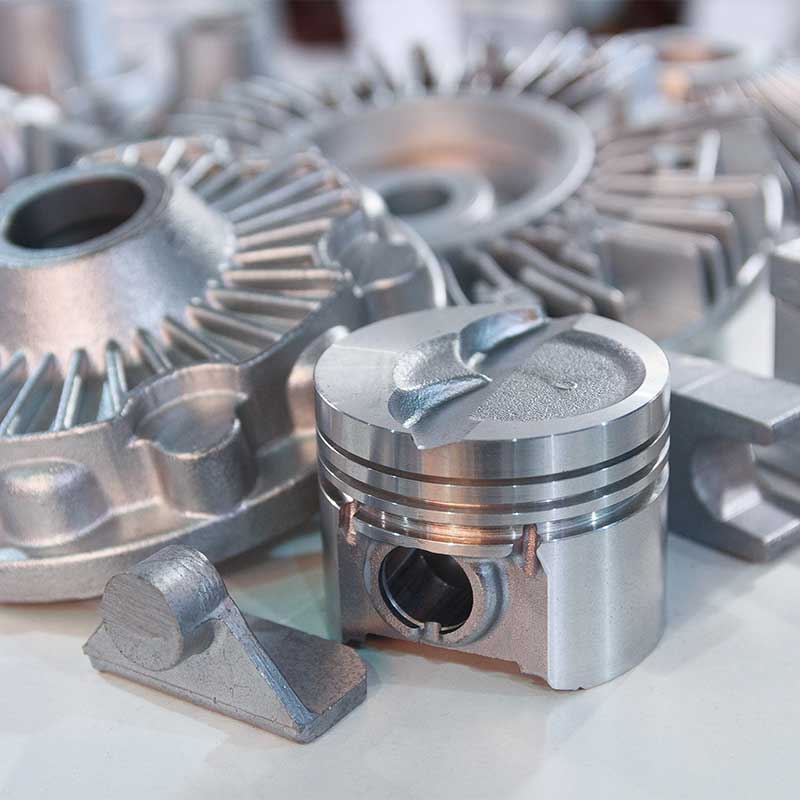
Aluminum alloys are a group of materials primarily composed of aluminum, often combined with other elements such as magnesium, silicon, copper, zinc, and manganese to enhance various properties. These alloys are renowned for their light weight, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ease of machinability, making them a popular choice in industries like aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction. Aluminum itself is a relatively soft metal, but alloying it with other elements significantly improves its mechanical properties, allowing it to compete with heavier materials like steel in many applications.
The advantages of aluminum alloys are extensive. They have excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for heat exchangers and electrical components. Aluminum alloys are also non-magnetic, non-sparking, and highly reflective, which adds to their versatility in specialized applications. Their natural corrosion resistance is due to the formation of a protective oxide layer on the surface, which can be further enhanced with treatments like anodizing. Moreover, aluminum alloys are recyclable, making them an environmentally friendly material choice.
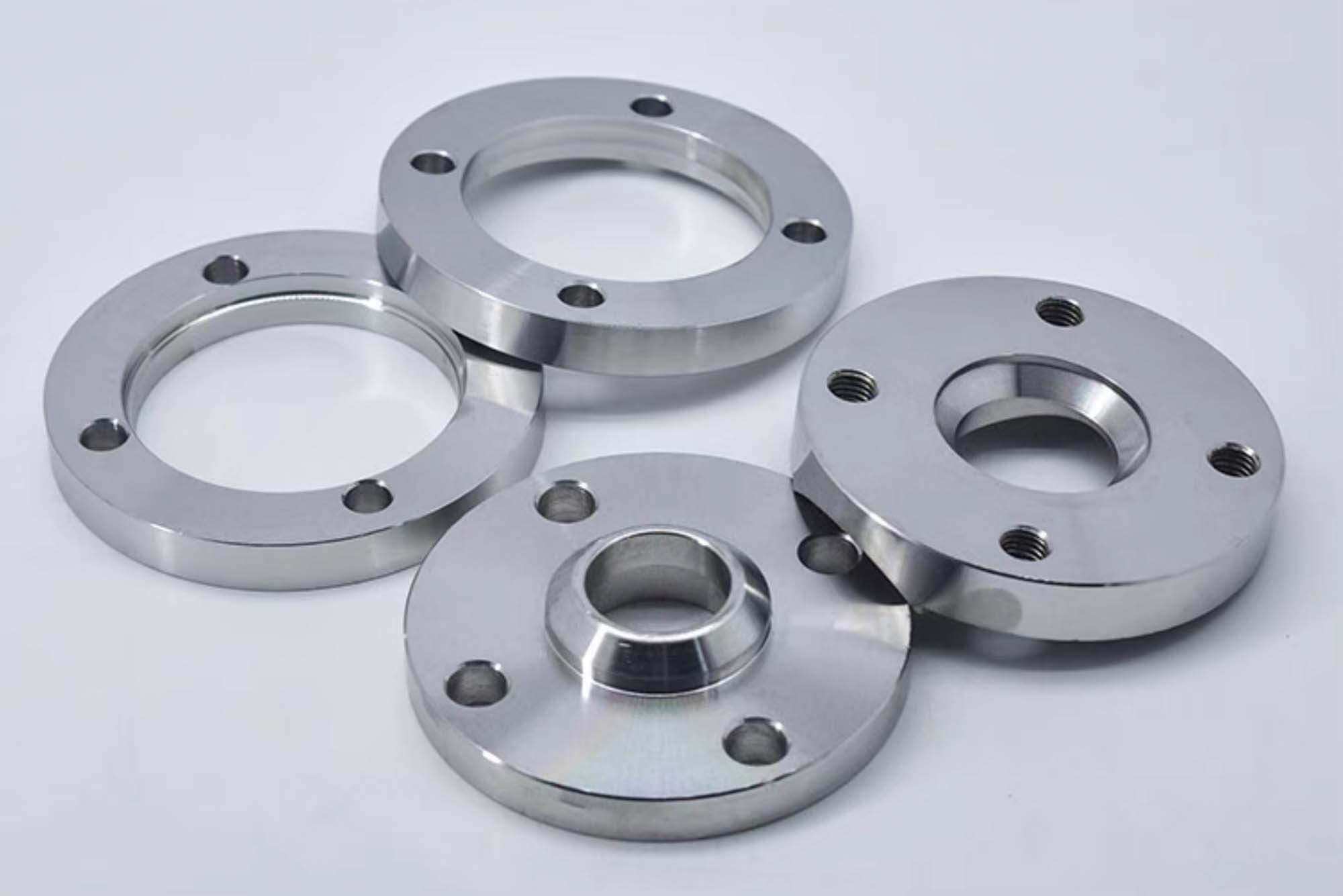
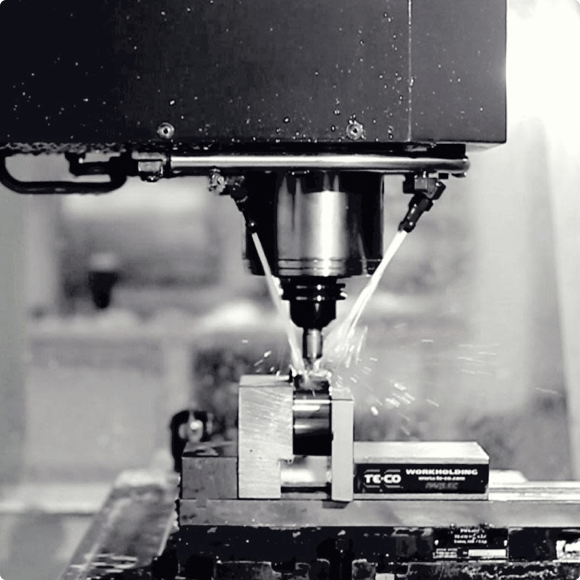
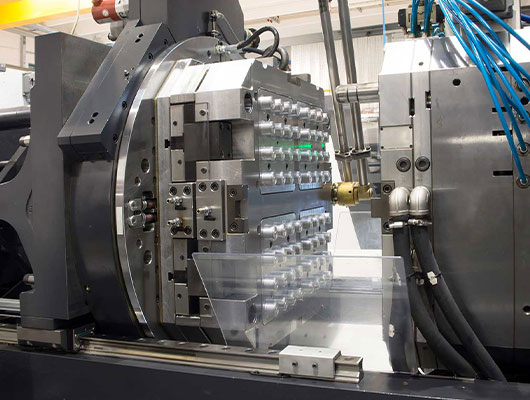
In CNC machining, aluminum alloys are widely preferred due to their machinability and the ease with which complex parts can be manufactured. Their lightweight nature also makes them easier to handle during machining, reducing tool wear and energy consumption. However, aluminum alloys vary greatly in terms of strength, hardness, and formability, so the appropriate choice depends on the specific application requirements. Some aluminum alloys are suited for high-strength applications, while others are optimized for corrosion resistance or thermal conductivity.









 Afrikaans
Afrikaans Albanian
Albanian Amharic
Amharic Arabic
Arabic Armenian
Armenian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Basque
Basque Belarusian
Belarusian Bengali
Bengali Bosnian
Bosnian Bulgarian
Bulgarian Catalan
Catalan Cebuano
Cebuano Chichewa
Chichewa Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Traditional)
Chinese (Traditional) Corsican
Corsican Croatian
Croatian Czech
Czech Danish
Danish Dutch
Dutch English
English Esperanto
Esperanto Estonian
Estonian Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish French
French Frisian
Frisian Galician
Galician Georgian
Georgian German
German Greek
Greek Gujarati
Gujarati Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Hausa
Hausa Hawaiian
Hawaiian Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Hmong
Hmong Hungarian
Hungarian Icelandic
Icelandic Igbo
Igbo Indonesian
Indonesian Irish
Irish Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Javanese
Javanese Kannada
Kannada Kazakh
Kazakh Khmer
Khmer Korean
Korean Kurdish (Kurmanji)
Kurdish (Kurmanji) Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz Lao
Lao Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Lithuanian
Lithuanian Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish Macedonian
Macedonian Malagasy
Malagasy Malay
Malay Malayalam
Malayalam Maltese
Maltese Maori
Maori Marathi
Marathi Mongolian
Mongolian Myanmar (Burmese)
Myanmar (Burmese) Nepali
Nepali Norwegian
Norwegian Pashto
Pashto Persian
Persian Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Punjabi
Punjabi Romanian
Romanian Russian
Russian Samoan
Samoan Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic Serbian
Serbian Sesotho
Sesotho Shona
Shona Sindhi
Sindhi Sinhala
Sinhala Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Somali
Somali Spanish
Spanish Sundanese
Sundanese Swahili
Swahili Swedish
Swedish Tajik
Tajik Tamil
Tamil Telugu
Telugu Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Urdu
Urdu Uzbek
Uzbek Vietnamese
Vietnamese Welsh
Welsh Xhosa
Xhosa Yiddish
Yiddish Yoruba
Yoruba Zulu
Zulu