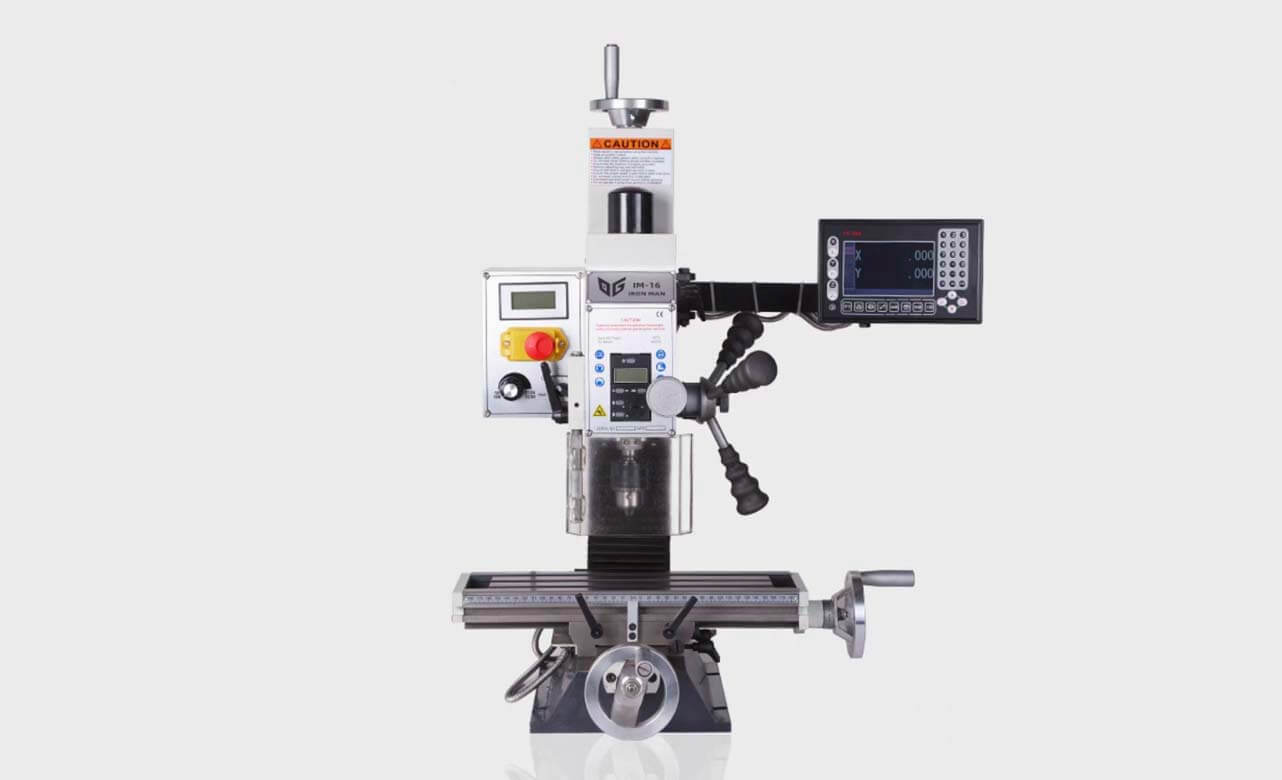
What is a Mini Milling Machine?
A mini milling machine is a compact, versatile tool that allows beginners and professionals alike to create intricate parts, customize small projects, and explore hands-on applications. I remember my own introduction to mini milling machines—seeing the potential to craft and shape raw materials right in my own workspace was thrilling. These machines are often smaller than traditional mills, making them ideal for personal workshops and compact spaces, yet they retain the essential features needed to produce quality cuts and components.
With this guide, I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about mini milling machines, from applications and choosing the right machine to practical tips, tricks, and maintenance. This guide is ideal for beginners who want to unlock the full potential of their mini milling machine, combining personal experience, expert insights, and essential data.
Applications of Mini Milling Machines
Mini milling machines are surprisingly versatile, fitting into numerous sectors and serving a wide range of needs. Let’s dive deeper into each application area.
1.1 Manufacturing and Machining
In small-batch production, mini milling machines provide an economical solution for creating custom parts and prototypes. By working on a mini mill, you can avoid the high costs and resource use of full-scale production, especially when developing unique or experimental parts.
I’ve found that the ability to test parts on a smaller scale first is invaluable. Not only does it allow for fast adjustments, but it also minimizes material waste, which is especially important when working with expensive materials.
| Manufacturing Application | Ideal Material | Machine Capability | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prototyping | Aluminum, steel | High precision | Custom components, automotive parts |
| Small Batch Production | Various metals | Consistent performance | Limited-edition hardware, fasteners |
| Detail Crafting | Brass, alloys | Fine-detail capability | Jewelry elements, art fixtures |
1.2 Education and Vocational Training
In educational settings, mini milling machines are excellent teaching tools. They’re safer and more accessible for students, while still providing hands-on experience with real-world machining processes. Many institutions integrate mini mills into their curriculum to prepare students for careers in machining, engineering, and design. In my experience, starting on a mini milling machine helped me develop confidence and hands-on skills before working with industrial machines.
For educational purposes, I recommend looking for mini milling machines with clear, user-friendly controls and safety features, as this makes it easier to focus on the core skills.
1.3 DIY and Maker Community
Mini milling machines are a game-changer for DIY enthusiasts and makers. These machines open up possibilities for at-home fabrication and personalized projects. With a mini mill, I’ve been able to work on a range of projects, from custom tool parts to unique furniture fittings. The size and versatility allow for creative freedom without requiring a large workshop or extensive technical knowledge.
| DIY Application | Material | Project Ideas | Tips for Beginners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model Building | Plastic, aluminum | Custom car parts, prototypes | Start with simple shapes for practice |
| Tool Customization | Steel | Personalized tool grips, handles | Use mild steel for easier cutting |
| Household Projects | Wood, metal | Furniture fittings, decor items | Test on scrap material to perfect setup |
1.4 Art and Jewelry Design
For artists, model makers, and jewelry designers, mini milling machines offer the fine precision necessary to create intricate designs. These machines are particularly suited for materials like gold, silver, and brass, where precision and delicacy are essential. In the past, I’ve used mini mills for small-scale metalworking projects that required fine cuts and intricate detailing.
Artisans appreciate mini mills for their ability to handle diverse materials and perform delicate operations without compromising accuracy.
How to Choose the Right Mini Milling Machine
With so many models available, choosing the right mini milling machine can be overwhelming. Here are some key factors to consider.
2.1 Types of Mini Milling Machines
The two primary types of mini milling machines are manual and CNC-controlled. Each has unique benefits, and the choice ultimately depends on your project needs and experience level.
| Machine Type | Benefits | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Mill | Simplicity, lower cost | Beginners, simple projects |
| CNC Mill | Precision, repeatability, automation | Complex shapes, small-batch production |
Manual mills are usually preferred by beginners and DIY hobbyists, as they are straightforward and don’t require computer programming knowledge. On the other hand, CNC mini mills excel in applications that require precision and repeatability, as they can automate complex processes and follow intricate designs.
2.2 Key Specifications Explained
When selecting a mini milling machine, certain specifications are crucial. Understanding these parameters will help you make an informed decision that matches your project needs.
- Spindle Speed: The spindle speed is critical for material compatibility. Softer materials require lower speeds, while harder materials benefit from higher speeds to achieve a cleaner finish.
- Table Size: Table dimensions limit the size of the workpiece. If you plan on working with larger pieces, choose a machine with a spacious table.
- Motor Power: A higher-powered motor will allow you to work with harder materials, but also consider that higher power increases energy consumption.
| Specification | Description | Typical Range | Importance Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spindle Speed | Speed at which cutting tool rotates | 500–3000 RPM | High |
| Table Size | Maximum space for holding workpieces | 200mm x 100mm to 300mm x 150mm | Moderate |
| Motor Power | Determines material and cut strength | 250W–600W | High |
2.3 Buying Guide for Different Needs
If you’re purchasing a mini milling machine for specific purposes, here’s a guide to help you pick the right one.
| Purpose | Recommended Machine Type | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner Projects | Manual Mill | Ease of use, cost-effective |
| Precision Work | CNC Mill | High accuracy, programmable |
| Art and Jewelry Design | CNC or Manual | Fine detail capability, small work area |
| Small Batch Production | CNC Mill | Repeatability, efficiency |
CNC Programming and Operation Guide
Even if you’re new to CNC programming, it’s fairly intuitive with mini milling machines. Let’s go over some basics.
3.1 Basics of CNC Programming
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) programming uses specific codes, such as G-code, to direct the machine’s movements. Although I was initially intimidated by CNC, I soon realized that learning the basics allowed me to work more efficiently and achieve far greater precision.
| CNC Code Type | Function | Example Command | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| G-code | Defines path for cutting and movement | G01 | Linear cutting path |
| M-code | Controls auxiliary functions | M03 | Starts spindle rotation |
3.2 CNC Operation Process
Operating a CNC mini mill involves several steps, from setup to the final cut.
- Prepare the Workpiece: Secure your material firmly to avoid vibration and misalignment.
- Program the Machine: Enter the desired G-code and M-code, which dictate the paths and functions.
- Run a Test Pass: Before cutting, run a test to ensure your setup is correct and the machine paths are clear.
- Execute the Final Run: Once you’re confident, execute the program for the full cut.
These steps are straightforward but can greatly impact the quality of the final product, especially for beginners.
Success Stories in DIY and Small-Batch Production
4.1 DIY Enthusiast Projects
One of the joys of having a mini milling machine is the ability to work on personal projects at home. I’ve used my machine for countless DIY tasks, from creating custom parts to modifying tools.
| Project | Material | Process Overview | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model Car Parts | Aluminum, plastic | Cutting, sanding, polishing | Functional model car parts |
| Custom Tool | Steel | Shaping, drilling, edge finishing | Enhanced tool functionality |
4.2 Small-Batch Production Applications
For small businesses, mini milling machines provide a practical solution for limited production runs. I’ve encountered several workshops that use mini mills to produce specialized parts in small batches.
In one case, a local hardware business used a mini milling machine to create custom-sized screws and fasteners. By using a mini mill instead of outsourcing production, they were able to cut costs and fulfill orders faster.
4.3 Creative and Art Projects
Mini milling machines are also fantastic for art projects. For example, jewelry designers use mini mills to create intricate patterns and unique custom pieces.
Cost and Brand Recommendations
5.1 Major Brands and Their Features
Several brands stand out for mini milling machines, each offering unique features.
| Brand | Model | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Grizzly | G8689 | Compact, affordable, user-friendly |
| Proxxon | 37110 MF 70 | High precision, small footprint |
| Sherline | 5400 Deluxe | High accuracy, CNC compatibility |
5.2 Performance Comparison Across Price Ranges
Different budgets can access different features, so it’s worth considering your specific needs against what each price point offers.
| Price Range | Suitable For | Example Model | Pros |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | DIY, hobbyists | Grizzly G8689 | Budget-friendly, easy to operate |
| Mid-Range | Small businesses, artists | Proxxon 37110 | Precise, compact, easy to control |
| High-End | Professionals,precision | Sherline 5400 | Advanced features, CNC-ready |
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Tips for Mini Milling Machines
A mini milling machine, like any tool, needs regular maintenance to keep it in good working condition. I’ve found that by following a simple maintenance routine, you can extend the machine’s life and ensure that it consistently delivers accurate results. Here are some essential maintenance tips and common troubleshooting steps.
6.1 Regular Maintenance Tasks
Basic maintenance can go a long way in keeping your mini milling machine running smoothly. Here’s a routine that has worked well for me:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Lubricate Moving Parts | Weekly | Apply machine oil to the spindle, screws, and other moving parts to reduce wear. |
| Clean Work Surfaces | After Each Use | Remove debris, shavings, and dust from the table, fixtures, and any exposed parts. |
| Inspect Belts and Gears | Monthly | Check for signs of wear or damage on belts and gears and replace if necessary. |
| Tighten Bolts and Screws | Monthly | Vibration during use can loosen screws over time; tighten to avoid misalignment. |
Keeping up with these tasks prevents buildup and wear, which can compromise the precision of your cuts. Plus, a clean and well-maintained machine is far safer to operate.
6.2 Common Troubleshooting Issues
Even with careful maintenance, you might occasionally run into issues. Below are some common problems and how to solve them.
- Problem: Inconsistent Cuts or Vibrations
Solution: Check that your workpiece is secured properly on the table. Tighten the machine’s bolts and ensure the table and spindle are free of debris. Also, verify that your cutting tool is sharp and undamaged. - Problem: Overheating
Solution: Excessive heat can cause wear on the spindle and other parts. Make sure you’re using the correct spindle speed for your material, and avoid overloading the machine. Also, consider pausing between cuts to let the machine cool down. - Problem: Misalignment
Solution: Misalignment can lead to inaccurate cuts. Recalibrate the machine by zeroing the table and spindle. You may also want to verify that all screws are tight and that the workpiece is correctly positioned. - Problem: Loud Noise or Grinding Sounds
Solution: Unusual sounds may indicate worn gears or belts. Inspect these parts for damage and replace them if necessary. Also, ensure the machine is well-lubricated, as dry parts can cause friction.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you’ll be able to address most common issues quickly and keep your machine in top shape.
Advanced Tips and Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can start exploring advanced techniques to get even more from your mini milling machine. Here are some techniques and tips I’ve picked up that have helped me produce even better results.
7.1 Using Jigs and Fixtures
Jigs and fixtures are invaluable accessories that help hold your workpiece steady and guide the cutting tool with greater precision. I’ve found that they significantly improve accuracy, especially for repetitive tasks.
| Jig or Fixture Type | Purpose | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Vise | Holds the workpiece securely | Securing metal for detailed cuts |
| Angle Plate | Allows for angled cuts | Creating beveled edges |
| Rotary Table | Enables circular cuts | Making gears, rounded shapes |
Experimenting with Different Materials
One of the most exciting aspects of mini milling is experimenting with various materials, from soft metals like aluminum to harder materials like stainless steel. Each material has unique characteristics, and knowing how to work with them opens up new project possibilities.
| Material | Recommended Spindle Speed | Cutting Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 1000–2500 RPM | Use a high spindle speed and coolant for smoother cuts |
| Brass | 1200–3000 RPM | Apply light pressure; avoid high heat |
| Steel | 500–1000 RPM | Lower speeds to prevent overheating |
7.3 High-Precision Cutting
If you’re aiming for high-precision results, here are some techniques I’ve found helpful:
- Use Sharp, Quality Cutting Tools: Dull tools can create rough edges and inaccurate cuts, so keep your cutting tools sharp.
- Adjust Feed Rate and Depth: A slower feed rate often provides more control, while shallow cuts help reduce strain on the machine and increase accuracy.
- Double-Check Setup and Alignment: Before each cut, confirm that the workpiece, cutting tool, and table are properly aligned. This extra check can prevent mistakes and improve the precision of your results.
7.4 Using a DRO (Digital Readout)
If your mini milling machine is equipped with a DRO, use it to monitor your cuts in real-time. I’ve found that this feature improves accuracy by allowing me to track even the smallest adjustments. If your machine doesn’t come with a DRO, it may be possible to add one as an aftermarket accessory.
Additional Data Tables for Advanced Techniques and Maintenance
Material-Specific Cutting Speeds and Feed Rates
Using the right cutting speed and feed rate for each material ensures a smooth finish and extends tool life. Below is a quick reference table I use when working with different materials.
| Material | Ideal Cutting Speed (SFM) | Feed Rate (IPM) | Depth of Cut (Inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 150–250 | 2–3 | 0.1–0.2 |
| Brass | 200–300 | 1.5–2.5 | 0.1 |
| Mild Steel | 70–120 | 1–2 | 0.05–0.1 |
| Stainless Steel | 50–80 | 0.5–1.5 | 0.03–0.08 |
| Plastic | 300–600 | 2–4 | 0.15–0.3 |
Maintenance Checklist for Extended Machine Life
Having a routine maintenance checklist can help you stay organized and ensure your machine remains reliable. Here’s a checklist I use:
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Clean Machine | After every use | Remove all debris and wipe down surfaces |
| Check Belt Tension | Monthly | Adjust if the belt is loose or slipping |
| Lubricate Bearings | Monthly | Apply machine oil to spindle and bearings |
| Inspect Cables | Quarterly | Ensure all cables are secure and undamaged |
| Recalibrate DRO | Quarterly | Necessary for maintaining high precision |
These tables serve as a valuable reference to optimize your cutting processes and maintain your mini milling machine for the long term.
Closing Thoughts
A mini milling machine is an incredibly versatile tool that allows both beginners and experienced machinists to explore a wide range of projects. From DIY crafts to small-batch production, a mini mill offers a balance of precision, functionality, and accessibility that’s hard to beat.
Starting with the basics and moving towards advanced techniques, I’ve covered all the steps to make the most of this compact machine. By understanding the applications, selecting the right tools, practicing routine maintenance, and following essential safety practices, you can confidently create quality parts and tackle intricate projects.
With the information provided, I hope you’ll find the right mini milling machine to meet your needs and help you achieve success in your machining endeavors.
FAQ
To further assist beginners and prospective buyers of mini milling machines, I’ve compiled answers to some of the most frequently asked questions. These responses draw from my own experiences and common industry standards.
1. What is a mini milling machine used for?
A mini milling machine is typically used for small-scale milling and machining tasks, such as creating custom parts, prototyping, and performing detailed work on small workpieces. It’s especially popular in DIY projects, model making, and jewelry design due to its compact size and versatility.
2. How does a mini milling machine differ from a regular milling machine?
The primary difference is size and capacity. Mini milling machines are smaller, making them ideal for personal workshops and limited-space environments. They typically have less power than standard milling machines but are sufficient for light-duty and medium-duty tasks on softer materials like aluminum, brass, wood, and plastics.
3. Can a mini milling machine work with hard metals like stainless steel?
Yes, but with limitations. While mini milling machines can work with hard metals, they require lower spindle speeds and lighter cuts to avoid overheating or straining the motor. It’s important to use high-quality, sharp cutting tools and go slow to achieve a smooth finish on hard metals.
4. What materials can be machined with a mini milling machine?
Mini milling machines can handle a range of materials, including:
- Soft metals: Aluminum, brass, and copper.
- Harder metals (with care): Mild steel and stainless steel.
- Non-metals: Plastics, wood, and acrylics.
Always refer to the machine’s manual to ensure compatibility with specific materials and check the recommended cutting speeds and feed rates.
5. Is a mini milling machine easy to learn for beginners?
Yes, mini milling machines are generally beginner-friendly. Their smaller size, simplified controls, and lower power make them suitable for beginners to learn the basics of milling and machining. Additionally, many models come with instructional materials or online tutorials that make it easier to get started.
6. How much does a mini milling machine cost?
The cost of a mini milling machine varies depending on the brand, features, and capabilities:
| Price Range | Typical Features | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|
| $300–$600 | Basic functionality, manual control | DIY hobbyists, basic projects |
| $600–$1,200 | Higher precision, digital readout (DRO) | Beginners, small-batch production |
| $1,200+ | CNC compatibility, advanced features | Professionals, high-precision work |
Mini milling machines at the lower end of this range are generally suited for beginners, while more advanced models with CNC capabilities can reach higher prices.
7. How do I maintain my mini milling machine?
Regular maintenance includes:
- Cleaning the work surfaces: After each use, clear debris and shavings.
- Lubricating moving parts: Apply machine oil weekly to prevent wear.
- Checking for loose bolts and screws: Monthly inspection helps maintain stability.
- Inspecting belts and gears: Replace worn parts to avoid mechanical issues.
Keeping up with these tasks will help ensure your machine performs consistently well.
8. Is it possible to convert a manual mini mill to a CNC mini mill?
Yes, many users convert their manual mini milling machines to CNC by adding a motorized axis and a CNC control system. Conversion kits are available from several manufacturers, allowing for greater precision and automation. However, conversions require technical know-how, so it’s ideal for users who already have some experience with machining.
9. What’s the best way to learn CNC programming for mini mills?
There are several ways to learn CNC programming:
- Online tutorials and courses: Many free and paid resources provide beginner-friendly lessons.
- Practice with simulation software: Some programs allow you to practice without risk to your machine.
- Start with basic G-code: G-code is the most common CNC language and is well-suited for mini milling applications.
10. What safety precautions should I follow when using a mini milling machine?
Basic safety precautions include:
- Wearing safety goggles: Protects your eyes from metal shavings and debris.
- Securing loose clothing and hair: Minimizes the risk of catching on rotating parts.
- Using a vise or clamps: Ensures the workpiece remains secure during cuts.
- Keeping hands away from cutting tools: Especially when the machine is powered on.
These safety steps help prevent accidents and make for a safer machining experience.
11. Can a mini milling machine handle batch production?
Yes, mini milling machines can handle small-batch production, especially for custom or low-volume runs. CNC-equipped mini mills are particularly effective for batch production, as they allow for repeatable precision and consistency across multiple units. However, their limited power and workspace mean that large-scale production isn’t feasible.
12. What’s the maximum workpiece size for a mini milling machine?
The maximum workpiece size depends on the machine’s table size and spindle clearance. Most mini mills can accommodate workpieces up to around 10–15 inches in length and 5–10 inches in width, though these dimensions vary by model. Always check the machine specifications for accurate measurements.
13. Do mini milling machines require special power requirements?
Mini milling machines generally run on standard household power (110V in the US), making them convenient for home workshops. However, higher-powered models may require 220V, so it’s essential to confirm your power source matches the machine requirements.
14. Can I use my mini milling machine for woodworking?
Yes, mini milling machines can handle wood, making them versatile for both metal and non-metal applications. When working with wood, it’s recommended to use higher spindle speeds and sharp cutting tools to prevent splintering.
15. What are the most popular brands of mini milling machines?
Some top brands for mini milling machines include:
- Grizzly: Known for affordable, entry-level models with good features.
- Proxxon: Offers high-precision machines suited for fine detail work.
- Sherline: Known for accuracy and a variety of accessories.
- LittleMachineShop: Provides a range of mini mills and accessories tailored for DIY use.
These brands offer machines that range from budget-friendly to high-end, providing options for various needs.
16. How do I choose the right cutting tools for my mini milling machine?
Choosing the right cutting tools depends on your material and intended project. Here’s a quick guide:
| Material | Recommended Tool Type | Tool Size (Diameter) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | High-speed steel (HSS) | 1/4 to 3/8 inch |
| Brass | Carbide-tipped, HSS | 1/8 to 1/4 inch |
| Steel | Carbide-tipped | 1/4 to 1/2 inch |
| Plastic/Wood | HSS or carbide for finer cuts | 1/8 to 3/8 inch |
Matching the tool type and size with your material will help improve cut quality and extend tool life.
17. Can I drill with a mini milling machine?
Yes, a mini milling machine can double as a drill press for smaller projects. By using the machine’s vertical spindle, you can drill accurate holes into materials. However, for heavy-duty drilling or large workpieces, a dedicated drill press might be more suitable.
18. What are the benefits of using a digital readout (DRO) on a mini milling machine?
A digital readout (DRO) enhances precision by displaying the position of the milling table in real-time. This feature is especially helpful for achieving accurate, repeatable cuts and reducing the margin for error. DROs are often built into higher-end models or available as aftermarket additions.
19. How much accuracy can I expect from a mini milling machine?
Most mini milling machines are accurate to within 0.001–0.005 inches, depending on the model and operator skill. For detailed or high-precision work, CNC control and quality tooling can improve accuracy further.
20. Can I create threads or tap holes with a mini milling machine?
Yes, threading or tapping holes is possible with a mini milling machine. By using specialized taps and dies, you can create internal or external threads in softer metals like aluminum and brass. For harder metals, using a tap guide helps achieve a straight, accurate thread.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- What maintenance and upkeep are required for a CNC drilling and milling machine?
A CNC drilling and milling machine is a versatile tool that can perform various processes such as drilling, milling, chamfering, and tapping. It operates through CAD/CAM software programming, CNC system…
- Mastering Milling Basics with CNC Machining Techniques and Tools
Milling is one of the most fundamental and widely used processes in CNC machining. Whether you are a technician looking to deepen your understanding of CNC milling or a procurement…
- Top 5 Desktop CNC Milling Machines
Desktop CNC milling machines are compact and powerful tools for prototyping or small-scale fabrication work. They enable users to create precise parts using various materials, such as wood, foam, and…
- Maximizing Precision in CNC Machining: Techniques and Tips
Importance of Precision in CNC Machining Precision is an fundamental component in the field of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. It entails producing parts that are not only accurate but…
- Case Reviews: How to Choose Materials for Milling Machine Parts
When it comes to creating prototypes for milling machine parts, the selection of suitable materials plays a crucial role in the overall success of the project. At Want.Net, we understand…
- Using the Right Milling Technique: Down Milling vs. Back Milling
In the world of CNC milling, experts employ a myriad of techniques to maximize the capabilities of their CNC machines. These techniques are tailored to the size, shape, features, and…