When it comes to CNC machining, understanding the intricacies of feed rate and spindle speed is essential, especially for thread turning. These two parameters play a pivotal role in determining the quality and precision of the threads you produce. Let’s dive into how to optimize feed rate and spindle speed to achieve the best results in your CNC turning for thread operations.
Understanding Feed Rate in CNC Thread Turning
Feed rate in thread turning refers to the distance the tool advances along the workpiece per revolution of the spindle. Unlike other machining operations where feed rate can be more flexible, thread turning requires precise control over this parameter. The feed rate is directly related to the thread’s pitch or lead, which is the distance between two consecutive thread peaks.
In metric threading, the feed rate is the pitch of the thread, while in inch-based systems, it’s derived from the threads per inch (TPI). For example, a 3 mm pitch thread will have a feed rate of 3 mm per revolution. Similarly, an 8 TPI thread will have a feed rate of 0.125 inches per revolution (1 inch/8).
Here’s a quick reference formula for calculating the feed rate:

where ( F ) is the feed rate in inches per revolution, and ( TPI ) is the threads per inch.
Calculating Spindle Speed
Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), needs to be carefully selected to ensure the cutting tool’s efficiency and longevity. The spindle speed should be set considering the material being machined, the type of cutting tool used, and the desired surface finish.
For thread turning, constant surface speed (CSS) should not be used. Instead, a fixed RPM should be set to maintain consistency. The correct spindle speed can be calculated using the following formula:

where the cutting speed is in feet per minute (FPM) or meters per minute (MPM), and the diameter is in inches or millimeters.
Practical Considerations
- Material Type: Different materials require different spindle speeds and feed rates. For instance, harder materials like stainless steel will need slower spindle speeds compared to softer materials like aluminum.
- Tool Geometry and Coating: The tool’s material, geometry, and any coatings (such as TiN or carbide) can significantly impact the optimal spindle speed and feed rate. Coated tools generally allow for higher speeds and feeds.
- Thread Type and Size: The size and type of thread (fine or coarse) also determine the feed rate and spindle speed. Larger threads typically require slower spindle speeds to maintain tool life and achieve the desired finish.
- Machine Capability: The maximum feed rate and spindle speed of your CNC machine will also limit your settings. Always refer to the machine’s manual to avoid exceeding these limits.
Avoiding Lead Error
Lead error, or pitch error, occurs when there is a discrepancy between the programmed feed rate and the actual movement of the tool. This can be minimized by ensuring that the spindle speed and feed rate are accurately synchronized.
For instance, if programming a 14 TPI thread, the ideal feed rate is approximately 0.071428 inches per revolution. However, programming limitations might force you to round this to 0.0714. Over a long thread, this small difference can accumulate, leading to significant lead error. Using more precise programming capabilities, like those that allow six decimal places, can help mitigate this issue.
Example Calculations
Let’s walk through a couple of examples to solidify these concepts:
- Metric Thread Example: For an M10x1.5 thread (where 1.5 mm is the pitch):
Feed Rate: 1.5 mm/rev
If the cutting speed for the material is 60 meters per minute and the diameter is 10 mm, the spindle speed is:
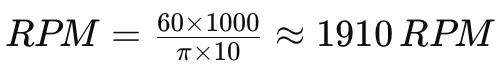
- Inch Thread Example: For a 1/2-20 UNF thread (where 20 TPI):
Feed Rate: 1/20= 0.05 inches/rev
If the cutting speed for the material is 100 FPM and the diameter is 0.5 inches, the spindle speed is:
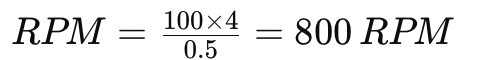
Data Table for Common Threads
Here’s a helpful table with recommended feed rates and spindle speeds for some common threads:
| Thread Type | TPI / Pitch (mm) | Feed Rate (in/rev or mm/rev) | Cutting Speed (FPM/MPM) | Diameter (in/mm) | Spindle Speed (RPM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M10x1.5 | 1.5 mm | 1.5 mm/rev | 60 MPM | 10 mm | 1910 |
| 1/2-20 UNF | 20 TPI | 0.05 in/rev | 100 FPM | 0.5 in | 800 |
| M24x3 | 3 mm | 3 mm/rev | 50 MPM | 24 mm | 663 |
| 3/4-10 UNC | 10 TPI | 0.1 in/rev | 80 FPM | 0.75 in | 427 |
Conclusion
Mastering the feed rate and spindle speed in CNC thread turning is crucial for producing high-quality threads. By understanding the relationship between these parameters and the specific requirements of your threading operations, you can optimize your CNC machining processes, reduce lead errors, and extend tool life. Always remember to consider the material, tool geometry, thread type, and machine capabilities when setting your feed rate and spindle speed.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Mastering Feed Rate Control for Perfect CNC Machining Parts
Controlling the feed rate is one of the most crucial aspects of programming CNC machines. The feed rate determines how fast the tool moves through the material, which directly affects…
- Feed Rate And Cutting Speed: What’s The Difference In CNC Machining
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that utilizes programmed codes to control the movement of the tool axis. These codes encompass cutting parameters such as tool movement, spindle speeds,…
- Mastering Single-Head Thread Turning in CNC Machining Parts
Thread turning is an essential process in machining, particularly in the realm of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) operations. It involves creating helical grooves on cylindrical or conical surfaces, essential for…
- Program Data Multipliers in CNC Machining Parts: Optimizing Speed and Feed Rates
In the realm of CNC machining, fine-tuning the machine's performance can lead to significant improvements in both efficiency and quality. One crucial aspect of this tuning process involves the use…
- How Does Feed Rate Influence the Durability of CNC Machining Parts Used in Dental Implants?
Introduction: The Crucial Role of Feed Rate in CNC Machining of Dental Implants In the sophisticated realm of medical device manufacturing, CNC machining stands out for its precision and repeatability,…
- Technical Decisions in CNC Machining Parts: Optimizing Speed, Feed, and Tool Paths
When it comes to CNC machining, making the right technical decisions is crucial. These decisions not only affect the quality of the final product but also the efficiency of the…