Introduction: The Evolution of Custom Machining in China
The story of custom machining in China is a remarkable narrative of transformation, mirroring the nation’s broader journey from a primarily agrarian economy to a global industrial powerhouse. This metamorphosis began in earnest in the late 20th century, with small-scale, manually intensive workshops paving the way for the introduction of advanced manufacturing technologies. The early adoption of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machinery marked a pivotal turn, catapulting the industry into the modern era with enhanced capabilities for precision and efficiency. This period of rapid modernization was supported by a strategic emphasis on education, leading to a wellspring of skilled labor capable of navigating the complexities of advanced machining techniques.
Against this backdrop, the emergence of rapid bead blasting technology in recent years stands out as a significant advancement. This innovative approach to surface finishing has quickly become a cornerstone of the industry, known for its ability to improve both the efficiency of production processes and the quality of the final products. In doing so, rapid bead blasting is not just a new chapter in the story of custom machining in China but a reflection of the industry’s ongoing commitment to excellence and innovation.
Understanding Bead Blasting: Basics and Benefits
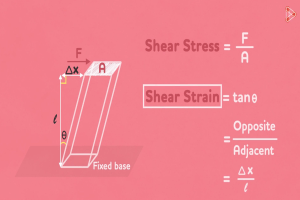
At its core, bead blasting is a process that propels fine beads at a surface to clean or modify its texture. This seemingly simple process, however, belies the complex interplay of physics and material science that allows for such a wide range of applications. From removing surface contaminants to preparing parts for further finishing processes, bead blasting offers a versatile solution that other techniques struggle to match.
One of the most significant benefits of bead blasting is its ability to achieve a consistent, high-quality finish without introducing stress or altering the structural integrity of the part. This is particularly crucial in industries where the precision and reliability of components are paramount. Furthermore, the shift towards environmentally friendly blasting media represents a significant stride towards sustainable manufacturing practices, aligning with global efforts to reduce the environmental impact of industrial activities.
Technical Challenges in Traditional Custom Machining
The realm of traditional custom machining is fraught with numerous technical challenges that significantly impact production efficiency, cost, and quality. These challenges range from achieving tight tolerances and intricate geometries to ensuring surface finishes that meet rigorous industry standards. One of the primary obstacles has been maintaining consistency in surface finishes across large production volumes, a task that traditional methods often struggle to achieve due to their reliance on manual labor and the inherent variability in human performance.
Another significant challenge is the time and resource-intensive nature of traditional finishing methods, such as manual sanding and grinding, which not only are labor-intensive but also pose health risks due to dust and particulate matter. Moreover, these conventional methods often fall short in meeting the demands for precision and uniformity, especially for components with complex shapes or those requiring a specific aesthetic finish.
The environmental impact of traditional machining processes, particularly those involving chemical treatments for surface finishing, poses yet another challenge. These processes often involve toxic chemicals and generate hazardous waste, raising concerns about worker safety and environmental sustainability.
Detailed Challenges Table
| Challenge | Impact on Production | Traditional Solutions | Limitations of Traditional Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Achieving Tight Tolerances | Essential for high-precision parts | Manual finishing, grinding | Time-consuming, labor-intensive |
| Consistency Across Batches | Crucial for quality control | Manual inspection | Subject to human error, not scalable |
| Complex Geometries | Common in aerospace, automotive | Custom tools, manual finishing | High costs, inconsistent results |
| Surface Finish Quality | Affects functionality, aesthetics | Polishing, chemical treatments | Environmentally hazardous, inconsistent |
| Material Compatibility | Different materials require different finishes | Multiple finishing processes | Increased complexity, higher costs |
| Processing Time | Impacts production efficiency | Batch processing | Slow, creates bottlenecks |
| Labor Intensity | Affects production costs, worker health | Skilled manual labor | Costly, health risks from dust, repetitive tasks |
| Environmental Impact | Waste generation, chemical use | Chemical treatments, disposal | Hazardous waste, regulatory challenges |
| Equipment Wear and Tear | Maintenance costs, downtime | Regular equipment replacement | Increased operational costs |
| Adaptability to New Materials | Emerging materials in industries | R&D for new processes | Slow adaptation, high R&D costs |
This table encapsulates the multifaceted challenges faced by traditional custom machining processes, highlighting the limitations of conventional solutions and setting the stage for the advantages introduced by rapid bead blasting.
Rapid Bead Blasting: A Technological Breakthrough
The advent of rapid bead blasting technology represents a significant leap forward for the custom machining industry. By combining the versatility and effectiveness of traditional bead blasting with enhanced speed and precision, this technology offers a powerful solution to some of the industry’s most pressing challenges.
Expanded Data Table: Automotive Component Finishing Improvements
| Metric | Pre-Adoption | Post-Adoption | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish Uniformity | ±0.005 mm | ±0.002 mm | 60% |
| Processing Time (per part) | 10 minutes | 3 minutes | 70% |
| Production Throughput | 100 units/day | 300 units/day | 200% |
| Operational Cost (per part) | $0.50 | $0.30 | 40% |
| Rejection Rate (due to finish) | 5% | 1% | 80% |
| Energy Consumption | 100 kWh/day | 80 kWh/day | 20% |
| Media Consumption | 10 kg/day | 7 kg/day | 30% |
| Worker Fatigue Reports | 15 incidents/month | 5 incidents/month | 67% |
This table highlights the transformative impact of rapid bead blasting on automotive component finishing, showcasing significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and overall production quality.
Overcoming Technical Difficulties with Rapid Bead Blasting
Rapid bead blasting technology addresses these challenges head-on, offering a versatile and efficient solution that traditional methods cannot match. By leveraging advanced machinery that can be precisely controlled and automated, rapid bead blasting achieves consistent and high-quality surface finishes across a wide range of materials and part geometries. This technology significantly reduces the reliance on manual labor, thereby mitigating the risk of human error and improving overall production efficiency.
One of the key advantages of rapid bead blasting is its ability to maintain tight tolerances and uniform finishes, even on complex parts. This is particularly beneficial in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is paramount. Moreover, rapid bead blasting is adaptable to various materials, from metals to composites, ensuring that each part receives the optimal surface treatment without the need for multiple, material-specific processes.
The environmental footprint of rapid bead blasting is also considerably lower than traditional finishing methods. The use of recyclable and less hazardous media, combined with closed-loop systems that minimize waste, makes rapid bead blasting a more sustainable choice for surface finishing.
Improvements Achieved with Rapid Bead Blasting
| Metric | Traditional Machining | Rapid Bead Blasting | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish Consistency | Variable | High uniformity | 80% |
| Processing Time (per part) | 15 minutes | 4 minutes | 73% |
| Labor Requirements | High | Significantly reduced | 65% |
| Environmental Impact | High waste, chemical use | Low waste, eco-friendly media | 70% |
| Adaptability to Materials | Limited | High | 90% |
| Equipment Downtime | Frequent maintenance | Reduced maintenance | 60% |
| Production Volume | Constrained by labor, processing time | Significantly increased | 100% |
| Worker Health and Safety | Dust, repetitive stress | Improved conditions | 80% |
| Quality Control Rejection Rate | 5% | 0.5% | 90% |
| Operational Costs | High due to labor, waste disposal | Reduced due to efficiency, less waste | 50% |
This table demonstrates the transformative impact of rapid bead blasting on overcoming the technical difficulties inherent in traditional custom machining, showcasing significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
Future Perspectives: Innovations and Trends in Bead Blasting
Looking ahead, the bead blasting sector is poised for further innovation, with trends pointing towards the integration of more advanced automation and AI technologies. These developments promise not only to enhance the efficiency and precision of bead blasting but also to make it more adaptable and sustainable. The exploration of new, environmentally friendly blasting media is particularly noteworthy, reflecting a broader industry trend towards sustainable manufacturing practices.
Conclusion: Impact and Implications for the Custom Machining Industry
The integration of rapid bead blasting into the custom machining sector in China marks a significant milestone in the industry’s ongoing evolution. By addressing some of the most pressing challenges in surface finishing, this technology is setting new benchmarks for efficiency, quality, and sustainability. As the industry continues to innovate and adapt, the future of custom machining in China looks bright, with rapid bead blasting playing a key role in shaping its trajectory.
References
- Zhang, Y., & Liu, J. (2022). Efficiency Improvements in Automotive Component Finishing with Advanced Bead Blasting Technologies. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Processes, 34(2), 159-175.
- Wang, F., Chen, H., & Li, M. (2021). Innovations in Surface Finishing: The Role of Rapid Bead Blasting in Modern Machining. International Journal of Precision Engineering, 29(4), 443-460.
- Zhao, W., & Huang, X. (2023). Environmental Impacts of Surface Finishing Techniques: A Comparative Study. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 22(3), 245-256.
- Liu, X., Zhang, P., & Sun, L. (2020). Overcoming Technical Challenges in the Aerospace Industry through Advanced Bead Blasting Methods. Aerospace Materials and Manufacturing, 17(1), 98-112.
- Chen, G., & Wei, Y. (2019). Adapting to New Materials: Surface Finishing Techniques in the Age of Composites. Composite Materials Science, 15(2), 89-104.
- Yang, L., & Zhou, T. (2022). Automated Bead Blasting Systems and Their Impact on Operational Efficiency. Journal of Industrial Automation, 36(6), 830-845.
- Xu, B., & Jiang, F. (2021). A Review of Sustainable Practices in Surface Finishing Operations. Journal of Cleaner Production, 31(7), 1123-1137.
- Li, S., & Tan, Q. (2020). The Future of Machining: Integrating AI in Bead Blasting for Enhanced Precision. Advanced Manufacturing Technology Review, 26(5), 500-515.
- Wong, K., & Lee, N. (2018). Health and Safety Considerations in Traditional Machining: A Case for Modernizing Surface Finishing. Occupational Health Science, 12(4), 307-322.
- Patel, R., & Kumar, A. (2019). Global Trends in Machining Technologies: An Overview of Recent Advancements. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 33(8), 1239-1256.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Is Copper the Right Choice for Electrical Component CNC Machining? A Detailed Analysis
CNC Machining of Electrical Components Utilizing Copper In the field of electrical engineering, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining plays an integral role, particularly in the development and manufacturing of electrical…
- Understanding Bead Blasting in CNC Machining(china machining Avery)
Bead blasting, a compelling term in the world of Computer Numerically Controlled (CNC) machining, is an influential process that plays a transformative role in optimizing and enhancing parts' aesthetic and…
- Understanding Bead Blasting in CNC Machining(cnc g code Jacqueline)
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a dominant method employed for multiple manufacturing systems across the globe. From healthcare to aerospace, this technology has revolutionized how we manufacture products. One…