The ever-changing needs of the market necessitate constant updates and advancements in manufacturing technology. In order to maintain a competitive edge, manufacturers must keep pace with these changes or risk being eliminated in the process of industrial upgrading. Though technology upgrades can be challenging, they are crucial for long-term development. In this article, we will delve into the world of Micro-Milling technology, offering you an understanding of its significance and how it can benefit your enterprise.
An Insight into Micro Milling
Micro-milling is a machining method used for mechanical parts, which follows the general principles of machining while possessing its own distinct characteristics. Although micro-milling technology is not as mature as traditional cutting methods, it has witnessed rapid development. CNC machining centers can efficiently process 2D and 2.5D simple features, as well as complex 3D curved surfaces. Micro-cutting technology finds wide application in the processing of delicate products, providing adaptability and high productivity. Currently, micro-machining technology offers high precision and fine sizing, making it an indispensable solution in the machining field.
Guidelines for Micro Milling
Requirements for Micro-Milling Machines
In micro-milling, the performance of a machine is only as good as its weakest component. Given the high tolerance demanded by micro-milling compared to traditional milling, each machine component must be suitable for its specific tasks.
Machine Geometry
The geometry of a machine is one of the most critical factors determining its overall performance. It directly influences stiffness, precision, thermal stability, damping characteristics, workload, and ease of operator use. Two popular types of vertical machine geometry are the bridge frame and the C frame, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
In most cases, the C frame offers optimal stiffness for micromachining, which directly affects precision. The main axis or z-axis is the sole axis of motion in the C frame design, resulting in a lighter structure with improved dynamic stiffness.
On the other hand, the bridge structure suspends the X-axis and Z-axis above the X-axis platform. Although the bridge can handle more weight, it provides less dynamic stiffness for micro-milling. The bridge frame is more suitable for high-speed processing of medium to large parts that require maximum Z stroke.
It is crucial to note that vibration poses a significant challenge when milling small and delicate parts. Stiffness and damping are key factors to control in micro-milling. Machine tools with enhanced damping properties effectively reduce and absorb vibrations caused by cutting. Many machine frames are constructed using iron or steel welds.
Drive and Motion
Various drive and motion technologies are available worldwide. One commonly used solution for micro-milling is the combination of ball screw and servomotor technology. This pairing remains an effective choice in the realm of micro-milling.
Multi-Axis Capability
The continuous growth of micro-milling applications is driven by multi-axis machining. A notable example is the use of 5-axis CNC machining for miniature impellers. 5-axis machines enable the operation of small tools with tilt options, eliminating the need for multiple tools and improving surface quality. When comparing conventional 5-axis applications with micro-milling, the latter requires greater flexibility in controlling tool orientation and the ability to track the stock model across multiple dimensions.
The Applications of Micro Milling
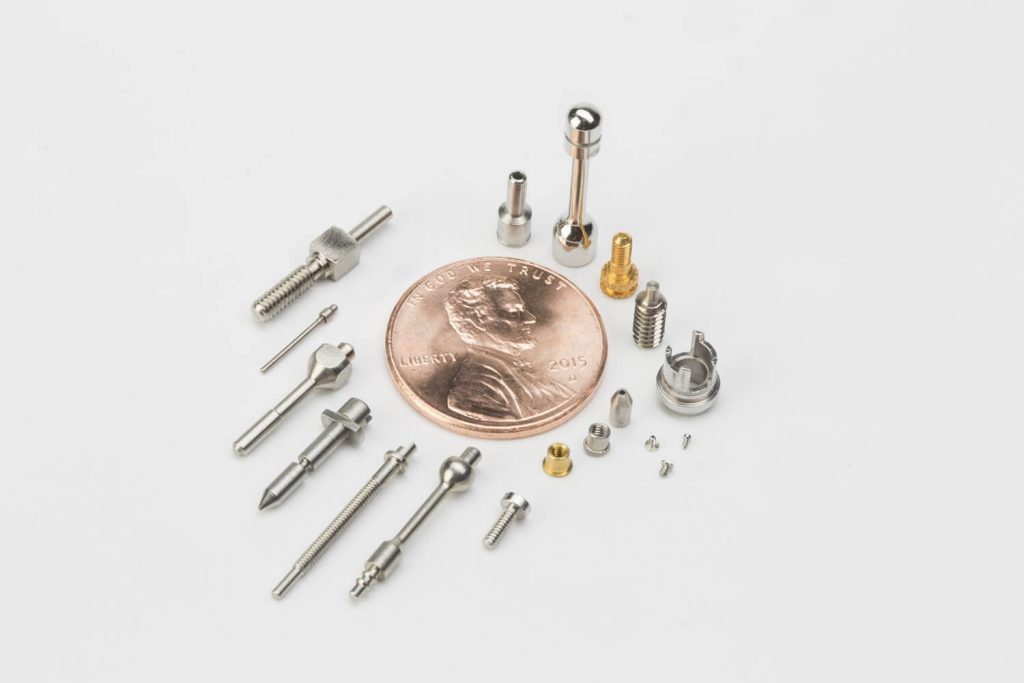

Micro-milling finds extensive application in various fields such as national defense, aviation, aerospace, and electronics. Industries such as metrology, biomedicine, electronic products, computers, and instrument science are also progressing towards miniaturization. Micro-milling technology holds immense potential in the development and production of micro machinery, micro-medical robots, micro-computers, and micro-precision instruments. As products continue to shrink in size while improving in functionality, micro-milling plays a significant role in driving innovation and production.
How Want.Net Supports Your Micro-Milling Success
At Want.net, our machine shop is equipped with 3-axis, 4-axis, and even 5-axis CNC milling machines. We not only ensure your success in micro-part manufacturing but also specialize in CNC aluminum machining. Moreover, we employ the latest diamond machining technology in conjunction with 5-axis micro-milling, enabling us to produce high-quality optical lenses and light guides.
If you wish to learn more, please reach out to us. We are eager to assist you on your micro-milling journey.
Recommended Reads:
- 5 Key Differences between CNC Routers and CNC Mills
- Discovering CNC Lathes: 10 Fascinating Features to Know
- Top 15 Terms in CNC Machining: A Beginner’s Glossary
- Minimizing Chatter in CNC Machining: Tips and Tricks for Better Surface Finish
- Aluminum for Milling: Ultimate Alloy Machining Guide
Other Articles You Might Enjoy
- Revolutionizing Renewable Energy with CNC Machined Components
Introduction: Renewable Energy and CNC Machined Components Renewable energy harnesses power from natural sources such as the sun, wind, and water, making it a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional…
- Is Copper the Right Choice for Electrical Component CNC Machining? A Detailed Analysis
CNC Machining of Electrical Components Utilizing Copper In the field of electrical engineering, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining plays an integral role, particularly in the development and manufacturing of electrical…
- CNC Machining Brass vs. Bronze: Cost, Properties, and Applications Showdown?
Introduction to CNC Machining Brass vs. Bronze: Cost, Properties, and Applications Showdown? In this article, we delve into the debate between brass and bronze machining for an important manufacturing process…









